例解BITMAP的数据格式
说明:由于这里不能上传bitmap图像,我将用到的3个bitmap图片(红色字体,第2、3两图是24bit的位图)文件放在:http://download.csdn.net/source/1377107。请下载(忘记设定不需要资源分了,需要1个资源分)后,对照本文阅读。
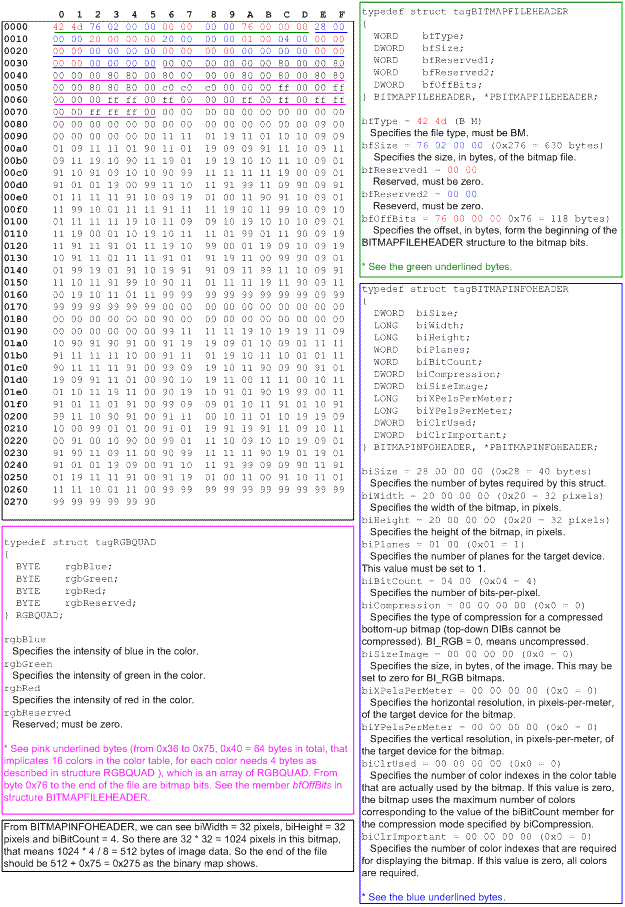
Bitmaps should be saved in a file that uses the established bitmap file format and assigned a name with the three-character .bmp extension. The established bitmap file format consists of a BITMAPFILEHEADER structure followed by a BITMAPINFOHEADER, BITMAPV4HEADER, or BITMAPV5HEADER structure. An array of RGBQUAD structures (also called a color table) follows the bitmap information header structure. The color table is followed by a second array of indexes into the color table (the actual bitmap data).
The bitmap file format is shown in the following illustration.
Windows 95, Windows NT 4.0: Replace the BITMAPINFOHEADER structure with the BITMAPV4HEADER structure.
Windows 98/Me, Windows 2000/XP: Replace the BITMAPINFOHEADER structure with the BITMAPV5HEADER structure.
The members of the BITMAPFILEHEADER structure identify the file; specify the size of the file, in bytes; and specify the offset from the first byte in the header to the first byte of bitmap data. The members of the BITMAPINFOHEADER, BITMAPV4HEADER, or BITMAPV5HEADER structure specify the width and height of the bitmap, in pixels; the color format (count of color planes and color bits-per-pixel) of the display device on which the bitmap was created; whether the bitmap data was compressed before storage and the type of compression used; the number of bytes of bitmap data; the resolution of the display device on which the bitmap was created; and the number of colors represented in the data. The RGBQUAD structures specify the RGB intensity values for each of the colors in the device's palette.
The color-index array associates a color, in the form of an index to an RGBQUAD structure, with each pixel in a bitmap. Thus, the number of bits in the color-index array equals the number of pixels times the number of bits needed to index the RGBQUAD structures. For example, an 8x8 black-and-white bitmap has a color-index array of 8 * 8 * 1 = 64 bits, because one bit is needed to index two colors. The Redbrick.bmp, mentioned in About Bitmaps, is a 32x32 bitmap with 16 colors; its color-index array is 32 * 32 * 4 = 4096 bits because four bits index 16 colors.
