Unshielded Twisted Pair - CAT5, 5e 6
为什么80%的码农都做不了架构师?>>> 
This section talks about the cabling used in today's networks. There's a lot of different type of cabling in today's networks and I am not going to cover all of them, but I will be talking about the most common cables, which include UTP CAT5 straight through and crossover, Coax and a few more.
Cabling is very important if you want a network to work properly with minimum problems and bandwidth losses. There are certain rules which must never be broken when you're trying to design a network, otherwise you'll have problems when computers try to communicate. I have seen sites which suffer from enormous problems because the initial desgin of the network was not done properly !
In the near future, cabling will probably be something old and outdated since wireless communication seems to be gaining more ground, day by day. With that in mind, around 95% of companies still rely on cables, so don't worry about it too much :)
Let's have a quick look at the history of cabling which will allow us to appreciate what we have today !
The Beginning
We tend to think of digital communication as a new idea but in 1844 a man called Samuel Morse sent a message 37 miles from Washington D.C. to Baltimore, using his new invention ‘The Telegraph’. This may seem a far cry from today's computer networks but the principles remain the same.

Morse code is type of binary system which uses dots and dashes in different sequences to represent letters and numbers. Modern data networks use 1s and 0s to achieve the same result. The big difference is that while the telegraph operators of the mid 19th Century could perhaps transmit 4 or 5 dots and dashes per second, computers now communicate at speeds of up to 1 Giga bit, or to put it another way, 1,000,000,000 separate 1s and 0s every second.
Although the telegraph and the teletypewriter were the forerunners of data communications, it has only been in the last 35 years that things have really started to speed up. This was borne out of the necessity for computers to communicate at ever ncreasing speeds and has driven the development of faster and faster networking equipment, higher and higher specification cables and connecting hardware.
Development of new network technology
Ethernet was developed in the mid 1970's by the Xerox Corporation at its Palo Alto Research Centre (PARC) in California and in 1979 DEC and Intel joined forces with Xerox to standardize the Ethernet system for everyone to use. The first specification by the three companies, called the 'Ethernet Blue Book', was released in 1980, it was also known as the 'DIX standard' after their initials.
It was a 10 Mega bits per second system (10Mbps, = 10 million 1s and 0s per second) and used a large coaxial backbone cable running throughout the building, with smaller coax cables tapped off at 2.5m intervals to connect to the workstations. The large coax, which was usually yellow, became known as 'Thick Ethernet' or 10Base5 - the '10' refers to the speed (10Mbps), the 'Base' because it is a base band system (base band uses all of its bandwidth for each transmission, as opposed to broad band which splits the bandwidth into separate channels to use concurrently) and the '5' is short for the system's maximum cable length, in this case 500m.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) released the official Ethernet standard in 1983 called the IEEE 802.3 after the name of the working group responsible for its development and, in 1985, version 2 (IEEE 802.3a) was released. This second version is commonly known as 'Thin Ethernet' or 10Base2; in this case the maximum length is 185m even though the '2' suggest that it should be 200m.
Since 1983, various standard have been introduced because of the increased bandwidth requirements, so far we are up to the Gigabit rate !
Introduction
Unshielded Twisted Pair cable is most certainly by far the most popular cable around the world. UTP cable is used not only for networking but also for the traditional telephone (UTP-Cat 1). There are 6+ different types of UTP categories and, depending on what you want to achieve, you would need the appropriate type of cable. UTP-CAT5e is the most popular UTP cable, it came to replace the well known coaxial cable which was not able to keep up with the continuous growth for faster and more reliable networks.
Characteristics
The characteristics of UTP are very good and make it easy to work with, install, expand and troubleshoot and we are going to look at the different wiring schemes available for UTP, how to create a straight through UTP cable, rules for safe operation and a lot of other cool stuff !
So let's have a quick look at each of the UTP categories available today:
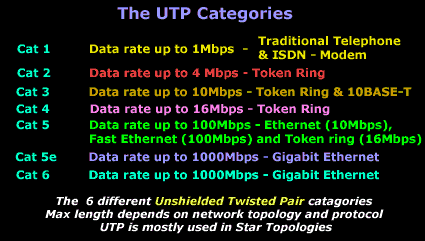
Category 1/2/3/4/5/6 – a specification for the type of copper wire (most telephone and network wire is copper) and jacks. The number (1, 3, 5, etc) refers to the revision of the specification and in practical terms refers to the number of twists inside the wire (or the quality of connection in a jack).
CAT1 is typically telephone wire. This type of wire is not capable of supporting computer network traffic and is not twisted. It is also used by phone companies who provide ISDN, where the wiring between the customer's site and the phone company's network uses CAT 1 cable.
