View的Measure流程总结
首先,Measure流程 是为了测量,并计算view的大小.宽mMeasuredWidth,高mMeasuredHeight,然后将宽高保存.为后续layout 和draw 提供数据支撑.而且measure过程不止一次.
数值保存MeasureSpec
父容器的layoutParams会确认MeasureSpec,即view的测量模式和大小
MeasureSpec包含一个32位的int值,高2位代表SpaceMode,低30位代表SpecSize.
MeasureSpec有三类.view会有两个MeasureSpec变量,分别为widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec.
以下结论会在getChildMeasureSpec中得到验证
EXACTLY:父容器已经测量出所需要的精确大小,这也是childview的最终大小------match_parent,精确值.ATMOST: child view最终的大小不能超过父容器的给的------wrap_content .UNSPECIFIED: 不确定,源码内部使用-------一般在ScrollView,ListView .
MeasureSpace大多数情况下是由父布局的MeasureSpace和自己的Layoutparams确定(当然,还有margin,padding).详情见viewgroup.getChildMeasureSpec()
View
View的关键方法
2. measure 父布局会在自己的onMeasure方法中,调用child.measure ,这就把measure过程转移到了子View中。
3. onMeasure 子View会在该方法中,根据父布局给出的限制信息,和自己的content大小,来合理的测量自己的尺寸。
4. setMeasuredDimension当View测量结束后,把测量结果保存起来,具体保存在mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight中。
View的测量过程
measure()-->onMeasure()-->setMeasuredDimension()
viewGroup
viewGroup的关键方法
1. getChildMeasureSpec(父容器space,padding,一般是父容器的layoutparam.width或heigh)为child计算MeasureSpec。该方法为每个child的每个维度(宽、高)计算正确的MeasureSpec。目标就是把当前viewgroup的MeasureSpec和child的LayoutParams结合起来,生成最合理的结果。
//主代码case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:if (childDimension >= 0) {resultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size. So be it.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be// bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;}一段通俗易懂的getChildMeasureSpec伪代码
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int 限制信息中的模式, int padding, int layoutparam.width或heigh) {获取限制信息中的尺寸和模式。switch (限制信息中的模式) {case 当前容器的父容器,给当前容器设置了一个精确的尺寸:if (子View申请固定的尺寸LayoutParams) {你就用你自己申请的尺寸值就行了;} else if (子View希望和父容器一样大) {你就用父容器的尺寸值就行了;} else if (子View希望包裹内容) {你最大尺寸值为父容器的尺寸值,但是你还是要尽可能小的测量自己的尺寸,包裹你的内容就足够了;} break;case 当前容器的父容器,给当前容器设置了一个最大尺寸:if (子View申请固定的尺寸) {你就用你自己申请的尺寸值就行了;} else if (子View希望和父容器一样大) {你最大尺寸值为父容器的尺寸值,但是你还是要尽可能小的测量自己的尺寸,包裹你的内容就足够了;} else if (子View希望包裹内容) {你最大尺寸值为父容器的尺寸值,但是你还是要尽可能小的测量自己的尺寸,包裹你的内容就足够了;} break;case 当前容器的父容器,对当前容器的尺寸不限制:if (子View申请固定的尺寸) {你就用你自己申请的尺寸值就行了;} else if (子View希望和父容器一样大) {父容器对子View尺寸不做限制。} else if (子View希望包裹内容) {父容器对子View尺寸不做限制。}break;} return 对子View尺寸的限制信息;}这个就是对应的结论图,前三项是方法参数,后两个为计算得到的值.
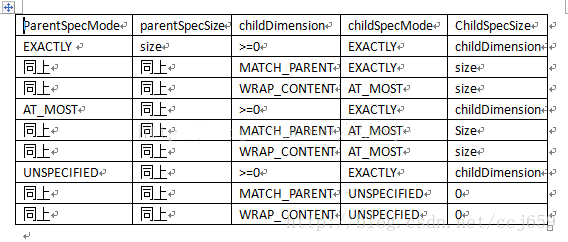
还有这个结论
EXACTLY:父容器已经测量出所需要的精确大小,这也是childview的最终大小------match_parent,确定值(不管你是0还是多少).ATMOST: child view最终的大小不能超过父容器的给的------wrap_content .UNSPECIFIED: 不确定,源码内部使用-------一般在ScrollView,ListView (我们一般用match_parent, wrap_content,还有确定值,这个不用).
2. measureChildren让所有子view测量自己的尺寸,需要考虑当前ViewGroup的MeasureSpec和Padding。跳过状态为gone的子view.
3. measureChild 测量单个view的尺寸.需要考虑当前ViewGroup的MeasureSpec和Padding.
