Mallet机器语言工具包-入门测试
Mallet主要用于文本分类,所以它设计思路都是偏向文本分类的。
由于需要用到里面的最大熵以及贝叶斯算法 所以 得研究一下
主页 :http://mallet.cs.umass.edu/index.php
参考文章:http://mallet.cs.umass.edu/classifier-devel.php
http://mallet.cs.umass.edu/import-devel.php
网上找了下,材料不多,只能自己苦逼地去看官方提供的一些guide还有API,然后就研究源代码了
我的目的是,把MALLET导入到自己的java项目中(用的是eclipse),然后灵活地用里面一些算法,bayes,和最大熵算法进行文本分类。
导入到工程部分:
下载链接:http://mallet.cs.umass.edu/download.php 我这个时候的最新版本是2.0.7
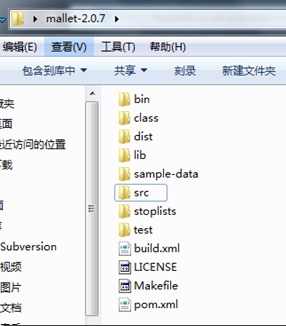 这是压缩包里面的内容,把src文件夹以及lib里面的jar包都拷贝到工程项目里面,把jar包都加载到工程上
这是压缩包里面的内容,把src文件夹以及lib里面的jar包都拷贝到工程项目里面,把jar包都加载到工程上
具体各个类的用法只能通过API和源码以及自己的测试去分析了。
为了生成一个Instance得搞定下图这几个东西啊..REF:http://mallet.cs.umass.edu/import-devel.php

需要Alphabet以及FeatureVetor,配合使用,Alphabet用来保存各个属性的名字,FeatureVector用来保存一个对象在各个属性下的值
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] attributeStr = new String[]{"长","宽","高"};
Alphabet dict = new Alphabet(attributeStr);
double[] values = new double[]{1,2,3};
FeatureVector vetor = new FeatureVector(dict, values);
System.out.println(vetor.toString());
}我们可以指定values对应与哪个属性值,从0开始,比如长对应0,宽对应1,高对应2,测试如下
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] attributeStr = new String[]{"长","宽","高"};
Alphabet dict = new Alphabet(attributeStr);
double[] values = new double[]{1,2,3};
int[] indices = new int[]{2,0,1};
FeatureVector vetor = new FeatureVector(dict, indices,values);
System.out.println(vetor.toString());
}一个比较地方需要注意的是如果指明的values的对应索引有重复,比如,2和3都指明它属于长,那么得到的值是累计的而不是覆盖的,值为5,这个就单词统计的效果吧
String[] attributeStr = new String[]{"长","宽","高"};
Alphabet dict = new Alphabet(attributeStr);
double[] values = new double[]{1,2,3};
int[] indices = new int[]{2,0,0};
FeatureVector vetor = new FeatureVector(dict, indices,values);
System.out.println(vetor.toString());好吧 先把Data搞定了。FeatureVector就是我需要的data
上面是源代码的一句话,Label需要通过LabelAlphabet来创建,所以再研究下LabelAlphabet,然后做以下测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
LabelAlphabet labels = new LabelAlphabet();
Label label = labels.lookupLabel("桌子");
System.out.println(label.toString());
}Name:作为一个instance的id号,那么就简单的用整型作为它的序号好了。
import cc.mallet.*;
import cc.mallet.classify.Classifier;
import cc.mallet.classify.ClassifierTrainer;
import cc.mallet.classify.MaxEntTrainer;
import cc.mallet.types.Alphabet;
import cc.mallet.types.FeatureVector;
import cc.mallet.types.Instance;
import cc.mallet.types.InstanceList;
import cc.mallet.types.Label;
import cc.mallet.types.LabelAlphabet;
import cc.mallet.types.Labeling;
public class test {
String label;//实例的类别
double length;//长度
double width;//宽度
double high;
public test(String label,double length,double width,double high){
this.label = label;
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
this.high = high;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LabelAlphabet labels = new LabelAlphabet();
String[] attributeName = new String[]{"长","宽","高"};
Alphabet dic = new Alphabet(attributeName);
labels.lookupIndex("桌子");
labels.lookupIndex("椅子");
InstanceList list = new InstanceList(dic,labels);
int id = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 100; ++i){
test temp = new test("桌子",4,2,3);
test temp2 = new test("椅子",0,0,0);
double[] tempArray = new double[3];
tempArray[0] = temp.length;
tempArray[1] = temp.width;
tempArray[2] = temp.high;
FeatureVector vec = new FeatureVector(dic, tempArray);
Instance ins = new Instance(vec, labels.lookupLabel(temp.label), ++id, null);
list.add(ins);
tempArray[0] = temp2.length;
tempArray[1] = temp2.width;
tempArray[2] = temp2.high;
vec = new FeatureVector(dic, tempArray);
ins = new Instance(vec, labels.lookupLabel(temp2.label), ++id, null);
list.add(ins);
}
//创造一个测试样本
test testTemp = new test("未知",0,0,2);
double[] tempArray = new double[3];
tempArray[0] = testTemp.length;
tempArray[1] = testTemp.width;
tempArray[2] = testTemp.high;
FeatureVector vec = new FeatureVector(dic, tempArray);
Instance testIns = new Instance(vec,null, ++id, null);
//进行最大熵分类
ClassifierTrainer trainer = new MaxEntTrainer();
Classifier classifier = trainer.train(list);
Labeling label = classifier.classify(testIns).getLabeling();
System.out.println(label.getBestLabel().toString());
}
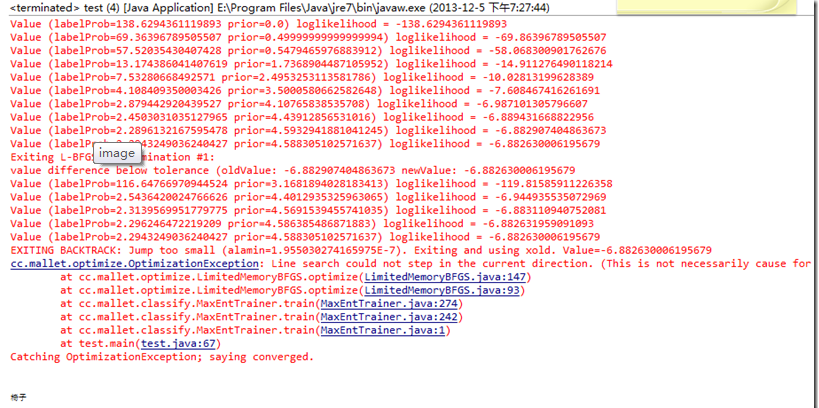
}
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/loma1990/1336673
Mallet机器语言工具包-入门测试相关推荐
- 信息学奥赛一本通——1000:入门测试题目
1000:入门测试题目 时间限制: 1000 ms 内存限制: 32768 KB 提交数: 149720 通过数: 89898 [题目描述] 求两个整数的和. [输入] 一行, ...