CAT2, CAT3, CAT4, CAT5 and CAT6 are network wire specifications. This type of wire can support computer network and telephone traffic. CAT2 is used mostly for token ring networks, supporting speeds up to 4 Mbps. For higher network speeds (100Mbps plus) you must use CAT5 wire, but for 10Mbps CAT3 will suffice. CAT3, CAT4 and CAT5 cable are actually 4 pairs of twisted copper wires and CAT5 has more twists per inch than CAT3 therefore can run at higher speeds and greater lengths. The "twist" effect of each pair in the cables will cause any interference presented/picked up on one cable to be cancelled out by the cable's partner which twists around the initial cable. CAT3 and CAT4 are both used for Token Ring and have a maximum length of 100 meters.
CAT6 wire was originally designed to support gigabit Ethernet (although there are standards that will allow gigabit transmission over CAT5 wire, that's CAT 5e). It is similar to CAT5 wire, but contains a physical separator between the 4 pairs to further reduce electromagnetic interference.
The next pages show you how UTP cable is wired and the different wiring schemes. It's well worth visiting and reading about.
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/qihh/blog/61080
Unshielded Twisted Pair - CAT5, 5e 6相关推荐
- 关于网线水晶头的接法详解(2)
OSI 七层模型 在 OSI 七层模型中, 路由器 和三层 交换机 是三层(网络层)设备,二层交换机是二层(数据链路层)设备,集线器是一层(物理层)设备. 路由器( ...
- 【集成】网络技术的学习-刘俊平
说在前面的话 系统集成考试需要涉及到集成技术的内容,特别是网络技术在每年的考试中显得格外重要,如何从宏观理解该部分的内容,下面的资料,我觉得条理还是很清楚,希望能对大家有所参考!@ 第三章电子 ...
- 五类 六类网线相关知识
双绞线常见的有3类线,5类线和超5类线.6类线,以及最新的7类线.前者线径细而后者线径粗,型号如下: 一类线:主要用于传输语音(一类标准主要用于八十年代初之前的电话线缆),不同于数据传输. 二类线:传 ...
- Demystifying Ethernet Types— Difference between Cat5e, Cat 6, and Cat7
Demystifying Ethernet Types- Difference between Cat5e, Cat 6, and Cat7 Ethernet represents the plu ...
- 通信工程实施的详细过程以及水晶头与网线馈线的接法
小组合作 1 网线接法 2 水晶头接法 3 通信工程实施是一项繁复而庞大的工程,需要遵循一系列的标准和规范.它包括建设和维护通讯网络.选定通讯设备.进行设备配置和测试等过程.其实际意义在于增强 ...
- 怎么区分五类线、超五类线和六类线
打个广告, ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- 计算机网络实验1线缆制作,计算机网络技术实验报告1双绞线的制作
1.实验题目:双绞线的制作 2.实验目的: 在实验中通过了解交叉.直通双绞线的制作过程,以达到对传输介质的进一步了解,尤其是在各特殊的情况下网线的制作,从而胜任网络管理.维护和网络布线的工作. 3.实 ...
- 网线水晶头接法(附图说明)
网友:gunny 发布于: 2008.07.21 12:31 工具: 驳线钳(用于接驳水晶头)(必备) 水晶头接法: 关于双绞线的色标和排列方法是有统一的国际标准严格规定的,现在常用的是TIA/EIA ...
- 网线制作:网线和水晶头的接法
工具: 驳线钳(用于接驳水晶头)(必备) 水晶头接法: 关于双绞线的色标和排列方法是有统一的国际标准严格规定的,现在常用的是TIA/EIA568B.在打线时应使用如下的顺序:(TIA/EIA568B) ...
最新文章
- FFmpeg将Jpeg 编码到视频中
- php 5.3.3 漏洞,PHP 5.3.10多个拒绝服务漏洞
- 国内Python最有钱途的方向,开发第二,它排第一!
- C#文件操作基础之File类和FileInfo类
- sql语法,未完待续
- CentOS硬盘挂载之fdisk命令进行查看/分区/格式化/挂载
- verilog异步复位jk触发器_以不变应万变的异步FIFO面试宝典(二)
- php数组合成函数,PHP合并数组函数array_merge用法分析
- java spring boot 项目 热加载 有利于快速开发
- tar打包文件如何排除文件夹
- 计算机应届生月薪大多是多少?
- 将多个sheet页拆分成多个单独的excel
- breakpoint()
- 基于ShineBlink物联网开发板和机智云平台开发的“针对短期内宠物无人照顾的智能宠物屋”系统
- 网站服务器欠费,网络连接正常,显示DNS不可用是否欠费?
- 电视剧名校分集剧情介绍二
- 最新!小红书达人排行榜来了!
- 2d开源游戏引擎linux,Corona实验室开源Corona,免费和跨平台2D游戏引擎
- 单片机 fir数字滤波c语言,单片机实时处理的简单FIR滤波器设计 - 控制/MCU - 电子发烧友网...
- python爬取学校教务管理系统_python requests模拟登陆正方教务管理系统,并爬取成绩...