4. measureChildWithMargins 测量单个View,需要考虑当前ViewGroup的MeasureSpec和Padding、margins.
viewGroup的测量流程
measureChildren()--> getChildMeasureSpec()-->child.measure()
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,//获取测量模式mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);//测量子view}综合流程
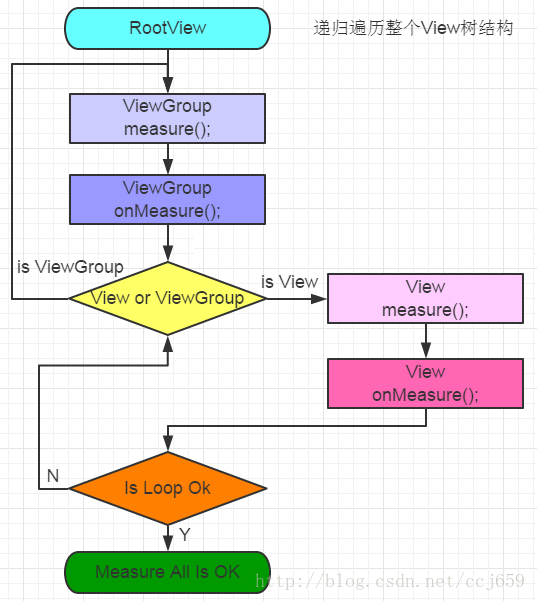
一个app启动之后,view树的measure过程从根节点DecordView开始,也就是从ViewGroup开始.
一般而言
首先从viewgroup. 测量自身
measure(),然后measureChildren()开始,遵循viewgroup的测量流程,measure()-->measureChild()测量子view-->getChildMeasureSpec()为child计算测量模式-->child.measure()子view开始测量.子view如果是viewgroup,则重复1,如果是view,则遵循view的测量流程
child.measure()-->measure()-->onMeasure()-->setMeasuredDimension()保存尺寸.遍历到最后一层,最后一个view.
把子view的尺寸告诉父布局,让父布局重新测量大小.
在measure过程中,ViewGroup会根据自己当前的状况,结合子View的尺寸数据,进行一个综合评定,然后把相关信息告诉子View,然后子View在onMeasure自己的时候,一边需要考虑到自己的content大小,一边还要考虑的父布局的限制信息,然后综合评定,测量出一个最优的结果。
measure实践
需求
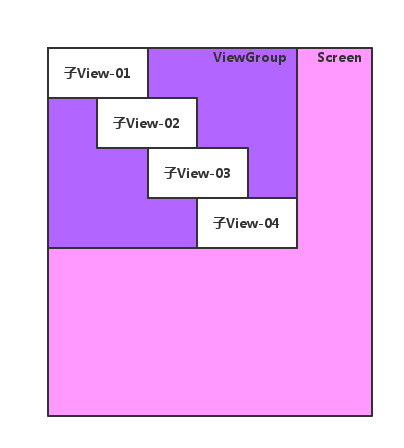
我们做这样一个view,view需要适配所有layoutParams类型.
思路
1.确定viewgroup的大小,
在onMeasure中,根据MeasuredSpace的不同,分别进行测量.
switch (widthMode) {case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://本容器为match_parent或者有精确大小时,容器width大小是测量的大小width = widthSize;break;case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST://本容器为wrap_content,容器width大小是 最大子view的width大小+pading+marginwidth = getWidth(widthSize, childCount);break;}2.确定子view的大小
在layout中,用for让每一个子view,都向右平移一些像素.
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { //依次 定位 每个 子viewView v = getChildAt(i);left = i * OFFSET;right = left + v.getMeasuredWidth();bottom = top + v.getMeasuredHeight();v.layout(left, top, right, bottom);top += v.getMeasuredHeight();}代码
/**
- Created by chenchangjun on 17/7/18.
*/
public class MyMeasureView extends ViewGroup {
private static final int OFFSET = 50;@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);int width = 0;int heigh = 0;int childCount = getChildCount();for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {View child = getChildAt(i);if (child.getVisibility()==GONE){continue;}ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = child.getLayoutParams();//获取子view的layoutParamsint childWithSpace = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, 0, layoutParams.width); //获取子view的测量模式(本容器的MeasureSpec,padding,子view的layoutParams中的width)int childHeighSpace = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec, 0, layoutParams.height);child.measure(childWithSpace, childHeighSpace); //子view进行测量}switch (widthMode) {case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY://本容器为match_parent或者有精确大小时,容器width大小是测量的大小width = widthSize;break;case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST://本容器为wrap_content,容器width大小是 最大子view的width大小+pading+marginwidth = getWidth(widthSize, childCount);break;}switch (heightMode) {case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:heigh = heightSize;break;case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:heigh = getHeigh(heightSize, childCount);break;}setMeasuredDimension(width, heigh);}@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {int left = 0;int right = 0;int top = 0;int bottom = 0;int childCount = getChildCount();for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { //依次 定位 每个 子viewView v = getChildAt(i);if (v.getVisibility()==GONE){continue;}left = i * OFFSET;right = left + v.getMeasuredWidth();bottom = top + v.getMeasuredHeight();v.layout(left, top, right, bottom);top += v.getMeasuredHeight();}}private int getHeigh(int heightSize, int childCount) {int heigh;heigh = heightSize;for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {View view = getChildAt(i);heigh = heigh + view.getMeasuredHeight();}return heigh;
}private int getWidth(int widthSize, int childCount) {int width;width = widthSize;for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {View view = getChildAt(i);if (view.getVisibility()==GONE){continue;}int widthOffset = i * OFFSET + view.getMeasuredHeight();width = Math.max(width, widthOffset); //此处wrap_Content取子view的最大width}return width;
}public MyMeasureView(Context context) {super(context);
}public MyMeasureView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);
}public MyMeasureView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public MyMeasureView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
}
###结果##参考[http://www.cnblogs.com/nanxiaojue/p/3536381.html](http://www.cnblogs.com/nanxiaojue/p/3536381.html)
�
[http://www.cnblogs.com/xyhuangjinfu/p/5435201.html](http://www.cnblogs.com/xyhuangjinfu/p/5435201.html)View的Measure流程总结相关推荐
- android自定义view流程,Android 自定义View--从源码理解View的绘制流程
前言 在Android的世界里,View扮演着很重要的角色,它是Android世界在视觉上的具体呈现.Android系统本身也提供了很多种原生控件供我们使用,然而在日常的开发中我们很多时候需要去实现一 ...
