[日更-2019.4.26、27、28] cm-14.1 Android系统启动过程分析(四)-应用程序进程启动过程...
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
声明
- 前阶段在项目中涉及到了Android系统定制任务,Android系统定制前提要知道Android系统是如何启动的;
- 本文参考了一些书籍的若干章节,比如《Android进阶解密-第3章-应用程序进程启动》、《深入理解Android系统-第9章-应用程序进程详解》等;
- 本文使用的代码是LineageOS的cm-14.1,对应Android 7.1.2,可以参考我的另一篇博客:[如何下载Nexus5的LineageOS14.1(cm-14.1)系统源码并编译、刷机](https://my.oschina.net/XiaoMaPedro/blog/3028748 "如何下载Nexus5的LineageOS14.1(cm-14.1)系统源码并编译、刷机");
- 很多代码注释待详细写;
0 写在前面
系统启动后,让系统丰富多彩的是各种应用程序,好奇的是应用程序是如何启动的呢?启动一个应用程序的前提是要保证应用程序的进程已经被启动,是不是有点拗口呢?所谓的应用程序的进程和应用程序之间是什么关系呢?
1 什么应用程序进程?
在启动一个应用程序时首先要保证这个应用程序所需要的应用程序进程已经启动。AMS在启动应用程序时会检查这个应用程序所需要的应用程序进程是否存在,不存在就会请求Zygote进程启动需要的应用程序进程。
我在[日更-2019.4.20、21] cm-14.1 Android系统启动过程分析(二)-Zygote进程启动过程中分析过Zygote在Java框架中创建了一个Server端Socket,来等待AMS请求创建新应用程序进程,Zygote通过fork自身来创建新的应用程序进程,以此方式使得应用程序进程获得Zygote进程在启动时创建的虚拟机实例。
应用程序进程的创建过程中,除了获取虚拟机实例以外,还创建了Binder线程池和消息循环以便应用程序能够使用Binder机制进行进程间通信并处理消息。
2 应用程序进程的启动过程
应用程序进程的启动基本分两部分:
- AMS发送启动应用程序进程的请求;
- Zygote接收到请求后去创建该应用程序进程;
2.1 AMS发送启动应用程序进程请求
AMS发送启动应用程序进程的请求时序图:
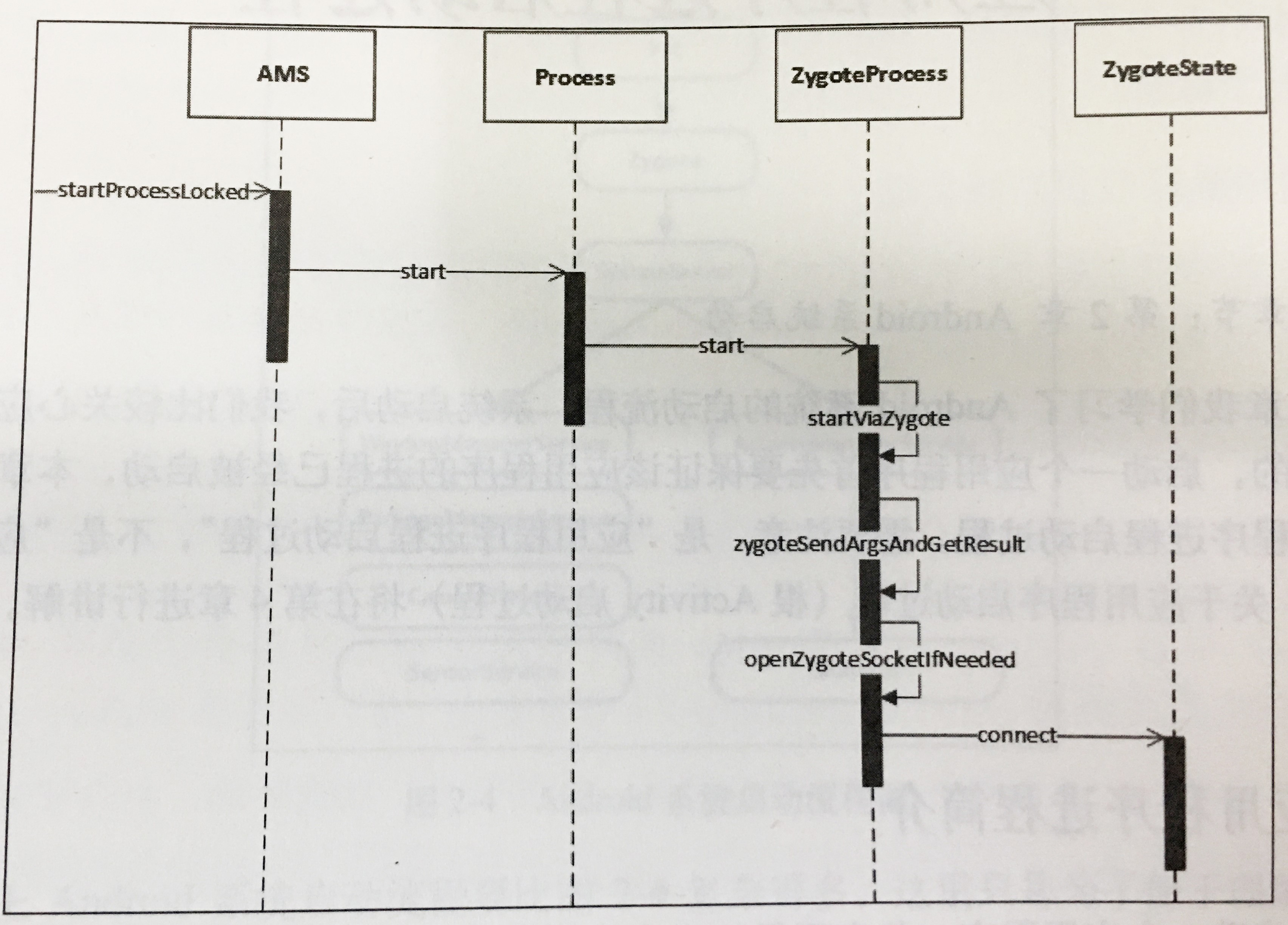
AMS通过调用startProcessLocked方法向Zygote进程发送请求,其在源码目录:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();if (app.pid > 0 && app.pid != MY_PID) {checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: removing from pids map");synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {mPidsSelfLocked.remove(app.pid);mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);}checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done removing from pids map");app.setPid(0);}if (DEBUG_PROCESSES && mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) Slog.v(TAG_PROCESSES,"startProcessLocked removing on hold: " + app);mProcessesOnHold.remove(app);checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: starting to update cpu stats");updateCpuStats();checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done updating cpu stats");try {try {final int userId = UserHandle.getUserId(app.uid);AppGlobals.getPackageManager().checkPackageStartable(app.info.packageName, userId);} catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowAsRuntimeException();}//【2-1-1】获取要创建的应用程序进程的用户IDint uid = app.uid;int[] gids = null;int mountExternal = Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_NONE;if (!app.isolated) {int[] permGids = null;try {checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: getting gids from package manager");final IPackageManager pm = AppGlobals.getPackageManager();permGids = pm.getPackageGids(app.info.packageName,MATCH_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING, app.userId);MountServiceInternal mountServiceInternal = LocalServices.getService(MountServiceInternal.class);mountExternal = mountServiceInternal.getExternalStorageMountMode(uid,app.info.packageName);} catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowAsRuntimeException();}/** Add shared application and profile GIDs so applications can share some* resources like shared libraries and access user-wide resources*///【2-1-2】对用户ID(gids)进行创建和赋值if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(permGids)) {gids = new int[2];} else {gids = new int[permGids.length + 2];System.arraycopy(permGids, 0, gids, 2, permGids.length);}gids[0] = UserHandle.getSharedAppGid(UserHandle.getAppId(uid));gids[1] = UserHandle.getUserGid(UserHandle.getUserId(uid));}checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: building args");if (mFactoryTest != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF) {if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL&& mTopComponent != null&& app.processName.equals(mTopComponent.getPackageName())) {uid = 0;}if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_HIGH_LEVEL&& (app.info.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_FACTORY_TEST) != 0) {uid = 0;}}int debugFlags = 0;if ((app.info.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_DEBUGGABLE) != 0) {debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER;// Also turn on CheckJNI for debuggable apps. It's quite// awkward to turn on otherwise.debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI;}// Run the app in safe mode if its manifest requests so or the// system is booted in safe mode.if ((app.info.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_VM_SAFE_MODE) != 0 ||mSafeMode == true) {debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_SAFEMODE;}if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("debug.checkjni"))) {debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI;}String genDebugInfoProperty = SystemProperties.get("debug.generate-debug-info");if ("true".equals(genDebugInfoProperty)) {debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_GENERATE_DEBUG_INFO;}if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("debug.jni.logging"))) {debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_JNI_LOGGING;}if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("debug.assert"))) {debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_ASSERT;}if (mNativeDebuggingApp != null && mNativeDebuggingApp.equals(app.processName)) {// Enable all debug flags required by the native debugger.debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ALWAYS_JIT; // Don't interpret anythingdebugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_GENERATE_DEBUG_INFO; // Generate debug infodebugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_NATIVE_DEBUGGABLE; // Disbale optimizationsmNativeDebuggingApp = null;}String requiredAbi = (abiOverride != null) ? abiOverride : app.info.primaryCpuAbi;if (requiredAbi == null) {requiredAbi = Build.SUPPORTED_ABIS[0];}String instructionSet = null;if (app.info.primaryCpuAbi != null) {instructionSet = VMRuntime.getInstructionSet(app.info.primaryCpuAbi);}app.gids = gids;app.requiredAbi = requiredAbi;app.instructionSet = instructionSet;// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.boolean isActivityProcess = (entryPoint == null);//【2-1-3】如果entryPoint == null,则赋值为"android.app.ActivityThread",其为应用程序进程主线程类名;if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Start proc: " +app.processName);checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: asking zygote to start proc");//【2-1-4】调用Process的start方法启动应用程序进程,将此前得到的应用程序进程的用户ID和组ID传入;Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: returned from zygote!");Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);mBatteryStatsService.noteProcessStart(app.processName, app.info.uid);checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done updating battery stats");EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROC_START,UserHandle.getUserId(uid), startResult.pid, uid,app.processName, hostingType,hostingNameStr != null ? hostingNameStr : "");try {AppGlobals.getPackageManager().logAppProcessStartIfNeeded(app.processName, app.uid,app.info.seinfo, app.info.sourceDir, startResult.pid);} catch (RemoteException ex) {// Ignore}if (app.persistent) {Watchdog.getInstance().processStarted(app.processName, startResult.pid);}checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: building log message");StringBuilder buf = mStringBuilder;buf.setLength(0);buf.append("Start proc ");buf.append(startResult.pid);buf.append(':');buf.append(app.processName);buf.append('/');UserHandle.formatUid(buf, uid);if (!isActivityProcess) {buf.append(" [");buf.append(entryPoint);buf.append("]");}buf.append(" for ");buf.append(hostingType);if (hostingNameStr != null) {buf.append(" ");buf.append(hostingNameStr);}Slog.i(TAG, buf.toString());app.setPid(startResult.pid);app.usingWrapper = startResult.usingWrapper;app.removed = false;app.killed = false;app.killedByAm = false;checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: starting to update pids map");ProcessRecord oldApp;synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {oldApp = mPidsSelfLocked.get(startResult.pid);}// If there is already an app occupying that pid that hasn't been cleaned upif (oldApp != null && !app.isolated) {// Clean up anything relating to this pid firstSlog.w(TAG, "Reusing pid " + startResult.pid+ " while app is still mapped to it");cleanUpApplicationRecordLocked(oldApp, false, false, -1,true /*replacingPid*/);}synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {this.mPidsSelfLocked.put(startResult.pid, app);if (isActivityProcess) {Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG);msg.obj = app;mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, startResult.usingWrapper? PROC_START_TIMEOUT_WITH_WRAPPER : PROC_START_TIMEOUT);}}checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done updating pids map");} catch (RuntimeException e) {Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting process " + app.processName, e);// Something went very wrong while trying to start this process; one// common case is when the package is frozen due to an active// upgrade. To recover, clean up any active bookkeeping related to// starting this process. (We already invoked this method once when// the package was initially frozen through KILL_APPLICATION_MSG, so// it doesn't hurt to use it again.)forceStopPackageLocked(app.info.packageName, UserHandle.getAppId(app.uid), false,false, true, false, false, UserHandle.getUserId(app.userId), "start failure");}}
【2-1-4】调用Process的start方法启动应用程序进程,其在源码目录:~/ChuWi/chuwi_hi9pro_hi10plus/alps/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java
/*** Start a new process.** <p>If processes are enabled, a new process is created and the* static main() function of a <var>processClass</var> is executed there.* The process will continue running after this function returns.** <p>If processes are not enabled, a new thread in the caller's* process is created and main() of <var>processClass</var> called there.** <p>The niceName parameter, if not an empty string, is a custom name to* give to the process instead of using processClass. This allows you to* make easily identifyable processes even if you are using the same base* <var>processClass</var> to start them.** @param processClass The class to use as the process's main entry* point.* @param niceName A more readable name to use for the process.