TensorFlow应用实战-18-Policy Gradient算法
Policy Gradient算法

policy Gradient算法不止一种。
有兴趣的话:
深度增强学习之Policy Gradient方法1
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/21725498
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-"""
Policy Gradient 算法(REINFORCE)。做决策的部分,相当于机器人的大脑
"""import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tftry:xrange = xrange # Python 2
except:xrange = range # Python 3# 策略梯度 类
class PolicyGradient:def __init__(self,lr, # 学习速率s_size, # state/observation 的特征数目a_size, # action 的数目h_size, # hidden layer(隐藏层)神经元数目discount_factor=0.99 # 折扣因子):self.gamma = discount_factor # Reward 递减率# 神经网络的前向传播部分。大脑根据 state 来选 actionself.state_in = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, s_size], dtype=tf.float32)# 第一层全连接层hidden = tf.layers.dense(self.state_in, h_size, activation=tf.nn.relu)# 第二层全连接层,用 Softmax 来算概率self.output = tf.layers.dense(hidden, a_size, activation=tf.nn.softmax)# 直接选择概率最大的那个 actionself.chosen_action = tf.argmax(self.output, 1)# 下面主要是负责训练的一些过程# 我们给神经网络传递 reward 和 action,为了计算 loss# 再用 loss 来调节神经网络的参数self.reward_holder = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.float32)self.action_holder = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.int32)self.indexes = tf.range(0, tf.shape(self.output)[0]) * tf.shape(self.output)[1] + self.action_holderself.outputs = tf.gather(tf.reshape(self.output, [-1]), self.indexes)# 计算 loss(和平时说的 loss 不一样)有一个负号# 因为 TensorFlow 自带的梯度下降只能 minimize(最小化)loss# 而 Policy Gradient 里面是要让这个所谓的 loss 最大化# 因此需要反一下。对负的去让它最小化,就是让它正向最大化self.loss = -tf.reduce_mean(tf.log(self.outputs) * self.reward_holder)# 得到可被训练的变量train_vars = tf.trainable_variables()self.gradient_holders = []for index, var in enumerate(train_vars):placeholder = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name=str(index) + '_holder')self.gradient_holders.append(placeholder)# 对 loss 以 train_vars 来计算梯度self.gradients = tf.gradients(self.loss, train_vars)optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=lr)# apply_gradients 是 minimize 方法的第二部分,应用梯度self.update_batch = optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(self.gradient_holders, train_vars))# 计算折扣后的 reward# 公式: E = r1 + r2 * gamma + r3 * gamma * gamma + r4 * gamma * gamma * gamma ...def discount_rewards(self, rewards):discounted_r = np.zeros_like(rewards)running_add = 0for t in reversed(xrange(0, rewards.size)):running_add = running_add * self.gamma + rewards[t]discounted_r[t] = running_addreturn discounted_r# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-"""
游戏的主程序,调用机器人的 Policy Gradient 决策大脑
"""import numpy as np
import gym
import tensorflow as tffrom policy_gradient import PolicyGradient# 伪随机数。为了能够复现结果
np.random.seed(1)env = gym.make('CartPole-v0')
env = env.unwrapped # 取消限制
env.seed(1) # 普通的 Policy Gradient 方法, 回合的方差比较大, 所以选一个好点的随机种子print(env.action_space) # 查看这个环境中可用的 action 有多少个
print(env.observation_space) # 查看这个环境中 state/observation 有多少个特征值
print(env.observation_space.high) # 查看 observation 最高取值
print(env.observation_space.low) # 查看 observation 最低取值update_frequency = 5 # 更新频率,多少回合更新一次
total_episodes = 3000 # 总回合数# 创建 PolicyGradient 对象
