[paper] Multiple Human Parsing
Towards Real World Human Parsing: Multiple-Human Parsing in the Wild
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.07206.pdf
提出多人语义分割数据集:4980张图片(训练/验证/测试:3000/1000/980),每张包含2-16人,18个语义标签。
多人分割模型MH-Parser包含5个组件:
Representation learner (FCN提特征)
Global parser (用特征生成分割图)
Candidate nominator (RPN生成bbox)
Local parser (使用特征和bbox生成局部分割)
Global-local aggregator (结合全局和局部信息得到最终每个人的分割)
we introduce the Multiple-Human Parsing (MHP) dataset, which contains multiple persons in a real world scene per single image.
The MHP dataset contains various numbers of persons (from 2 to 16) per image with 18 semantic classes for each parsing annotation. Persons appearing in the MHP images present sufficient variations in pose, occlusion and interaction.
To tackle the multiple-human parsing problem, we also propose a novel Multiple-Human Parser (MH-Parser), which considers both the global context and local cues for each person in the parsing process.
Introduction
all the human parsing datasets only contain one person per image, while usually multiple persons appear simultaneously in a realistic scene.
Previous work on human parsing mainly focuses on the problem of parsing in controlled and simplified conditions.
simultaneous presence of multiple persons.
we tackle the problem of person detection and human parsing simultaneously so that both the global information and the local information are employed.
contributions:
We introduce the multiple-human parsing problem that extends the research scope of human parsing and matches real world scenarios better in various applications.
We construct a new large-scale benchmark, named Multiple-Human Parsing (MHP) dataset, to advance the development of relevant techniques.
We propose a novel MH-Parser model for multiple-human parsing, which integrates global context as well as local cues for human parsing and significantly outperforms the naive “detect-and-parse” approach.
Related work
Human parsing
Instance-aware object segmentation
The MHP dataset
this is the first large scale dataset focusing on multiple-human parsing.
4980 images, each image contains 2 to 16 humans, totally there are 14969 person level annotations.
Image collection and annotation methodology
we manually specify several underlying relationships (e.g., family, couple, team, etc.), and several possible scenes (e.g., sports, conferences, banquets, etc.)
The first task is manually counting the number of foreground persons and duplicating each image into several copies according to that number.
the second is to assign the fine-grained pixel-wise label for each instance.
Dataset statistics
training/validation/test: 3000/1000/980 (randomly choose)
The images in the MHP dataset contain diverse human numbers, appearances, viewpoints and relationships (see Figure 1).
Multiple-Human Parsing Methods
MH-Parser
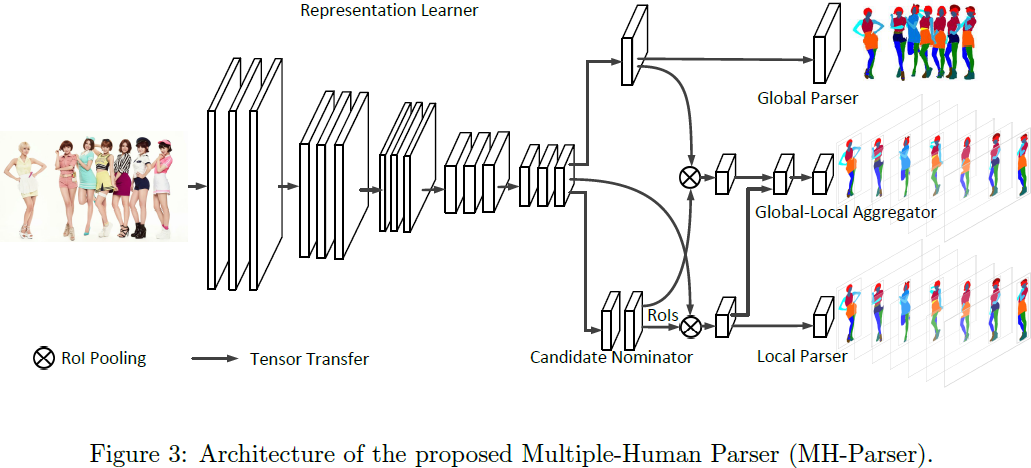
The proposed MH-Parser has five components:
Representation learner
We use a trunk network to learn rich and discriminative representations. we preserve the spatial information of the image by employing fully convolutional neural networks.
images and annotations => representations
Global parser
capture the global information of the whole image. The global parser takes the representation from the representation learner and generates a semantic parsing map of the whole image.
representations => a semantic parsing map of the whole image
Candidate nominator
We use a candidate nominator to generate local regions of interest. The candidate nominator consists of a Region Proposal Network (RPN).
representations => candidate box
Local parser
give a fine-grained prediction of the semantic parsing labels for each person in the image.
representations, candidate box => semantic parsing labels for each person
Global-local aggregator
leverages both the global and local information when performing the parsing task of each person.
the hidden representations from both the local parser and the global parser => a set of semantic parsing predictions for each candidate box
Detect-and-parse baseline
In the detection stage, we use the representation learner and the candidate nominator as the detection model.
In the parsing stage, we use the representation learner and the local prediction as the parsing model.
Experiments
Performance evaluation
The goal of multiple-human parsing is to accurately detect the persons in one image and generate semantic category predictions for each pixel in the detected regions.
Mean average precision based on pixel (mAPpmAP^p)
we adopt pixel-level IOU of different semantic categories on a person.
