置信区间估计 预测区间估计_估计,预测和预测
置信区间估计 预测区间估计
Estimation implies finding the optimal parameter using historical data whereas prediction uses the data to compute the random value of the unseen data.
估计意味着使用历史数据找到最佳参数,而预测则使用该数据来计算未见数据的随机值 。
The highlighted words in the above statement need some context setting before we proceed further:
在继续进行之前,上述语句中突出显示的词需要进行一些上下文设置:
We need lot of historical data to learn dependencies for machine learning and modelling. The data typically involves multiple observations, where each observation consists of multiple variables. This multivariate observation x belongs to random variable X whose distribution lies in the realm of a finite set of possible distributions called as ‘the states of nature’.
我们需要大量的历史数据来学习机器学习和建模的依赖关系。 数据通常包含多个观察值,其中每个观察值都包含多个变量。 该多元观测值x属于随机变量X,其分布位于称为“自然状态”的有限分布的可能范围内。
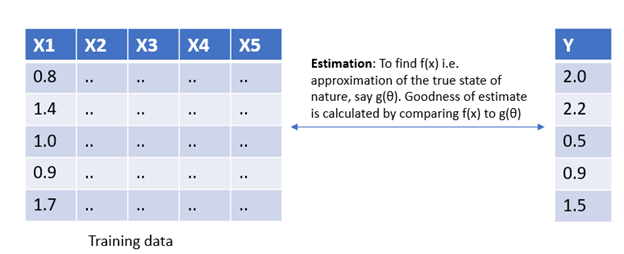
Estimation is the process of optimizing the true state of nature. Loosely speaking, estimation is related to model building i.e. finding the most appropriate parameter that best describes the multivariate distribution of historical data, for e.g. if we have five independent variables, X1, X2….X5 and Y as the target variable. Then, estimation involves the process of finding f(x) which is the closest approximation of the true state of nature denoted by g(θ).
估计是优化自然真实状态的过程 。 宽松地说,估计与模型构建有关,即找到最能描述历史数据多元分布的最合适参数,例如,如果我们有五个独立变量X1,X2….X5和Y作为目标变量。 然后,估计涉及寻找f(x)的过程,f(x)是由g(θ)表示的真实自然状态的最近似值。
Whereas, prediction leverages the already built model to compute the out of sample values. It is a process of calculating the value of another random variable Z whose distribution is related to the true state of the nature (this property plays a pivotal role in any machine learning algorithm). Predictions are considered good when they agree over all the possible values of Z, on an average.
而预测则利用已经建立的模型来计算样本外值。 这是计算另一个随机变量Z的值的过程,该变量的分布与自然的真实状态有关(此属性在任何机器学习算法中都起着关键作用)。 平均而言,当预测与Z的所有可能值一致时,这些预测就被认为是好的。

There are multiple ways to interpret the difference between the two, let’s also explore the Bayesian intuition:
解释两者之间差异的方法有多种,让我们还探讨贝叶斯直觉 :
Estimation is after the occurrence of the event i.e. posterior probability. Prediction is a kind of estimation before the occurrence of the event i.e. apriori probability.
估计是在事件发生之后,即后验概率。 预测是在事件发生之前进行的一种估计,即先验概率。
Let’s summarize our understanding on estimation and prediction: To make predictions on unseen data, we fit a model on training dataset that learns an estimator f(x), which is used to make predictions on new data.
让我们总结一下对估计和预测的理解:为了对看不见的数据进行预测,我们在训练数据集上拟合了一个模型,该模型学习了估计器f(x),该函数用于对新数据进行预测。
Now, that we understand what the prediction is, let’s see how it is different from forecasting.
现在,我们了解了预测是什么,让我们看看它与预测有何不同。
Forecasting problems are a subset of prediction problems wherein both use the historical data and talk about the future events. The only difference between forecasting and prediction is the explicit addition of temporal dimension in forecasting.