agent = PolicyGradient(lr=0.01,a_size=env.action_space.n, # 对 CartPole-v0 是 2, 两个 action,向左/向右s_size=env.observation_space.shape[0], # 对 CartPole-v0 是 4h_size=8)with tf.Session() as sess:# 初始化所有全局变量sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())# 总的奖励total_reward = []gradient_buffer = sess.run(tf.trainable_variables())for index, grad in enumerate(gradient_buffer):gradient_buffer[index] = grad * 0i = 0 # 第几回合while i < total_episodes:# 初始化 state(状态)s = env.reset()episode_reward = 0episode_history = []while True:# 更新可视化环境env.render()# 根据神经网络的输出,随机挑选 actiona_dist = sess.run(agent.output, feed_dict={agent.state_in: [s]})a = np.random.choice(a_dist[0], p=a_dist[0])a = np.argmax(a_dist == a)# 实施这个 action, 并得到环境返回的下一个 state, reward 和 done(本回合是否结束)s_, r, done, _ = env.step(a) # 这里的 r(奖励)不能准确引导学习x, x_dot, theta, theta_dot = s_ # 把 s_ 细分开, 为了修改原配的 reward# x 是车的水平位移。所以 r1 是车越偏离中心, 分越少# theta 是棒子离垂直的角度, 角度越大, 越不垂直。所以 r2 是棒越垂直, 分越高r1 = (env.x_threshold - abs(x)) / env.x_threshold - 0.8r2 = (env.theta_threshold_radians - abs(theta)) / env.theta_threshold_radians - 0.5r = r1 + r2 # 总 reward 是 r1 和 r2 的结合, 既考虑位置, 也考虑角度, 这样学习更有效率episode_history.append([s, a, r, s_])episode_reward += rs = s_# Policy Gradient 是回合更新if done: # 如果此回合结束# 更新神经网络episode_history = np.array(episode_history)episode_history[:, 2] = agent.discount_rewards(episode_history[:, 2])feed_dict = {agent.reward_holder: episode_history[:, 2],agent.action_holder: episode_history[:, 1],agent.state_in: np.vstack(episode_history[:, 0])}# 计算梯度grads = sess.run(agent.gradients, feed_dict=feed_dict)for idx, grad in enumerate(grads):gradient_buffer[idx] += gradif i % update_frequency == 0 and i != 0:feed_dict = dictionary = dict(zip(agent.gradient_holders, gradient_buffer))# 应用梯度下降来更新参数_ = sess.run(agent.update_batch, feed_dict=feed_dict)for index, grad in enumerate(gradient_buffer):gradient_buffer[index] = grad * 0total_reward.append(episode_reward)break# 每 50 回合打印平均奖励if i % 50 == 0:print("回合 {} - {} 的平均奖励: {}".format(i, i + 50, np.mean(total_reward[-50:])))i += 1A3c实现3d赛车游戏: 成果展示
python play.py --num-workers 2 --log-dir neonrace
numworkders是 客户端。
重制: 任天堂版权问题
TensorKart
https://github.com/kevinhughes27/TensorKart
这个例子是截取屏幕上的截图,使用卷积神经网络训练。
实现步骤
- 游戏环境,设置
- 机器人大脑
- 游戏主程序
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-"""
配置 Neon Race(霓虹赛车)的游戏环境,以方便我们训练
"""import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import logging
import gym
from gym import spaces
from gym.spaces.box import Box
import universe
from universe import vectorized
from universe import spaces as vnc_spaces
from universe.spaces.vnc_event import keycode
from universe.wrappers import BlockingReset, GymCoreAction, EpisodeID, Unvectorize, Vectorize, Vision, Logger# 配置日志系统
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
universe.configure_logging()# 游戏:Neon Race
GAME = "flashgames.NeonRace-v0"# 创建并配置游戏环境
def create_env(client_id, remotes):env = gym.make(GAME)env = Vision(env)env = Logger(env)env = BlockingReset(env)reg = universe.runtime_spec('flashgames').server_registryheight = reg[GAME]["height"]width = reg[GAME]["width"]env = CropScreen(env, height, width, 84, 18)env = Rescale(env)# 可用的按键:左,右,上,左上,右上,下,用 Turbo 来加速keys = ['left', 'right', 'up', 'left up', 'right up', 'down', 'up x']env = DiscreteToFixedKeysVNCActions(env, keys)env = EpisodeID(env)env = DiagnosticsInfo(env)env = Unvectorize(env)env.configure(fps=5.0, remotes=remotes, start_timeout=15 * 60, client_id=client_id, vnc_driver='go', vnc_kwargs={'encoding': 'tight', 'compress_level': 0,'fine_quality_level': 50, 'subsample_level': 3})return env# 给环境加上记录诊断信息的功能
def DiagnosticsInfo(env, *args, **kwargs):return vectorized.VectorizeFilter(env, DiagnosticsInfoI, *args, **kwargs)# 诊断信息的类
