hdu 3016 Man Down(简单线段树简单DP)
Man Down
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others)Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1410Accepted Submission(s): 492
http://hi.baidu.com/abcdxyzk/blog/item/16398781b4f2a5d1bd3e1eed.html
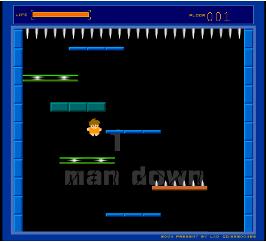
We take a simplified version of this game. We have only two kinds of planks. One kind of the planks contains food and the other one contains nails. And if the man falls on the plank which contains food his energy will increase but if he falls on the plank which contains nails his energy will decrease. The man can only fall down vertically .We assume that the energy he can increase is unlimited and no borders exist on the left and the right.
First the man has total energy 100 and stands on the topmost plank of all. Then he can choose to go left or right to fall down. If he falls down from the position (Xi,Yi),he will fall onto the nearest plank which satisfies (xl <= xi <= xr)(xl is the leftmost position of the plank and xr is the rightmost).If no planks satisfies that, the man will fall onto the floor and he finishes his mission. But if the man’s energy is below or equal to 0 , he will die and the game is Over.
Now give you the height and position of all planks. And ask you whether the man can falls onto the floor successfully. If he can, try to calculate the maximum energy he can own when he is on the floor.(Assuming that the floor is infinite and its height is 0,and all the planks are located at different height).
For each test case, The first line contains one integer N (2 <= N <= 100,000) representing the number of planks.
Then following N lines representing N planks, each line contain 4 integers (h,xl,xr,value)(h > 0, 0 < xl < xr < 100,000, -1000 <= value <= 1000), h represents the plank’s height, xl is the leftmost position of the plank and xr is the rightmost position. Value represents the energy the man will increase by( if value > 0) or decrease by( if value < 0) when he falls onto this plank.
题意:
题目是以"是男人就下一百层"游戏为背景。不过加以简化了。就说只有两种木板了。一种到达上面后可以得到上面的分数。另一种就减相应的分数。每一个木板会给你它的左右端点的坐标。[xl,xr]。然后小人会到达高度比当前木板低。
且满足。xl'<=xl<=xr'或。xl'<=xr<=xr'。的最近木板上。因为它只能从当前木板的左边或右边下去嘛。
如果不存在这样的木板。他就完成了它的使命。(因为玩过这个游戏的缘故我开始以为他挂掉了然后wa了数次)
还有如果中途分数小于或等于0的话那么它就挂掉了。初始分为100.
思路:
由于这是在线段树专题里找的题。于是拼命往线段树上想。白白YY那么久。其实这题就是一简单DP因为对于一个木板要么从左边下去。要么从右边下去。但由于高度不连续所以处理有点不同。这题关键在处理最近上。我们可以用一颗线段树来维护。先把木板高度按高度升序排序。然后对于当前木板。查一下它左右端点被谁覆盖了用数组记录下来。因为是升序排序的。查到的一定是最近的。然后再用这木板去覆盖点。循环做。我开始想着从终点倒着走回去
就不用记录了。但发现有bug。因为有可能存在正这走挂了。倒着走不挂的情况。
4
5 2 6 100
4 1 4 -200
3 5 8 -200
2 1 10 500
所以只能走。
详细见代码:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<sstream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn=100010;
int dp[maxn],id[maxn<<2],li[maxn],ri[maxn];
struct node
{int h,xl,xr,val;
} plan[maxn];
bool cmp(node a,node b)
{return a.h<b.h;
}
void btree(int L,int R,int k)
{int ls,rs,mid;id[k]=0;if(L==R)return ;ls=k<<1;rs=ls|1;mid=(L+R)>>1;btree(L,mid,ls);btree(mid+1,R,rs);
}
void pushdown(int k)
{int ls,rs;ls=k<<1;rs=ls|1;id[ls]=id[rs]=id[k];id[k]=0;
}
void update(int L,int R,int l,int r,int k,int d)
{int ls,rs,mid;if(l==L&&r==R){id[k]=d;return;}if(id[k])pushdown(k);ls=k<<1;rs=ls|1;mid=(L+R)>>1;if(l>mid)update(mid+1,R,l,r,rs,d);else if(r<=mid)update(L,mid,l,r,ls,d);else{update(L,mid,l,mid,ls,d);update(mid+1,R,mid+1,r,rs,d);}
}
int qu(int L,int R,int p,int k)
{int ls,rs,mid;if(L==R||id[k])return id[k];ls=k<<1;rs=ls|1;mid=(L+R)>>1;if(p>mid)return qu(mid+1,R,p,rs);elsereturn qu(L,mid,p,ls);
}
int main()
{int n,i,lim;while(~scanf("%d",&n)){lim=0;plan[0].val=0;dp[0]=-INF;for(i=1;i<=n;i++){scanf("%d%d%d%d",&plan[i].h,&plan[i].xl,&plan[i].xr,&plan[i].val);lim=max(lim,plan[i].xr);dp[i]=-INF;}sort(plan+1,plan+n+1,cmp);btree(1,lim,1);for(i=1;i<=n;i++){li[i]=qu(1,lim,plan[i].xl,1);ri[i]=qu(1,lim,plan[i].xr,1);update(1,lim,plan[i].xl,plan[i].xr,1,i);}dp[n]=100+plan[n].val;for(i=n;i>=1;i--){if(dp[i]>0)//题目数据有点水。不加这个判断也能过。{dp[li[i]]=max(dp[li[i]],dp[i]+plan[li[i]].val);dp[ri[i]]=max(dp[ri[i]],dp[i]+plan[ri[i]].val);}}if(dp[0]<=0)dp[0]=-1;printf("%d\n",dp[0]);}return 0;
}
/*
4
5 2 6 100
4 1 4 -200
3 5 8 -200
2 1 10 500
2
5 2 6 100
4 1 4 -200
*/
/*
-1//数据水了。不是-1也行。
100
*/
hdu 3016 Man Down(简单线段树简单DP)相关推荐
- HDU 3016 Man Down (线段树+dp)
HDU 3016 Man Down (线段树+dp) Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Ja ...
