applicationcontext and webapplicationcontext
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
Web Application context extended Application Context which is designed for work with the standardjavax.servlet.ServletContext so it's able to communicate with the container.
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext { ServletContext getServletContext(); }Beans, instantiated in WebApplicationContext will also be able to use ServletContext if they implement ServletContextAware interface
package org.springframework.web.context; public interface ServletContextAware extends Aware { void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext); }There many things possible to do with the ServletContext instance, for example accessing WEB-INF resources(xml configs and etc.) by calling the getResourceAsStream() method. Typically all application contexts defined in web.xml in a servlet Spring application are Web Application contexts, this goes both to the root webapp context and the servlet's app context.
Also, depending on web application context capabilities may make your application a little harder to test, and you may need to use MockServletContext class for testing.
Difference between servlet and root context Spring allows you to build multilevel application context hierarchies, so the required bean will be fetched from the parent context if it's not present in the current aplication context. In web apps as default there are two hierarchy levels, root and servlet contexts: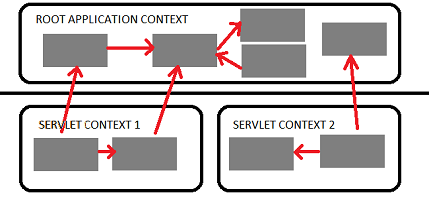
such thing allows you to run some services as the singletons for the entire application(Spring Security beans and basic database access services typically reside here) and another as separated services in the corresponding servlets to avoid name clashes between beans. For example one servlet context will be serving the web pages and another will be implementing a stateless web service.
This two level separation comes out of the box when you use the spring servlet classes: to configure the root application context you should use context-param tag in your web.xml
<context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value> /WEB-INF/root-context.xml/WEB-INF/applicationContext-security.xml </param-value> </context-param>(the root application context is created by ContextLoaderListener which is declared in web.xml
<listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> ) and servlet tag for the sevlet application contexts
<servlet> <servlet-name>myservlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>app-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet>please note that if init-param will be omitted, then spring will use myservlet-servlet.xml in this example.
See also: difference between applicationContext and spring-servlet.xml in spring
Spring lets you define multiple contexts in a parent-child hierarchy.
The applicationContext.xml defines the beans for the "root webapp context", i.e. the context associated with the webapp.
The spring-servlet.xml (or whatever else you call it) defines the beans for one servlet's app context. There can be many of these in a webapp, one per Spring servlet (e.g. spring1-servlet.xmlfor servlet spring1, spring2-servlet.xml for servlet spring2).
Beans in spring-servlet.xml can reference beans in applicationContext.xml, but not vice versa.
All Spring MVC controllers must go in the spring-servlet.xml context.
In most simple cases, the applicationContext.xml context is unnecessary. It is generally used to contain beans that are shared between all servlets in a webapp. If you only have one servlet, then there's not really much point, unless you have a specific use for it.
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/u/138995/blog/301396
applicationcontext and webapplicationcontext相关推荐
- Spring的三大核心接口——BeanFactory、ApplicationContext、WebApplicationContext
之前也在用这三个接口,但是对于他们的概念还是处于朦胧状态,同时,也不知道他们之间是一个什么关系,趁着现在有点时间总结一下吧,也需要对你有所帮助. 一.BeanFactory 基本认识: ...
- 【Spring MVC学习】WebApplicationContext初始化的三种方式
ApplicationContext是Spring的核心,Context我们通常解释为上下文环境,我想用"容器"来表述它更容易理解一些,ApplicationContext则是&q ...
- WebApplicationContext初始化
<WebApplicationContext初始化 ApplicationContext是Spring的核心,Context我们通常解释为上下文环境,我想用"容器"来表述它更 ...
- SpringMVC工作原理详解
点击上方"方志朋",选择"置顶或者星标" 你的关注意义重大! 先来看一下什么是 MVC 模式 MVC 是一种设计模式. MVC 的原理图如下: SpringMV ...
- Spring学习笔记(二)——Spring相关配置属性注入Junit整合
一.Spring的相关配置 1.1 Bean元素 class属性:被管理对象的完整类名 name属性:给Bean起个名字,能重复,能使用特殊字符.后来属性 id属性:给Bean起个名字,不能重复,不能 ...
- spring初始化web_了解Spring Web初始化
spring初始化web 几年前,我们大多数人习惯到处编写XML配置文件,甚至可以设置简单的Java EE应用程序. 如今,使用Java或Groovy来配置项目已成为首选方式–您只需要看一下Sprin ...
- spring bean生命周期管理--转
Life Cycle Management of a Spring Bean 原文地址:http://javabeat.net/life-cycle-management-of-a-spring-be ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之前传---FrameworkServlet
做项目时碰到Controller不能使用aop进行拦截,从网上搜索得知:使用spring mvc 启动了两个context:applicationContext 和WebapplicationCont ...
- Spring-WebApplicationContext解读
概述 Web应用环境下Bean的作用域 WebApplicationContext类体系结构 ConfigurableWebApplication WebApplicationContext初始化 使 ...
最新文章
- 驱动人生(离线网卡版)_驱动人生8.0版正式发布,最新功能速看
- leetcode114. 二叉树展开为链表(深度优先搜索)
- 【Java数据结构与算法】第七章 冒泡排序、选择排序、插入排序和希尔排序
- 鸿蒙第三代手机,荣耀Magic 3最新确认,鸿蒙系统+双6400万,最期待的荣耀来了
- 老生常谈的一个问题,转行学习编程,是自学还是报班
- i++,++i 作为参数
- 轻量级网络——ShuffleNetV2
- python右对齐输出数字怎么办_解决python让数字右对齐的方法
- 9个方法,教你用Google Drive做好云端档案管理
- P3376 【模板】网络最大流【EK算法+Dinic算法解】
- Nginx架构四之七层负载均衡
- 灵感来了挡也挡不住,基于Redis解决业务场景中延迟队列
- 西岸风格合成器-Eventide Newfangled Audio Generate 1.2.1 WiN
- 单基因gsea_一个低调奢华有内涵的单基因分析思路
- 基于.Net TcpListener 实现 WebSocketServer 通讯
- 我在上海赶飞机 出租司机给我上了一堂MBA课
- 一种无需调查船上坞的调查设备安装测量方法和安装测量系统
- Pulsar 社区周报 2020-09-12 ~ 09-18
- 一种自动化挖掘联网车辆协议中的拒绝服务漏洞的方案
- 人性的劣根 — 如何战胜另一个你
热门文章
- VisualGDB调试,实现VS环境下调试Android
- 大数据之-Hadoop3.x_MapReduce_outputformat案例需求分析---大数据之hadoop3.x工作笔记0121
- AndroidStudio_安卓原生开发_sharedpreferences清空---Android原生开发工作笔记150
- mybatis工作笔记003---Mybatis批量删除deleteByIds的用法
- JAVA学习笔记001---认识了解NIO
- Alt+/ 快速提示快捷键修复及ecplise心得
- 2011浙大878计算机专业基础综合大题答案解析
- SVM支持向量机,我用到的自学材料
- stl之截取:以一段字符串截取字符串
- delphi的 PosEx 函数功能介绍
