HTTPS and the TLS handshake protocol阅读笔记
目的
为能够透彻理解HTTPS报文交互过程,做此笔记。
本文大部分内容来自 : http://albertx.mx/blog/https-handshake/
http://www.cnblogs.com/svan/p/5090201.html
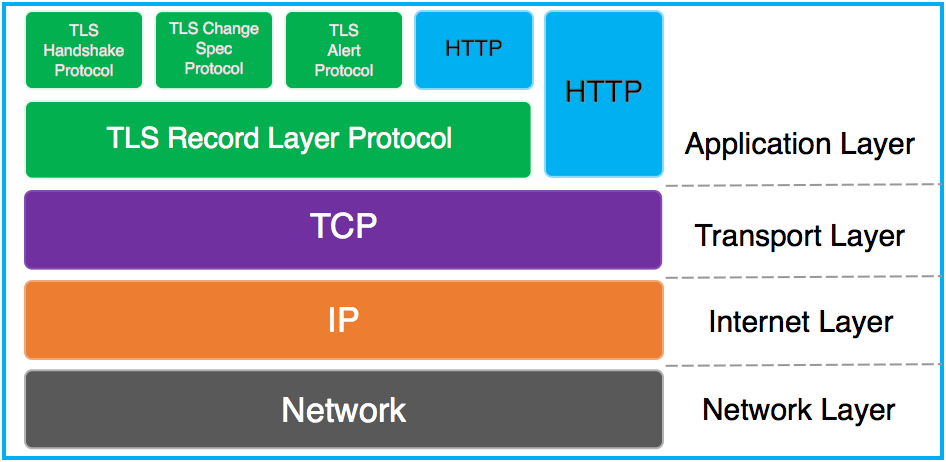
TLS Handshake Protocol
The TLS Handshake its like a sub-protocol of the TLS protocol. Its purpose is to define the algorithms and keys to authenticate the parties, verify and encrypt the data.
一次完整的http交互如下:
client hello -- 客户端向服务器打招呼 (带着 支持的 ciper suites)
server hello -- 服务器响应客户端 (告诉客户端, 我选择了哪一个 ciper suite)
Certificate Server hello done -- 服务器向客户端送证书(表明自己的身份)
Client Key Exchange, change ciper spec, encrypted handshake message -- 客户端发送密钥, 告诉服务器开始传送密文数据了, 传送一个加密的握手数据
New Session Ticket, change ciper spec, encrypted handshake message -- 服务器建立会话凭据, 告诉客户端开始传送密文数据了,传送一个加密的握手数据。

流程如下:
http://security.stackexchange.com/questions/20803/how-does-ssl-tls-work/20847#20847
Client ServerClientHello -------->ServerHelloCertificate*ServerKeyExchange*CertificateRequest*<-------- ServerHelloDoneCertificate*ClientKeyExchangeCertificateVerify*[ChangeCipherSpec]Finished -------->[ChangeCipherSpec]<-------- FinishedApplication Data <-------> Application Data
Client Hello
- The version of SSL that the client is trying to use for negotiating with the server
- Some random bytes generated by the client that will be used next to generate a master key for encryption.
- A list of encryption algorithms called cipher_suites. The client tells the server which cipher suites it understands.
主要传送 客户端支持的 加密算法列表:

Cipher Suites
包括四个部分:
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
DHE -- 密码交换加密算法
RSA -- 认证算法
AES_256_CBC -- 数据交换加密算法
SHA -- 数据完整性算法
Now, let me talk about the cipher suites listed above. If you review the image posted in the client hello section you will see a list. This list indicates the algorithms that will be used during the handshake and data transmission. The protocol needs 4 algorithms to work:
- Authentication algorithm
- Key Exchange algorithm
- Bulk cipher algorithm
- Message Authentication algorithm
These 4 algorithms are specified in the cipher suite.
Analyzing the first suite in the list we have the text: TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA.