- 1000:入门测试题目 【信息学奥赛一本通(C++版)在线评测系统】
为了更好的阅读体验,建议您移步至我的博客园来阅读此文章. 传送门 「原题」 1000:入门测试题目 时间限制: 1000 ms 内存限制: 32768 KB 提交数: 0 通过数: 0 [题目描述] ...
- 信息学奥赛一本通(c++):1000:入门测试题目
一.题目 1000:入门测试题目 时间限制: 1000 ms 内存限制: 32768 KB [题目描述]求两个整数的和. [输入]一行,两个用空格隔开的整数. [输出]两个整数的和. ...
- 信息学奥赛一本通(C++)版在线评测系统 1000 入门测试题目
1000 入门测试题目 时间限制: 1000 ms 内存限制: 32768 KB 提交数: 254022 通过数: 152601 [题目描述] 求两个整数的和 [输入] 一行 ...
- 信息学奥赛一本通-1000 入门测试题目 题解
1000:入门测试题目 时间限制: 1000 ms 内存限制: 32768 KB [题目描述] 求两个整数的和. [输入] 一行,两个用空格隔开的整数. [输出] 两个整数的和. [输 ...
- 信息学奥赛_1000_ 入门测试题目
信息学奥赛_1000_ 入门测试题目 [题目描述] 求两个整数的和. [输入] 一行,两个用空格隔开的整数. [输出] 两个整数的和. [输入样例] 2 3 [输出样例] 5 [源码] #includ ...
- python入门测试教程_Python测试入门
python入门测试教程 This tutorial is for anyone who has written a fantastic application in Python but hasn' ...
- 零基础入门测试该学什么?最全整理,照着学就对了
对于很多小白而言,想要转行软件测试岗位,却又怕自己从来没有接触过计算机,底子很薄弱,从而还没开始就打起了退堂鼓.也有许多初学者,在入门的过程中,苦于不知道该学什么,又该从何学起,常常搞得一团乱麻. 随 ...
- 数组业务场景,算卦程序入门测试
最简单基础的入门程序,调试 #region 数组业务场景测试0.3 // 数字类型数组int[] a = { 11, 2, 3 };Console.WriteLine("打印出来数组中的第一 ...
最新文章
- java 解决Html table的rowspan问题(osc处女作)
- 粒子追踪 matlab,用粒子滤波器实现的多目标跟踪代码
- redis介绍及保持session会话
- Lucene使用案例(包括索引的维护)
- python 百度百科 爬虫_爬虫爬取百度百科数据
- 5G手机将不用流量可免费看电视,网友:流量免费,内容付费?
- 大数据之-Hadoop完全分布式_SCP案例_同时在1000台服务器上安装JDK_配置环境变量---大数据之hadoop工作笔记0031
- 聊天宝解散,多闪、马桶MT还会远吗?| 畅言
- 思科警告:IOS 路由器中含有多个严重缺陷,可导致“系统完全受陷”
- UITableView的分割线不满屏的解决方法
- WordPress纯代码纯静态开启七牛CDN并集成七牛缩略图和水印功能
- js模板引擎—art-template的使用
- 简述et代理换ip软件网络功能。
- Linux学习笔记(四)Linux基础操作
- “无边框”引发口水大战 供应链考验手机硬件创新
- vite alias配置路径地址别名
- 正式加入阿里巴巴!跟Android初学者分享几点经验,附超全教程文档
- 回忆篇,那些抹不去的童年记忆
- iOS内购项目的接入与审核问题
- opencv(c++)几何变换------图像平移、旋转、缩放、翻转、剪贴
热门文章
- zookeeper 伪分布式安装
- 编写多线程Java应用程序常见问题
- 11.PHP与MySQL
- hdu1828 线段树扫描线求矩形面积的周长
- 【数字信号处理】卷积编程实现 ( Matlab 卷积和多项式乘法 conv 函数 | 使用 matlab 代码求卷积并绘图 )
- 【错误记录】Git 使用报错 ( git: ‘switch‘ is not a git command. See ‘git --help‘. )
- 【Android FFMPEG 开发】FFMPEG 获取 AVStream 音视频流 ( AVFormatContext 结构体 | 获取音视频流信息 | 获取音视频流个数 | 获取音视频流 )
- 【bzoj3105】新Nim游戏
- 第4周小组作业:WordCount优化
- Doubly Linked List,( Aizu - ALDS1_3C )