class DiagnosticsInfoI(vectorized.Filter):def __init__(self, log_interval=503):super(DiagnosticsInfoI, self).__init__()self._episode_time = time.time()self._last_time = time.time()self._local_t = 0self._log_interval = log_intervalself._episode_reward = 0self._episode_length = 0self._all_rewards = []self._num_vnc_updates = 0self._last_episode_id = -1def _after_reset(self, observation):logger.info('重置环境中')self._episode_reward = 0self._episode_length = 0self._all_rewards = []return observationdef _after_step(self, observation, reward, done, info):to_log = {}if self._episode_length == 0:self._episode_time = time.time()self._local_t += 1if info.get("stats.vnc.updates.n") is not None:self._num_vnc_updates += info.get("stats.vnc.updates.n")if self._local_t % self._log_interval == 0:cur_time = time.time()elapsed = cur_time - self._last_timefps = self._log_interval / elapsedself._last_time = cur_timecur_episode_id = info.get('vectorized.episode_id', 0)to_log["diagnostics/fps"] = fpsif self._last_episode_id == cur_episode_id:to_log["diagnostics/fps_within_episode"] = fpsself._last_episode_id = cur_episode_idif info.get("stats.gauges.diagnostics.lag.action") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/action_lag_lb"] = info["stats.gauges.diagnostics.lag.action"][0]to_log["diagnostics/action_lag_ub"] = info["stats.gauges.diagnostics.lag.action"][1]if info.get("reward.count") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/reward_count"] = info["reward.count"]if info.get("stats.gauges.diagnostics.clock_skew") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/clock_skew_lb"] = info["stats.gauges.diagnostics.clock_skew"][0]to_log["diagnostics/clock_skew_ub"] = info["stats.gauges.diagnostics.clock_skew"][1]if info.get("stats.gauges.diagnostics.lag.observation") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/observation_lag_lb"] = info["stats.gauges.diagnostics.lag.observation"][0]to_log["diagnostics/observation_lag_ub"] = info["stats.gauges.diagnostics.lag.observation"][1]if info.get("stats.vnc.updates.n") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/vnc_updates_n"] = info["stats.vnc.updates.n"]to_log["diagnostics/vnc_updates_n_ps"] = self._num_vnc_updates / elapsedself._num_vnc_updates = 0if info.get("stats.vnc.updates.bytes") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/vnc_updates_bytes"] = info["stats.vnc.updates.bytes"]if info.get("stats.vnc.updates.pixels") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/vnc_updates_pixels"] = info["stats.vnc.updates.pixels"]if info.get("stats.vnc.updates.rectangles") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/vnc_updates_rectangles"] = info["stats.vnc.updates.rectangles"]if info.get("env_status.state_id") is not None:to_log["diagnostics/env_state_id"] = info["env_status.state_id"]if reward is not None:self._episode_reward += rewardif observation is not None:self._episode_length += 1self._all_rewards.append(reward)if done:logger.info('回合结束: 回合奖励=%s 回合长度=%s', self._episode_reward, self._episode_length)total_time = time.time() - self._episode_timeto_log["global/episode_reward"] = self._episode_rewardto_log["global/episode_length"] = self._episode_lengthto_log["global/episode_time"] = total_timeto_log["global/reward_per_time"] = self._episode_reward / total_timeself._episode_reward = 0self._episode_length = 0self._all_rewards = []return observation, reward, done, to_log# 限定的按键状态