- TLS: This is Transport Layer Security, the protocol we are using in the negotiation
- DHE: Denotes Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman. Diffie-Hellman is an algorithm for key exchanging cryptographic keys. Diffie-Hellman in ephemeral mode enhances its security
- RSA: This is the algorithm used for authentication. The most used algorithm in public-key cryptography (Rivest, Shamir and Adleman)
- WITH_AES_256_CBC: Advanced Encryption Standard is one of the best algorithms used in symmetric cryptography. Its key size can be of 128 bits, 192 bits or 256 bits. In this case the key size is 256 bits. CBC stands for Cipher-block Chaining one mode of operation in encryption. It means that the algorithm will encrypt the bytes of data by blocks and then it will link the encrypted blocks like a chain.
- SHA: Secure Hash Algorithm will be used for message authentication creating a hash of each block of the message to verify the integrity of such message.
Server Hello
- Some random bytes now generated by the server that will be used to generate a master key.
- The cipher suite selected by the server (from the previous list sent by the client) that will be used for authentication, encryption and verification of the messages
告诉客户端,我选择的算法。

Certificate
The Certificate command is usually sent again from server to client. In this command the information transmitted is the list of certificates that the client needs to have in order to authenticate the server and to encrypt some information. This can be one, two or more certificates.
证书用于认证服务器端的身份,防止被钓鱼等攻击。 其中也包括 服务器端的 公钥, 用于加密数据。
证书 可以是多个, 呈现链式法则。

Server Hello Done
Immediately after the Certificate message the server sends the Server Hello Done message. At this point the client has all the information it needs to generate the key material that both parties will need to encrypt the data. This key material is sent in the next handshake message…
服务器端,告诉客户端, 你已经具备产生密钥的条件, 快生成吧。
Client Key Exchange
The client generates some bytes of data, encrypt them with the public key of the certificate it received and then sends the encrypted data to the server (this is called PreMaster secret and will be used to generate the Master secret). The algorithm by which the client protects the data is defined during the Client Hello and Server Hello messages. It can be RSA or Diffie-Hellman.
客户端生成 一串随机的byte(PreMaster secret), 使用公钥加密后,传给服务器。 加密的算法hello过程已经确定。
关于master secret 生成, 见如下文章介绍(在第五点告诉你 master secret产生):
http://www.cnblogs.com/svan/p/5090201.html
使用RSA算法的SSL握手过程是这样的
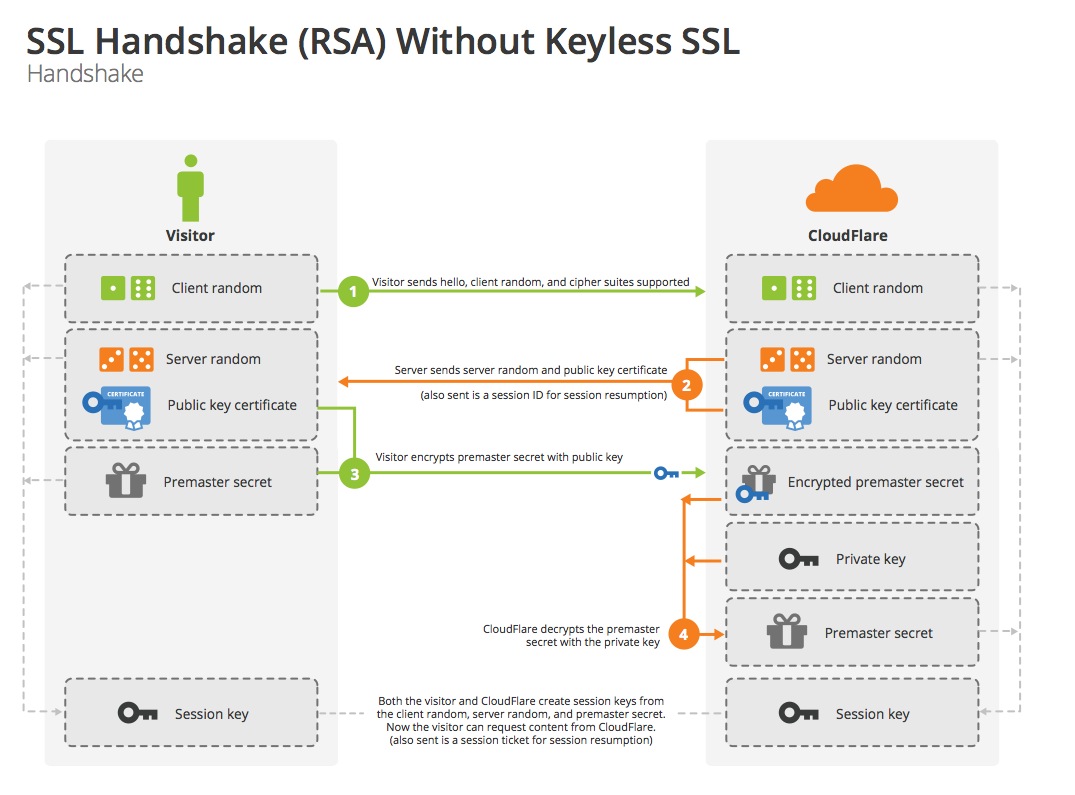
Source: Keyless SSL: The Nitty Gritty Technical Details
- [明文] 客户端发送随机数
client_random和支持的加密方式列表 - [明文] 服务器返回随机数