To create a color-index array for a top-down bitmap, start at the top line in the bitmap. The index of the RGBQUAD for the color of the left-most pixel is the first n bits in the color-index array (where n is the number of bits needed to indicate all of the RGBQUAD structures). The color of the next pixel to the right is the next n bits in the array, and so forth. After you reach the right-most pixel in the line, continue with the left-most pixel in the line below. Continue until you finish with the entire bitmap. If it is a bottom-up bitmap, start at the bottom line of the bitmap instead of the top line, still going from left to right, and continue to the top line of the bitmap.
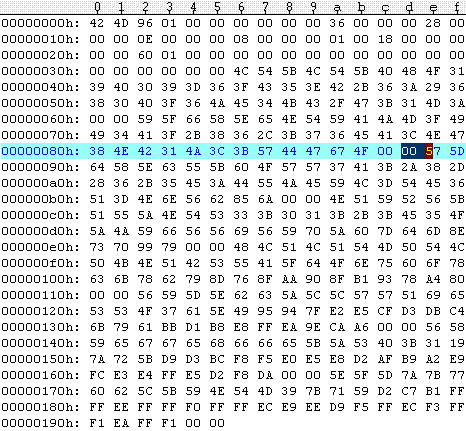
The following hexadecimal output shows the contents of the file Redbrick.bmp.
第一图
The following table shows the data bytes associated with the structures in a bitmap file.
|
Structure |
Corresponding bytes |
|
BITMAPFILEHEADER |
0x00 0x0D |
|
BITMAPINFOHEADER |
0x0E 0x35 |
|
RGBQUAD array |
0x36 0x75 |
|
Color-index array |
0x76 0x275 |
第一图的存储结构:
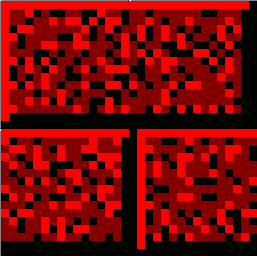
32 * 32 pixels (8 times enlarged redbrick.bmp) :
Color table:
0 00 00 00 00
1 00 00 80 00
2 00 80 00 00
3 00 80 80 00
4 80 00 00 00
5 80 00 80 00
6 80 80 00 00
7 80 80 80 00
8 c0 c0 c0 00
9 00 00 ff 00
A 00 ff 00 00
B 00 ff ff 00
C ff 00 00 00
D ff 00 ff 00
E ff ff 00 00
F ff ff ff 00
The first three lines of Redbrick.bmp (bottom-up)
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 09 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
11 11 01 19 11 01 10 10 09 09 01 09 11 11 01 90
From the above data, we can see the first line of the picture should be black (index 0 means black from the color table), the second line is black except 18th pixels in line 2 is red (index 09 mean red from the color table). Obviously, we have the same result while look that enlarged redbrick.bmp above (bottom-up).