* @param uid The user-id under which the process will run.* @param gid The group-id under which the process will run.* @param gids Additional group-ids associated with the process.* @param debugFlags Additional flags.* @param targetSdkVersion The target SDK version for the app.* @param seInfo null-ok SELinux information for the new process.* @param abi non-null the ABI this app should be started with.* @param instructionSet null-ok the instruction set to use.* @param appDataDir null-ok the data directory of the app.* @param zygoteArgs Additional arguments to supply to the zygote process.** @return An object that describes the result of the attempt to start the process.* @throws RuntimeException on fatal start failure** {@hide}*/public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,final String niceName,int uid, int gid, int[] gids,int debugFlags, int mountExternal,int targetSdkVersion,String seInfo,String abi,String instructionSet,String appDataDir,String[] zygoteArgs) {try {//【2-1-5】调用Process的startViaZygote方法让Zygite进程创建一个应用程序进程;return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, zygoteArgs);} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {Log.e(LOG_TAG,"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");throw new RuntimeException("Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);}}
【2-1-5】调用Process的startViaZygote方法(此方法主要是:创建字符串列表argsForZygote,并将应用程序进程的启动参数保存在argsForZygote中,最后通过Process的zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法请求Zygote进程创建应用程序):
/*** Starts a new process via the zygote mechanism.** @param processClass Class name whose static main() to run* @param niceName 'nice' process name to appear in ps* @param uid a POSIX uid that the new process should setuid() to* @param gid a POSIX gid that the new process shuold setgid() to* @param gids null-ok; a list of supplementary group IDs that the* new process should setgroup() to.* @param debugFlags Additional flags.* @param targetSdkVersion The target SDK version for the app.* @param seInfo null-ok SELinux information for the new process.* @param abi the ABI the process should use.* @param instructionSet null-ok the instruction set to use.* @param appDataDir null-ok the data directory of the app.* @param extraArgs Additional arguments to supply to the zygote process.* @return An object that describes the result of the attempt to start the process.* @throws ZygoteStartFailedEx if process start failed for any reason*/private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,final String niceName,final int uid, final int gid,final int[] gids,int debugFlags, int mountExternal,int targetSdkVersion,String seInfo,String abi,String instructionSet,String appDataDir,String[] extraArgs)throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {synchronized(Process.class) {//【2-1-6】创建字符串列表argsForZygote,并将应用程序进程的启动参数保存在argsForZygote中;ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String>();// --runtime-args, --setuid=, --setgid=,// and --setgroups= must go firstargsForZygote.add("--runtime-args");argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_JNI_LOGGING) != 0) {argsForZygote.add("--enable-jni-logging");}if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_SAFEMODE) != 0) {argsForZygote.add("--enable-safemode");}if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER) != 0) {argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");}if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI) != 