server_random,选择的加密方式和服务器证书链 - [RSA] 客户端验证服务器证书,使用证书中的公钥加密
premaster secret发送给服务端 - 服务端使用私钥解密
premaster secret - 两端分别通过
client_random,server_random和premaster secret生成master secret,用于对称加密后续通信内容
master secret是如何计算的
master_secret = PRF(pre_master_secret, "master secret",ClientHello.random + ServerHello.random)[0..47];
Change Cipher Spec
This is also sent from client to server indicating that the server MUST be prepared to receive the data in encrypted format and not in readable format because all the previous messages exchanged between client and server had been readable. This is the last message sent from client to server as readable. After this all the data sent to the server will be encrypted and we will not be able to read the contents with wireshark or any other sniffer tool. Proof of this is that in the below image the message after the Change Cipher Spec is an Encrypted Handshake Message.
客户端告诉服务器, 下一个报文开始传送 密文 了噢。

Finished
This is the first message protected by the algorithms and keys negotiated between the entities (this is the Encrypted Handshake Messsage we saw in the image). Both client and server send the Finished message but the first to do it is the client. If the server receives the message and could decrypt and understand it, it means the the server is reading the encrypted information in the right way. Now the only missing part is that client could decrypt the information sent by the server. To do that the server must send a Change Cipher Spec message too followed by the Finished message in the encrypted way. Exactly the same as client did. Again if the client could decrypt the Finished message it means that both parties are in frequency and they can talk to each other protecting all the data in transit.
客户端先想服务器端, 发送一个加密的报文, 如果服务器能够解密,并理解无误(客户端加密的内容, 是之前明文报文的一个摘要, 服务器端解密后, 计算其受到报文的摘要,并跟解密的摘要比较, 如果相等,则服务器接受客户端数据通道无误。)
然后服务器端,也一致, 需要按照客户端的做法, 先发送一个 change ciper spec消息, 告诉客户端要发送 密文了准备接受哦,
然后发送一个验证性通道畅通的加密报文, 客户端解密OK, 并可以理解(同上), 则两端握手成功。
开始传送应用数据。
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/lightsong/p/5174164.html
HTTPS and the TLS handshake protocol阅读笔记相关推荐
- Deciphering Malware‘s use of TLS (without Decryption)阅读笔记
文章目录 前言 一.简介 二.数据集 三.特征提取 四.实验结果 前言 本文是关于个人阅读Deciphering Malware's use of TLS (without Decryption)时的 ...
- docker: Error response from daemon: Get https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/: net/http: TLS handshake ti
docker: Error response from daemon: Get https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/: net/http: TLS handshake ti ...
- TLS Handshake failed: tls: server selected unsupported protocol version 301
TLS Handshake failed: tls: server selected unsupported protocol version 301 问题 问题分析 解决方法 问题 使用gorm链接 ...