- 线段树-简单线段树模板
简单线段树 2021年7月30 线段树是干什么的? 更新,维护,查询某区间的某项值,如区间和等. 线段树的原理 与树状数组类似,线段树通过直接建树来保存区间的结点,如图: 如何建图? 下面以求序列区间 ...
- 线段树简单入门 (含普通线段树, zkw线段树, 主席树)
线段树简单入门 递归版线段树 线段树的定义 线段树, 顾名思义, 就是每个节点表示一个区间. 线段树通常维护一些区间的值, 例如区间和. 比如, 上图 \([2, 5]\) 区间的和, 为以下区间的和 ...
- HDU 5454 Excited Database【线段树】
简单线段树,就是推公式的过程有点不是特别熟练. 按照叉姐的方法,可以用三个树状数组维护,三种情况. 按照坦克工程师的方法,用容斥,将一个矩形分解成三个三角形,一个大的直角三角形减去两个小的直角三角形, ...
- HDU 1166 敌兵布阵(线段树:点更新,区间求和)
HDU 1166 敌兵布阵(线段树:点更新,区间求和) http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1166 题意: 给你n个整数,然后给你多条命令,每条命令如 ...
- 2019CCPC网络赛 1002 HDU 6703(权值线段树)
2019CCPC网络赛 1002 HDU 6703(权值线段树) 思路:用权值线段树存题目给的数据后,2操作就是求权值线段树中大于等于k的部分中,靠近左端点的第一个大于r的值(这个求出来的只是原序列中 ...
- Codeforces Round #343 (Div. 2) D. Babaei and Birthday Cake 线段树维护dp
D. Babaei and Birthday Cake 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/629/problem/D Description As you ...
- YBTOJ:采矿战略(线段树维护dp、树链剖分)
文章目录 题目描述 解析 代码 题目描述 所谓线段树维护dp,就是在线段树上维护dp (逃) 解析 把树剖一下后就变成了区间问题 考虑建一棵线段树,每一个结点都是一个背包 这样就能区间查询,也能带修了 ...
- 埃森哲杯第十六届上海大学程序设计联赛春季赛暨上海高校金马五校赛H题小Y与多米诺骨牌(线段树优化dp)
题意 题目链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/91/H 来源:牛客网 题解 设l[i]l[i]l[i]为向左推第iii个骨牌最远能影响到的骨牌的编号,r[i ...
最新文章
- 计算机科学中最重要的32个算法(转)
- allegro怎么设置孔的属性_两种在Allegro中增加过孔的方法
- win 7 系统ie浏览器升级11版本后,f12功能不可用的问题
- 在IIS中寄存已有WCF服务
- 8年了,开始写点东西了
- COCO 数据集格式及mmdetection中的转换方法
- python使用UUID生成唯一标识
- 正交法设计测试用例时可以使用的工具allpairs---生成正交表
- Oracle P6培训系列:06创建项目日历
- sci论文发表的难度高吗
- 计算机网络准入技术,计算机网络终端准入控制技术课件.pdf
- ARM linux解析之压缩内核zImage的启动过程
- NGINX源码之:listen和server_name命令与listening监听创建
- electron仿微信截图工具(初学者的尝试笔记)
- 这个必用的开发框架,是多少程序员头秃的存在?
- Docker Images Containers
- HANA Native SQL
- 如何解决软电话中的来电转移问题
- 当Python邂逅Javascript擦出一款蠢萌蠢萌的可视化工具
- 全国计算机二级考试操作题是原题吗,2017全国计算机二级office考试操作题