预测问题是预测问题的子集,其中既使用历史数据,又谈论未来事件。 预测与预测之间的唯一区别是在预测中显式增加了时间维度。
Forecast is a time-based prediction i.e. it is more appropriate while dealing with time series data. Prediction, on the other hand, need not be time based only, it can be based on multiple causal factors that influence the target variable.
预测是基于时间的预测,即在处理时间序列数据时更合适。 另一方面,预测不必仅基于时间,它可以基于影响目标变量的多个因果因素。
I stumbled across a very fresh perspective of explaining the difference between the prediction and forecast using the analogy of the origin of the words themselves.
我偶然发现了一个非常新颖的观点,即使用单词本身的起源来解释预测与预测之间的差异。
I will brief on this innovative illustration in this post, but you can read more about it at the original post here.
我将在这篇文章中简要介绍这个创新的插图,但是您可以在此处的原始文章中了解更多有关它的信息。
Forecast is more process-oriented and follows a certain methodology of doing something. In a way, it assumes that the past behavior is a good enough indicator of what is going to happen in the future.
预测更注重过程,并遵循某种方法进行工作。 在某种程度上,它假设过去的行为足以说明将来会发生什么。
Prediction considers all historical processes, influencing variables and interactions to reveal the future.
预测考虑了所有历史过程,影响变量和相互作用以揭示未来。
In summary, all forecasts are predictions but not all predictions are forecasts.
总之,所有预测都是预测,但并非所有预测都是预测。
Hope you now have clarity on the difference between estimation and prediction. The post also highlights the distinction between prediction vs forecast.
希望您现在对估计和预测之间的区别有所了解。 该帖子还强调了预测与预测之间的区别。
Happy Reading!!!
阅读愉快!
References: https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/17773/what-is-the-difference-between-estimation-and-prediction/17789#17789
参考: https : //stats.stackexchange.com/questions/17773/what-is-the-difference-between-estimation-and-prediction/17789#17789
翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/estimation-prediction-and-forecasting-40c56a5be0c9
置信区间估计 预测区间估计
http://www.taodudu.cc/news/show-997569.html
相关文章:
- 地图 c-suite_C-Suite的模型
- sap中泰国有预扣税设置吗_泰国餐厅密度细分:带有K-means聚类的python
- 傅里叶变换 直观_A / B测试的直观模拟
- 鸽子 迷信_人工智能如何帮助我战胜鸽子
- scikit keras_Scikit学习,TensorFlow,PyTorch,Keras…但是天秤座呢?
- 数据结构两个月学完_这是我作为数据科学家两年来所学到的
- 迈向数据科学的第一步:在Python中支持向量回归
- 使用Python和MetaTrader在5分钟内开始构建您的交易策略
- ipywidgets_未来价值和Ipywidgets
- 用folium模块画地理图_使用Folium表示您的地理空间数据
- python创建类统计属性_轻松创建统计数据的Python包
- knn分类 knn_关于KNN的快速小课程
- 机器学习集群_机器学习中的多合一集群技术在无监督学习中应该了解
- 政府公开数据可视化_公开演讲如何帮助您设计更好的数据可视化
- 消费者行为分析_消费者行为分析-是否点击广告?
- 魅族mx5游戏模式小熊猫_您不知道的5大熊猫技巧
- 数据科学中的数据可视化
- 多重线性回归 多元线性回归_了解多元线性回归
- 如何使用Python处理丢失的数据
- 为什么印度盛产码农_印度农产品价格的时间序列分析
- tukey检测_回到数据分析的未来:Tukey真空度的整洁实现
- 到2025年将保持不变的热门流行技术
- 马尔科夫链蒙特卡洛_蒙特卡洛·马可夫链
- 数据分布策略_有效数据项目的三种策略
- 密度聚类dbscan_DBSCAN —基于密度的聚类方法的演练
- 从完整的新手到通过TensorFlow开发人员证书考试
- 移动平均线ma分析_使用动态移动平均线构建交互式库存量和价格分析图
- 静态变数和非静态变数_统计资料:了解变数
- 不知道输入何时停止_知道何时停止
- 掌握大数据数据分析师吗?_要掌握您的数据吗? 这就是为什么您应该关心元数据的原因...