- Android自定义view之measure、layout、draw三大流程
自定义view之measure.layout.draw三大流程 一个view要显示出来,需要经过测量.布局和绘制这三个过程,本章就这三个流程详细探讨一下.View的三大流程具体分析起来比较复杂,本文不 ...
- View系列 (三) — Measure 流程详解
Measure 流程详解 一.概述 二.单一 View 的测量流程 1. 流程图 2. 源码分析 三.ViewGroup 的测量流程 1. 流程图 2. 源码分析 一.概述 测量过程分为 View的m ...
- Android布局measure,Android View的Measure测量流程全解析
相信绝大多数Android开发者都有自定义View来满足各种各样需求的经历,也知道一个View的绘制展示要经过measure.layout.draw三大流程,三者中measure的过程相比是稍微复杂一 ...
- View的绘制流程-measure、layout、draw
承接上文--Window.DecorView.ViewRootImp详解 我们打开一个Activity后,在ActivityThread中 的performLaunchActivity方法中,回调Ac ...
- Android View的工作流程(二) measure过程
一.View的measure过程 View的measure过程是由View的measure方法完成的,他是一个被final关键字修饰的方法,我们无法重写该方法,但是measure方法中会调用onMe ...
- View 体系详解:View 的工作流程
1.View 树的加载流程 当我们调用 startActivity() 方法的时候,会调用到 ActivityThread 中的 performLaunchActivity() 获取一个 Activi ...
- Android之View的绘制流程解析
转载请标明出处:[顾林海的博客] 个人开发的微信小程序,目前功能是书籍推荐,后续会完善一些新功能,希望大家多多支持! ##前言 自定义View在Android中占据着非常重要的地位,因此了解View的 ...
- Android O: View的绘制流程(二):测量
在前一篇博客Android O: View的绘制流程(一): 创建和加载中, 我们分析了系统创建和加载View的过程,这部分内容完成了View绘制的前置工作. 本文开始分析View的测量的流程. 一 ...
最新文章
- WPF Snoop 2.7 源码研究
- Sencha-概念-Layouts(布局)(官网文档翻译8)
- 我从500个技术号,选出这10个厉害的推荐给你!
- 【迈克尔・乔丹:人工智能,革命远未发生】
- Apache用户认证、域名跳转、Apache访问日志
- asp.net 2.0小TIPS两则
- VScode 乱装插件环境破坏踩坑自我反思总结
- 【PyQT5编程】Pycharm结合QtDesigner使用示例:创建登录窗体
- 【超坑人的面试题】switch没有break
- css高清动图,CSS3+PNG实现GIF动画效果
- 三十万,买一只基金,放着不管,五年后会怎么样?
- java中的锁池和等待池
- 免拆破解电信机顶盒TY1208-Z,绝对成功
- jquery1.7版本核心模块测试封装
- 记忆日语的奥秘—日语汉字读音变化
- matlab8邻域搜索算法,一种基于可搜索连续邻域A*算法的路径规划方法与流程
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 266(C- G)「判凸包」「dp」「期望」「基环树」「组合数」
- Python2中使用input出现的NameError: name ‘***‘ is not defined问题原因及解决办法
- TensorFlow笔记-06-神经网络优化-损失函数,自定义损失函数,交叉熵
- 浏览器无法渲染php,解决lighttpd运行后浏览器无法渲染html
热门文章
- 大连理工计算机专业等级,大连理工计算机专业全国排第几呀
- 学php为什么要学linux,为什么 PHP 程序员应该学习使用 Swoole
- MySQL数据库如何杀死会话_如何彻底杀掉不良用户会话
- 现在好用的mysql客户端_还在用 Navicat 的,可以试试这几款免费且好用的 MySQL 客户端...
- 【Linux】虚拟机 Ubuntu sudo指令实现Gparted安装和 dsv/sda1 内存扩展
- 【杂谈】为了让大家学好深度学习模型设计和优化,有三AI都做了什么
- 【分享预告】细数GAN和图像分类的前世今生
- 中国水处理行业深度监测及投资发展可行性分析报告2022-2027年新版
- 注重经营管理谋定市场开发-农业大健康·台湾:有机农业借鉴
- JuJu团队12月28号工作汇报