第2图
Englarged MSNFaceTest.bmp
第2图前128字节的数据如下:
00000000h 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
00000010h 42 4D 36 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 36 00 00 00 28 00
00000020h 00 00 10 00 00 00 10 00 00 00 01 00 18 00 00 00
00000030h 00 00 00 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00000040h 00 00 00 00 00 00 22 19 15 23 1A 16 24 1B 17 24
00000050h 1C 15 22 1C 15 22 1C 15 1F 1C 14 25 24 1A 23 27
00000060h 1C 25 2B 20 28 32 26 28 37 29 27 38 2A 22 37 28
00000070h 1F 24 25 24 37 26 24 1E 19 21 1B 16 20 1A 15 21
00000080h 1B 14 22 1C 15 22 1C 15 1E 1C 14 1E 1F 15 23 29
BITMAPFILEHEADER
-----------------------
WORD bfType; 0x42 0x4D = BM
DWORD bfSize; 0x0336 = 822 bytes
WORD bfReserved1; 0x00
WORD bfReserved2; 0x00
DWORD bfOffBits; 0x36 = 54 bytes
BITMAPINFOHEADER
------------------------
DWORD biSize; 0x28 = 40 bytes
LONG biWidth; 0x10 = 16 pixels
LONG biHeight; 0x10 = 16 pixels
WORD biPlanes; 0x01 = 1
WORD biBitCount; 0x18 = 24 bits-per-pixels
DWORD biCompression; 0x00
DWORD biSizeImage; 0x300 = 768 bytes
LONG biXPelsPerMeter; 0x00 = 0 pixels-per-meter
LONG biYPelsPerMeter; 0x00 = 0 pixels-per-meter
DWORD biClrUsed; 0x00
DWORD biClrImportant; 0x00
RGBQUAD array (color table)
----------------------------
NO COLOR TABLE
BITMAP BITS (The first 2 pixels in the first line - bottom-up)
--------------------------------------------------------------
22 19 15 23 1A 16 (B-G-R)
第三图(MSNFaceTest01.bmp)
要注意的一点是在BMP位图中,位图的每行像素值要填充到一个四字节边界,即位图每行所占的存储长度为四字节的倍数,不足时将多余位用0填充
前面两图都刚好每一像素行都是4字节的倍数,因此没有碰到上面的情况。第一图是32 *32像素,每像素4-bit颜色值(在color table里面的index,color table的大小为16,即16种颜色),所以每行的字节数为32 *4 /8 = 16字节,显然为4的倍数,因此不需要补0;第二图是16*16像素,每像素为24 bits,因此每行的大小为 16 * 24 /8 = 48字节,显然也为4的倍数,故而也不存在补0的情况。下面给出一个需要补0的图形。
第3图
放大后的情形如下:
第3图的存储结构:
BITMAPFILEHEADER
-----------------------
WORD bfType; 0x42 0x4D = BM
DWORD bfSize; 0x0196 = 406 bytes
WORD bfReserved1; 0x00
WORD bfReserved2; 0x00
DWORD bfOffBits; 0x36 = 54 bytes
BITMAPINFOHEADER
------------------------
DWORD biSize; 0x28 = 40 bytes
LONG biWidth; 0x0E = 14 pixels
LONG biHeight; 0x08 = 8 pixels
WORD biPlanes; 0x01 = 1
WORD biBitCount; 0x18 = 24 bits-per-pixels
DWORD biCompression; 0x00
DWORD biSizeImage; 0x160 = 352 bytes
LONG biXPelsPerMeter; 0x00 = 0 pixels-per-meter
LONG biYPelsPerMeter; 0x00 = 0 pixels-per-meter
DWORD biClrUsed; 0x00
DWORD biClrImportant; 0x00
RGBQUAD array (color table)
----------------------------
NO COLOR TABLE
BITMAP BITS
图像的尺寸为14*8像素,每个像素的颜色值占24bit,那么由此可以得到图像数据的大小应该为14 * 8 * 24/8 = 336字节,但是从从上面我们可以看到图像数据(BITMAP BYTES)的大小为352字节。两种算法所得的结果为什么会不同呢?这就要考虑到图像每行都必须是4字节的倍数,如果不是则要补0,知道这行图像数据为4的倍数。
在上面我们以及知道图像的宽度为14像素,每个像素的颜色值占25bit即3字节,那么每行的字节数为14 * 3 = 42字节,不是4的倍数,那么就需要补2字节0,使每行为44字节,这样就变成了4的倍数,从而符合bmp的文件格式了。补0后的每行字节数为44,共有8行,因此图像数据的大小为44 * 8 = 352字节。这样就biSizeImage和一致了。
从上图中我们看到00000060h和00000061h处补了2字节0(第一行),在0000008ch和0000008dh处补了2字节0(第二行)
例解BITMAP的数据格式相关推荐
- ZIP文件格式详解(一)——文件数据格式
ZIP文件格式详解(一)--文件数据格式 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- 安川机器人焊管子编程_“例解+图解”安川机器人的典型编程案例!
原标题:"例解+图解"安川机器人的典型编程案例! 中国制造业面临着向高端转变.承接国际先进制造.参与国际分工的巨大挑战,加快工业机器人技术的研究.开发与应用是抓住这个历史机遇的主要 ...