置信区间估计 预测区间估计_估计,预测和预测相关推荐
- 时间序列预测 预测时间段_什么是时间序列预测
时间序列预测 预测时间段 Notwithstanding the time series analysis is widely implemented for the business and soc ...
- 使用机器学习预测天气_如何使用机器学习预测着陆
使用机器学习预测天气 Based on every NFL play from 2009–2017 根据2009-2017年每场NFL比赛 Ah, yes. The times, they are c ...
- lstm预测单词_下一个单词预测完整指南
lstm预测单词 As part of my summer internship with Linagora's R&D team, I was tasked with developing ...
- 使用机器学习预测天气_使用机器学习来预测患者是否会再次入院
使用机器学习预测天气 We are in a age where machines are utilizing huge data and trying to create a better worl ...
- python预测房价走势_如何用 Python 预测房价走势?
原标题:如何用 Python 预测房价走势? 买房应该是大多数都会要面临的一个选择,当前经济和政策背景下,未来房价会涨还是跌?这是很多人都关心的一个话题.今天分享的这篇文章,以波士顿的房地产市场为例, ...
- python回归算法预测数据_数据回归分类预测的基本算法及python实现
数据回归分类预测的基本算法及python实现 关于数据的回归和分类以及分析预测.讨论分析几种比较基础的算法,也可以算作是比较简单的机器学习算法. 一.KNN算法 邻近算法,可以用来做回归分析也可以用来 ...
- python模型预测足球_采用 Python 机器学习预测足球比赛结果!买谁赢就谁赢!
采用 Python 机器学习预测足球比赛结果 足球是世界上最火爆的运动之一,世界杯期间也往往是球迷们最亢奋的时刻.比赛狂欢季除了炸出了熬夜看球的铁杆粉丝,也让足球竞猜也成了大家茶余饭后最热衷的话题.甚 ...
- python预测比赛_快手活跃用户预测竞赛的第一名解决方案
作者按:由于比赛时间仓促,这份代码中有些地方写的并不规范.更规范的tensorflow RNN构建,可以参考作者的另外一个项目tenosrflow-RNN-toolkit,该项目使用更高程度抽象的bu ...
- python泰坦尼克号生存预测论文_【数据分析】预测泰坦尼克号存活率 -- Python决策树...
此博客仅为我业余记录文章所用,发布到此,仅供网友阅读参考,如有侵权,请通知我,我会删掉. 前言 最近学习了 预测泰坦尼克号存活率,是一个烂大街的项目了,它是kaggle科学竞赛网站上一个入门的数据分析 ...
- python对电影进行预测评分_推荐系统—影视评分预测
本文根据Andrew Ng的 Machine Learning 的课写就. ======================================= 一.预测电影评分 ============= ...
最新文章
- php xml表格形式输出,PHP XML如何输出nice格式
- 工作397-Wxml
- 到底该不该上马Vista 中小企业升级全攻略(上)
- ExtJs 备忘录(2)—— Form表单(二) [ 控件封装 ]
- 二叉搜索树的删除操作可以交换吗_一文看懂数据结构中的树
- php静态stitac,php静态static介绍
- 外媒:伊朗政府封锁加密通讯应用Signal
- mysql命令:set sql_log_bin=on/off
- 推荐系统评测指标—精准率(Precision)、召回率(Recall)、F值(F-Measure)
- 手机无线电驾驶与马歇尔·麦克卢汉的哲学
- 笔试占比近40%,中国人民大学高瓴人工智能学院2022年夏令营来袭
- UE基础知识:虚幻引擎编辑器界面-英汉对照表
- 安全的远程访问是保护知识产权的关键
- 假如给我三天光明阅读心得收获
- 账户经常被盗号怎么办?防盗“黑科技”了解一下
- SIwave仿真手册——软件基础(一)
- 智能化里面计算机网络设计思路,智能化设计思路.doc
- 计算机英语ADD全称,计算机 加法器add简介.ppt
- 程序员有必要参加软考吗?软考有什么用?
- 【编程语言】Lua完全自学手册