- [置顶] Linux协议栈代码阅读笔记(一)
Linux协议栈代码阅读笔记(一) (基于linux-2.6.21.7) (一)用户态通过诸如下面的C库函数访问协议栈服务 int socket(int domain, int type, int p ...
- Xilinx AXI USB2.0 Device IP 手册阅读笔记
目录 1. 前言 2. 概要 2.1 USB2.0协议特点: 2.2 The AXI USB 2.0 Device介绍 2.2.1 Endpoint0: 2.2.2 Endpoint1~7: 3. 详 ...
- 点云配准论文阅读笔记--Comparing ICP variants on real-world data sets
目录 写在前面 点云配准系列 摘要 1引言(Introduction) 2 相关研究(Related work) 3方法( Method) 3.1输入数据的敏感性 3.2评价指标 3.3协议 4 模块 ...
- 《图解TCP/IP》阅读笔记
<图解TCP/IP>阅读笔记 第一章 网络基础知识 计算机网络发展的7个阶段 Batch Processing 批处理 TSS(Time Sharing System) 分时系统 The ...
- 源码阅读笔记 BiLSTM+CRF做NER任务 流程图
源码阅读笔记 BiLSTM+CRF做NER任务(二) 源码地址:https://github.com/ZhixiuYe/NER-pytorch 本篇正式进入源码的阅读,按照流程顺序,一一解剖. 一.流 ...
- Mina源码阅读笔记(一)-整体解读
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 今天的这一节,将从整体上对mina的源代码进行把握,网上已经有好多关于mina源码的阅读笔记,但好多都是列举了一下每个接口或者 ...
- “CoreCLR is now Open Source”阅读笔记
英文原文:CoreCLR is now Open Source 阅读笔记如下: CoreCLR是.NET Core的执行引擎,功能包括GC(Garbage Collection), JIT(将CIL代 ...
最新文章
- 基于InfluxDB+Grafana打造大数据监控利器--转
- ZOJ-1654 Place the Robots 拆行拆列构图+二分匹配 Or 最大独立点集+TLE
- JAVA程序设计----集合基础之Collection
- 用户画像|产品经理应该如何定位用户
- Hibernate 简介(百度)
- 文件的创建与读取 文件的数据添加
- c++ 低位在前 高位在后_A股市场:如果股票涨停后第二天“高开低走”,你知道怎么操作才能利益最大化吗?...
- ubuntu使用python读串口_ubuntu16.04上Python串口编程学习1
- react antd 更改table 表头和表行样式
- [转]C# 中的常用正则表达式总结
- 阿里巴巴 JAVA开发手册 内含大量规范,应用范例.涉及数据库,高并发,集合,索引等等大量干货
- 控制工程实践(11)——控制系统辨识
- 单片机广告灯实验总结_关于单片机的一些小实验lowbar;01点亮一个灯
- 苹果6显示连接id服务器出错,科技知识:如果连接appleid时发生服务器出错应该如何处理...
- HC05蓝牙模块主机与从机进行连接通信
- 【使用zookpeer】模拟 hadoop的 datenode与namenode 的master-slaves的 关系
- 用户信息管理系统测试报告
- 【Hadoop】Build and Execute
- 最大回撤和夏普比率的概念
- c语言bnd文件,Unix环境下嵌入式C程序编译
热门文章
- 【Django 2021年最新版教程26】模板语言 前端if判断怎么用 实例
- Mac如何删除python Python cannot be opened because of a problem
- 微信小程序云开发教程-产品原型的意义
- 大华平台linux命令,大华平台软件简介.docx
- atlas 力矩计算_Atlas 2.1.0 实践(2)—— 安装Atlas
- Android LitePal
- java rome,ROME - RSS聚合类库 - 组件类库 - JAVA开源项目 - 开源吧
- ccfcsp化学方程式java_化学方程式-ccf
- rsa算法的java实现,RSA算法的实现——java版
- java多线程-线程的实现方式