0) {argsForZygote.add("--enable-checkjni");}if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_GENERATE_DEBUG_INFO) != 0) {argsForZygote.add("--generate-debug-info");}if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ALWAYS_JIT) != 0) {argsForZygote.add("--always-jit");}if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_NATIVE_DEBUGGABLE) != 0) {argsForZygote.add("--native-debuggable");}if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_ASSERT) != 0) {argsForZygote.add("--enable-assert");}if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT) {argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-default");} else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_READ) {argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-read");} else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_WRITE) {argsForZygote.add("--mount-external-write");}argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);//TODO optionally enable debuger//argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");// --setgroups is a comma-separated listif (gids != null && gids.length > 0) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append("--setgroups=");int sz = gids.length;for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {if (i != 0) {sb.append(',');}sb.append(gids[i]);}argsForZygote.add(sb.toString());}if (niceName != null) {argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName);}if (seInfo != null) {argsForZygote.add("--seinfo=" + seInfo);}if (instructionSet != null) {argsForZygote.add("--instruction-set=" + instructionSet);}if (appDataDir != null) {argsForZygote.add("--app-data-dir=" + appDataDir);}argsForZygote.add(processClass);if (extraArgs != null) {for (String arg : extraArgs) {argsForZygote.add(arg);}}//【2-1-7】最后Process的zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法;return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);}}
【2-1-7】处调用Process的zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法: 此方法主要将传入的应用程序进程启动参数argsForZygote写入ZygoteState类的对象中,ZygoteState类是Process的静态内部类,用于表示与Zygote进程通信的状态。传入的ZygoteState对象其实是通过【2-1-7】中调用Process的openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi)返回的,其代码在zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法后贴出。
/*** Sends an argument list to the zygote process, which starts a new child* and returns the child's pid. Please note: the present implementation* replaces newlines in the argument list with spaces.** @throws ZygoteStartFailedEx if process start failed for any reason*/private static ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList<String> args)throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {try {// Throw early if any of the arguments are malformed. This means we can// avoid writing a partial response to the zygote.int sz = args.size();for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {if (args.get(i).indexOf('\n') >= 0) {throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("embedded newlines not allowed");}}/*** See com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.readArgumentList()* Presently the wire format to the zygote process is:* a) a count of arguments (argc, in essence)* b) a number of newline-separated argument strings equal to count** After the zygote process reads these it will write the pid of* the child or -1 on failure, followed by boolean to* indicate whether a wrapper process was used.