Percentage of correctly segmented body parts (PCP)
evaluate how well different semantic categories on a human are segmented.
Global Mean IOU
evaluates how well the overall parsing predictions match the overall global parsing labels.
Implementation details
representation learner
adopt a residual network [19] with 50 layers, contains all the layers in a standard residual network except the fully connected layers.
input: an image with the shorter side resized to 600 pixels and the longer side no larger than 1000 pixels
output: 1/16 of the spatial dimension of the input image
global parser
add a deconvolution layer after the representation learner.
output: a feature map with spatial dimension 1/8 of the input image
candidate nominator
use region proposal network (RPN) to generate region proposals.
output: region proposals
local parser
based on the region after Region of Interest (ROI) pooling from the representation learner and the size after pooling is 40.
global-local aggregator
the local part is from the hidden layer in the local parser, and the global part uses the feature after ROI pooling from the hidden layer of the global parser with the same pooled size.
The network is optimized with one image per batch and the optimizer used is Adam [20].
Experimental analysis
Overall performance evaluation
RL stands for the representation learner, G means the global parser, L denotes the local parser, A for aggregator.
Qualitative comparison
We can see that the MH-Parser captures more fine-grained details compared to the global parser, as some categories with a small number of pixels are accurately predicted.
Conclusion and future work
In this paper, we introduced the multiple-human parsing problem and a new large-scale MHP dataset for developing and evaluating multiple-human parsing models.
We also proposed a novel MH-Parser algorithm to address this new challenging problem and performed detailed evaluations of the proposed method with different baselines on the new benchmark dataset.
[paper] Multiple Human Parsing相关推荐
- 【论文阅读】Graphonomy: Universal Human Parsing via Graph Transfer Learning通过图迁移学习进行的通用人体解析
Problem问题 人体解析是指将在图像中捕获的人分割成多个语义上一致的区域,例如, 身体部位和衣物.作为一种细粒度的语义分割任务,它比仅是寻找人体轮廓的人物分割更具挑战性. 人体解析对于以人为中心的 ...
- 多人部件解析--Towards Real World Human Parsing: Multiple-Human Parsing in the Wild
Towards Real World Human Parsing: Multiple-Human Parsing in the Wild https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.0720 ...
- Human Parsing 数据预处理使用指南
CIHP_PGN使用指南 # 1.进入目录 & 激活conda cd ~/cz/CIHP_PGN && conda activate CIHP_PGN # 2.处理数据(已将m ...
- Look into Person: Self-supervised Structure-sensitive Learning and A New Benchmark for Human Parsing
0.Abstract : 说明本篇文章的主要工作 : 一是提出了一个用于人体解析的大数据集 Look into Person (LIP), 这个数据集相比之前的数据集更大,覆盖情景更多,更复杂,作者还 ...
- [paper] CE2P
Devil in the Details: Towards Accurate Single and Multiple Human Parsing CE2P是一个端到端的人体解析的框架,现已开源,代码连 ...
- 【ECCV2020】接收论文列表part1
ECCV2020将于2020年8月23-28日在线上举行,今年共接受了1361篇论文,本文是接收论列表的第一部分,第二部见链接 Paper ID Paper Title Category 267 Qu ...
- AAAI-19录用论文清单
AAAI-19于1月27日在夏威夷召开,今年是33届会议. 会议录用论文清单, workshop16个,tutorials24个. 标题的词云分析: 作者单位词云(按作者人数计算/一篇文章可能有多个作 ...
- 【论文汇总】Semantic-Segmentation(语义分割)
语义分割 关于语义分割的所有论文和资源的列表. 数据集重要性 语义分割-深度学习 DL模型语义分割的若干实现 数据集 voc2012 CitySpaces Mapillary ADE20K PASCA ...
- 计算机视觉领域热门研究方向state-of-art算法实时更新
目录 细粒度识别 目标检测 视觉目标跟踪 多目标跟踪 语义分割 人体解析 人体位姿估计 密集场景人脸识别(人脸计数) 超分辨重建 边缘检测(简笔画/素描) 人脸关键点检测 注意事项 本篇博客不再更新, ...
最新文章
- 一个项目从开工到交付使用需要经历的过程
- 四十二、深入Java中的文件读取操作
- 十七、频繁模式、关联和相关性的基本概念和方法
- 元素的样式设置 元素类样式的操作 开关灯效果 获取兄弟元素 当前元素的兄弟元素样式
- mybatis plus骚操作之逻辑删除
- Jquery mobile问题总汇
- 模拟地铁乘车推荐c语言,模拟地铁新手攻略 新手必看三要素
- Springboot2.x 拦截器
- linux 格式化 lvm2,fedora 23 lvm2格式 根目录磁盘空间不足 扩容方法
- 苹果cmsV10简约白色风格自适应模板
- 【转】分辨率。各种vga和各种dpi
- 周年更名,元宇宙产业委再上新台阶
- 今日算法笔试练习【5】(08-06)(历年笔试题)
- 手把手教你使用R语言做出SCI论文中的表二(单因素分析表)(3)
- 二次元RPG游戏:Tap Fantasy
- DPC集群搭建手册-附考试心得
- 基于JavaScript实现网红太空人表盘
- 点云孔洞定位_孔洞修补研究总结
- 一小部分机器学习算法小结: 优化算法、逻辑回归、支持向量机、决策树、集成算法、Word2Vec等...
- PDF转换器注册码(支持所有版本)