class FixedKeyState(object):def __init__(self, keys):self._keys = [keycode(key) for key in keys]self._down_keysyms = set()def apply_vnc_actions(self, vnc_actions):for event in vnc_actions:if isinstance(event, vnc_spaces.KeyEvent):if event.down:self._down_keysyms.add(event.key)else:self._down_keysyms.discard(event.key)def to_index(self):action_n = 0for key in self._down_keysyms:if key in self._keys:# 如果按下多个 key(按键),只用第一个 keyaction_n = self._keys.index(key) + 1breakreturn action_n# 定义一个确定的 action space(动作空间)
class DiscreteToFixedKeysVNCActions(vectorized.ActionWrapper):def __init__(self, env, keys):super(DiscreteToFixedKeysVNCActions, self).__init__(env)self._keys = keysself._generate_actions()self.action_space = spaces.Discrete(len(self._actions))# 生成 actiondef _generate_actions(self):self._actions = []uniq_keys = set()for key in self._keys:for cur_key in key.split(' '):uniq_keys.add(cur_key)for key in [''] + self._keys:split_keys = key.split(' ')cur_action = []for cur_key in uniq_keys:cur_action.append(vnc_spaces.KeyEvent.by_name(cur_key, down=(cur_key in split_keys)))self._actions.append(cur_action)self.key_state = FixedKeyState(uniq_keys)def _action(self, action_n):# 每个 action 可能是一个长度为 1 的 np.array# 转换成 int 类型,以避免 warning(警告)return [self._actions[int(action)] for action in action_n]# 裁剪屏幕区域
class CropScreen(vectorized.ObservationWrapper):"""从左上角开始裁剪 height(高)x width(宽)大小的区域"""def __init__(self, env, height, width, top=0, left=0):super(CropScreen, self).__init__(env)self.height = heightself.width = widthself.top = topself.left = leftself.observation_space = Box(0, 255, shape=(height, width, 3))def _observation(self, observation_n):return [ob[self.top:self.top+self.height, self.left:self.left+self.width, :] if ob is not None else Nonefor ob in observation_n]# 处理 Frame(帧)
def _process_frame(frame):frame = cv2.resize(frame, (200, 128))frame = frame.mean(2).astype(np.float32)frame *= (1.0 / 255.0)frame = np.reshape(frame, [128, 200, 1])return frame# 调节观测空间的大小
class Rescale(vectorized.ObservationWrapper):def __init__(self, env=None):super(Rescale, self).__init__(env)self.observation_space = Box(0.0, 1.0, [128, 200, 1])def _observation(self, observation_n):return [_process_frame(observation) for observation in observation_n]推荐强化学习的博客:
https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/reinforcement-learning/
https://github.com/MorvanZhou/Reinforcement-learning-with-tensorflow
深度增强学习(DRL) 漫谈 从AC 到 A3C
https://blog.csdn.net/jinzhuojun/article/details/72851548
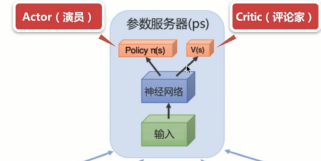
演员评论家
结合了 基于策略 和 基于价值
Actor-Critic 是演员-评论家 算法 结合了 Poilcy Gradient 和 Q 学习
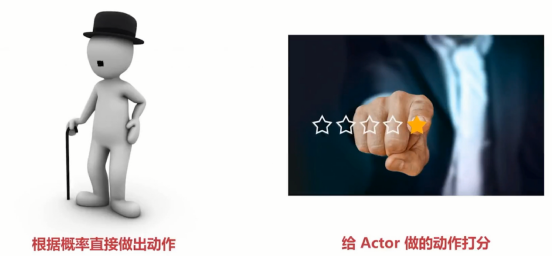
Actor 负责表演 基于Policy(策略) 的算法。选取Action来执行
Critic负责给Actor打分,基于Value(值)的算法。Q-learning
什么是A3C?
https://medium.com/emergent-future/simple-reinforcement-learning-with-tensorflow-part-8-asynchronous-actor-critic-agents-a3c-c88f72a5e9f2
Asynchronous Actor-Critic Agents (A3C)
异步 优势 演员-评论家
几个人同时玩游戏,玩游戏的经验上传到一个中央大脑。
几个人从中央大脑中获取最新最强的玩游戏方法
A3C 算法英文:

分布式TensorFlow,有效利用分布式
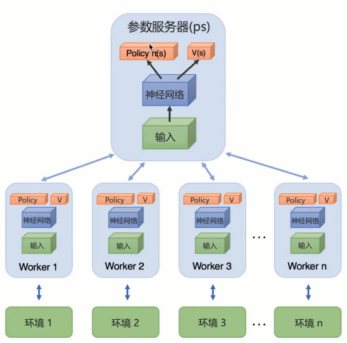
分布式(Distributed) TensorFlow
可以高效利用Cpu多核,达到近似GPU的训练速度
PS: Parameter Server 缩写。类似于全局的网络服务器
worker:客户端。从ps拉取pull参数/推送(push)参数到ps
https://www.tensorflow.org/deploy/distributed
TensorFlow分布式全套(原理 部署 实例)
https://blog.csdn.net/luodongri/article/details/52596780
https://blog.csdn.net/CodeMaster_/article/details/76223835
基于Google的gRPC通信框架来做的。
TensorFlow学习笔记
https://blog.csdn.net/u012436149/article/details/53140869
TensorFlow应用实战-18-Policy Gradient算法相关推荐
- 【强化学习】DDPG(Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient)算法详解
http://www0.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/d.silver/web/Teaching.html 引用莫凡老师的素材 https://morvanzhou.github.io/tut ...