- SQL 连接 JOIN 例解
SQL 连接 JOIN 例解.(左连接,右连接,全连接,内连接,交叉连接,自连接) 最近公司在招人,同事问了几个自认为数据库可以的应聘者关于库连接的问题,回答不尽理想- 现在在这写写关于它们的作用 假 ...
- java ooa编程,例解基于UML的OOA、OOD
搜索热词 内容已了然于胸,所以将不会过多阐述,而将重点放在应用过程上.本文的目的是通过一个完整的实例,展现基于UML的OOA&D过程的一个简化模式,帮助朋友们更好的认识UML在 OOA& ...
- 图文详解YUV420/YUV422数据格式(转)
一.YUV格式与RGB格式的换算 以下是标准公式 RGB 转换成 YUV Y = (0.257 * R) + (0.504 * G) + (0.098 * B) + 16 Cr = V = (0.43 ...
- android bitmap 无损压缩,详解Bitmap尺寸压缩与质量压缩
转载请注明出自flowsky37的博客,尊重他人辛苦劳动! 在Android系统中,关于图片处理的是一个既常见又比较棘手的问题.一个应用中,存在需要展示大量的图片的布局,那我们必须要小心翼翼的处理了, ...
- .wav文件详解,PCM数据格式,.wav生成C语言数组
.WAV文件,PCM数据 1. 音频简介 经常见到这样的描述: 44100HZ 16bit stereo 或者 22050HZ 8bit mono 等等.44100HZ 16bit stereo: 每 ...
- 用python解“混合类型数据格式输入”题
7-6 混合类型数据格式化输入 本题要求编写程序,顺序读入浮点数1.整数.字符.浮点数2,再按照字符.整数.浮点数1.浮点数2的顺序输出. 输入格式: 输入在一行中顺序给出浮点数1.整数.字符.浮点数 ...
- 例解基于UML的面向对象分析与设计
摘要 本文以实例的方式,展示了如何使用UML进行面向对象的分析与设计.本文将假设读者对UML.面向对象等领域的基本内容已了然于胸,所以将不会过多阐述,而将重点放在应用过程上.本文的目的是通过一个完整的 ...
最新文章
- 遴选中计算机类,计算机卓越班遴选办法-计算机学院
- python手机端给电脑端发送数据_期货交易软件有哪些比较好用?分手机端和电脑端...
- C++ 一个程序获取另一个程序Edit控件的内容
- 使用windbg通过vtable找到优化后的this指针
- Tableau上面地图与条形图结合_Tableau 全新地图实战演示,更快、更高、更强
- opengl 矩阵投影代码 shade_LookAt、Viewport、Perspective矩阵
- ubuntu 18.04 LTS 安装SecureCRT
- 史上最全使用Nexus搭建Maven服务器详细配置
- pandavan路由器升级php到7,下载宝pandavan固件+H3C交换机单线复用问题讨论
- 《Metasploit魔鬼训练营》 第二、三章
- 有关网线接法的几个问题
- Linux下线程(LWP)的相关概念
- vue2+element ui 导入和导出后端传过来的文件
- java curator_关于Curator学习过程问题
- 自定义Spark累加器
- 这些曾经世界第一的手游,现在全都凉了
- matlab如何查看眼图q值,详解:什么是眼图、眼图怎么看?
- 这个面试题有点意思哦
- linux下将qt打包为可执行文件
- Unity实现体积雾与体积光
热门文章
- Comsol中Absolute Pressure的解释
- 《Web安全之机器学习入门》笔记:第七章 7.6朴素贝叶斯检测DGA域名
- 老罗抖音推荐EcoFlow正浩户外电源,小众科技为何被选中?
- 计算机公式above,word表格中求和公式是SUM(ABOVE).请问:括号中ABOVE是什么意思呢?
- Resource not found问题
- 如何解决Oracle GoldenGate 没有主键的问题?
- Koa 框架 koa-better-body
- Spring Boot(四)-- 中的application.properties配置简介 2
- 常见钽电容尺寸和耐压
- 怎样才能批量查询网站的谷歌PR权重?把手教你批量查询网站谷歌PR权重值