- 强化学习(4):策略梯度Policy Gradient算法
本章内容主要参考了UC Berkeley Deep RL Bootcamp的内容,由作者按照自己的理解整理而成 终于到Policy Gradient方法了! 一.引言 reinforcement le ...
- 【强化学习】Policy Gradient算法详解
DeepMind公开课https://sites.google.com/view/deep-rl-bootcamp/lectures David Silver教程 http://www0.cs.ucl ...
- 【RL笔记】基于tensorflow实现RL的policy based算法
前言 Reinforcement Learning是AI的一个重要方向,本文实现来基于tensorflow的policy based算法 代码 import numpy as np import te ...
- 强化学习系列之Policy Gradient算法
一. 背景 1.1 基础组成部分 强化学习里面包含三个部件:Actor,environment,reward function Actor : 表示角色,是能够被玩家控制的. Policy of Ac ...
- 神经网络训练 policy gradient 算法时 梯度消失问题
再训练算法时 发现梯度输出为none 试了好几次 从源头找原因 最后得出的loss 一定要是 grad_fn=sumbackward 类似的类型 不然他没有梯度 再次记录
- 深度强化学习-Policy Gradient基本实现
全文共2543个字,2张图,预计阅读时间15分钟. 基于值的强化学习算法的基本思想是根据当前的状态,计算采取每个动作的价值,然后根据价值贪心的选择动作.如果我们省略中间的步骤,即直接根据当前的状态来选 ...
- 强化学习(二):Policy Gradient理解
上一章已经介绍了基于值函数方法的简单的DQN的理解,而在深度强化学习领域另一种基于端到端思路的策略梯度(Policy Gradient)算法相较而言可能取得更好的结果,也更加方便理解.于是,本章我们就 ...
- 【强化学习】Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient(DDPG)算法详解
1 DDPG简介 DDPG吸收了Actor-Critic让Policy Gradient 单步更新的精华,而且还吸收让计算机学会玩游戏的DQN的精华,合并成了一种新算法,叫做Deep Deterini ...
- Policy Gradient 之 A3C 与 A2C 算法
Policy Gradient 之 A3C 与 A2C 算法 Motivation Background Algorithm Policy Gradient Actor-Critic A3C A2C ...
最新文章
- 双非高校浙工大,一年2项研究上Nature,校友纷纷打Call:欠一个211名头
- ASP.NET模板引擎技术
- python 两两组合
- L1-073 人与神 (5 分)-PAT 团体程序设计天梯赛 GPLT
- 缓存失效和命名是计算机科学两大难题,命名也是一种艺术
- MAYA安装包+安装教程
- SQL Sever 2008 R2安装步骤
- windows 修改MySQL默认3306端口
- Python打字练习程序
- WPS添加宋体等字体问题
- python视频补帧_视频补帧软件(DAIN APP)软件下载_视频补帧软件(DAIN APP)v0.40官方版 - Windows10系统之家...
- 什么是边界扫描(boundary scan)?
- 单模光纤VS多模光纤
- MKS Robin nano V3.0主板使用RRF 固件教程
- 2022年秋招总结暨acm退役记
- 公网访问阿里云RDS云数据库
- 《罗曼蒂克消亡史》影评
- zxing扫描条形码 ios
- 双评价技术指南2020_2020年双十一/双11购买恒温花洒套装不被挖坑的选购指南
- JAVA高级基础(26)---File的常用方法