*/final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer;final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream;writer.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));writer.newLine();for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {String arg = args.get(i);writer.write(arg);writer.newLine();}writer.flush();// Should there be a timeout on this?ProcessStartResult result = new ProcessStartResult();// Always read the entire result from the input stream to avoid leaving// bytes in the stream for future process starts to accidentally stumble// upon.result.pid = inputStream.readInt();result.usingWrapper = inputStream.readBoolean();if (result.pid < 0) {throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");}//Zygote进程接收到数据后创建新的应用程序进程,并将新进程的PID返回给AMS;return result;} catch (IOException ex) {zygoteState.close();throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);}}
【2-1-7】处调用openZygoteSocketIfNeeded方法(此方法作用是:创建一个连接到Zygote进程的本地对象LocalSocket):
/*** Tries to open socket to Zygote process if not already open. If* already open, does nothing. May block and retry.*/private static ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {try {//【2-1-8】与Zygote进程建立Socket连接,这个ZYGOTE_SOCKET的值为“zygote”,并返回ZygoteState类型的primaryZygoteState对象;primaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(ZYGOTE_SOCKET);} catch (IOException ioe) {throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to primary zygote", ioe);}}//【2-1-9】连接Zygote主模式返回的ZygoteState是否与启动应用程序进程所需的ABI版本匹配;if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {return primaryZygoteState;}//【2-1-10】如果不匹配,则尝试连接Zygote辅模式;if (secondaryZygoteState == null || secondaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {try {//secondaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_SOCKET);} catch (IOException ioe) {throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to secondary zygote", ioe);}}//【2-1-11】连接Zygote辅模式返回的ZygoteState是否与启动应用程序进程所需的ABI版本匹配;if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {return secondaryZygoteState;}//【2-1-12】如果不匹配则抛出ZygoteStartFailedEx异常;throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi);}
2.2 Zygote接收AMS的请求并创建应用程序进程
Zygote接收AMS的请求并创建应用程序进程的时序图:
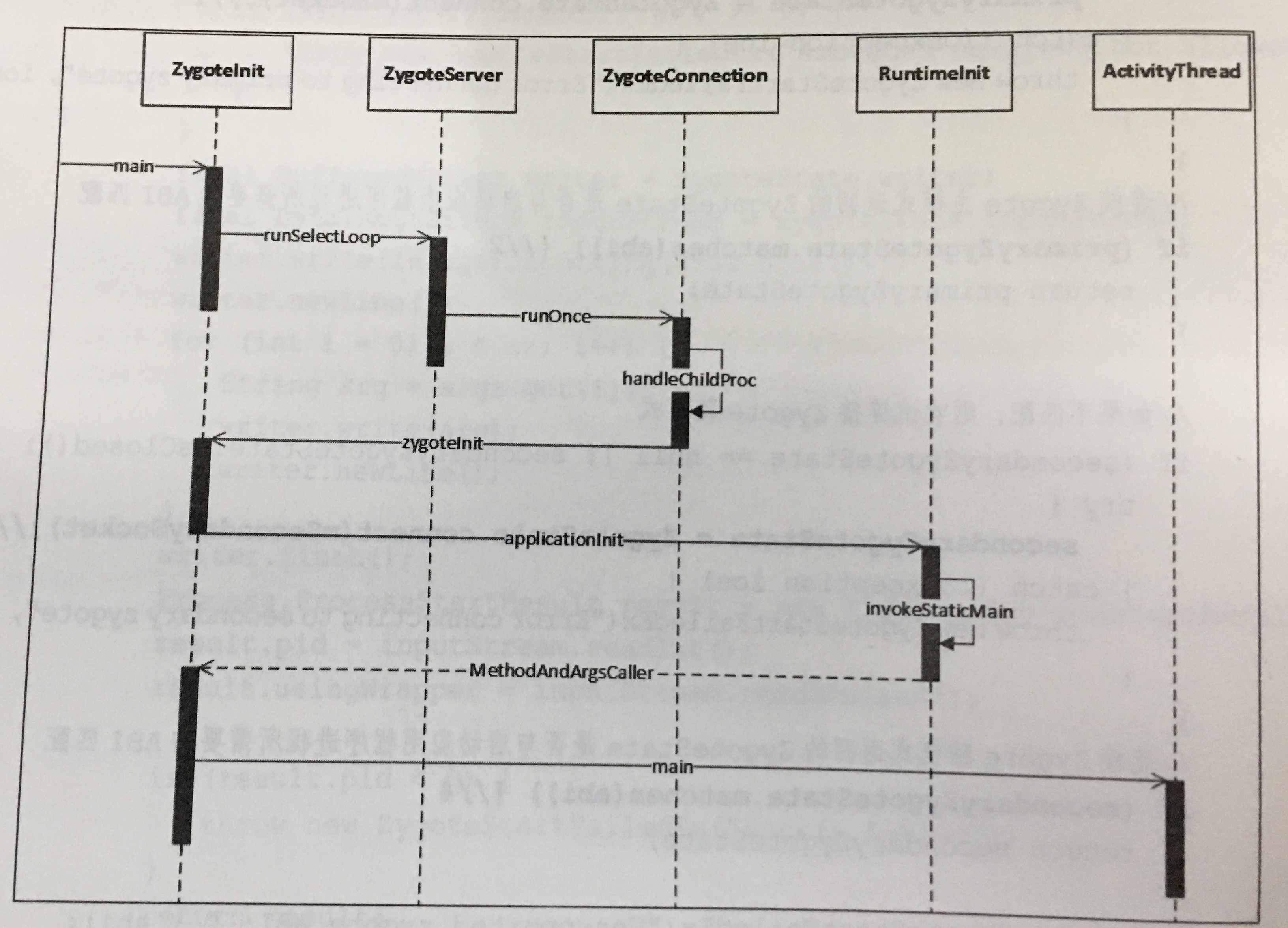
【2-1-7】分析zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法,其会将应用程序进程启动参数argsForZygote写入ZygoteState中,这样的话Zygote进程就会收到一个创建新的应用程序进程的请求,如上图所示,打开源码目录:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java,查看其main方法:
public static void main(String argv[]) {// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw// an error.ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();try {Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "ZygoteInit");RuntimeInit.enableDdms();// Start profiling the zygote initialization.SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();boolean startSystemServer = false;String socketName = "zygote";String abiList = null;for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {startSystemServer = true;} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());} else {throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);}}if (abiList == null) {throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");}//【2-2-1】创建一个Server端的Socket,socketname的值为“zygote”;registerZygoteSocket(socketName);Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "ZygotePreload");EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,SystemClock.uptimeMillis());//【2-2-2】预加载类和资源;preload();EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,SystemClock.uptimeMillis());Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();// Do an initial gc to clean up after startupTrace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PostZygoteInitGC");gcAndFinalize();Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from// Zygote.Trace.setTracingEnabled(false);// Zygote process unmounts root storage spaces.Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();if (startSystemServer) {//【2-2-3】启动SystemServer进程startSystemServer(abiList, socketName);}Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");//【2-2-4】进入无限循环,在前面创建的Socket接口中等待ActivityManagerService请求,以创建新的应用程序进程;至于AMS如何与Zygote链接的等我分析AMS时再详细描述!runSelectLoop(abiList);closeServerSocket();} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {【2-2-19】捕获到MethodAndArgsCaller异常时调用run方法,MethodAndArgsCaller是ZygoteInit的内部类;caller.run();} catch (Throwable ex) {Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);closeServerSocket();throw ex;}}
在注释【2-2-4】处,Zygote进程进入runSelectLoop循环等待AMS请求创建新的应用程序进程:
/*** Runs the zygote process's select loop. Accepts new connections as* they happen, and reads commands from connections one spawn-request's* worth at a time.** @throws MethodAndArgsCaller in a child process when a main() should* be executed.*/private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller {ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();//【2-2-5】ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());peers.add(null);while (true) {StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;}try {Os.poll(pollFds, -1);} catch (ErrnoException ex) {throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);}for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {continue;}if (i == 0) {ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);peers.add(newPeer);fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());} else {//【2-2-6】当AMS请求数据送达时,会调用ZygoteConnection的runOnce方法处理请求数据;boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce();if (done) {peers.remove(i);fds.remove(i);}}}}}
【2-2-6】处的runOnce()方法代码:
/*** Reads one start command from the command socket. If successful,* a child is forked and a {@link ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller}* exception is thrown in that child while in the parent process,* the method returns normally. On failure, the child is not* spawned and messages are printed to the log and stderr. Returns* a boolean status value indicating whether an end-of-file on the command* socket has been encountered.** @return false if command socket should continue to be read from, or* true if an end-of-file has been encountered.* @throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller trampoline to invoke main()* method in child process*/boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {String args[];Arguments parsedArgs = null;FileDescriptor[] descriptors;try {//【2-2-7】获得要创建应用程序进程的参数;args = readArgumentList();descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();} catch (IOException ex) {Log.w(TAG, "IOException on command socket " + ex.getMessage());closeSocket();return true;}if (args == null) {// EOF reached.closeSocket();return true;}/** the stderr of the most recent request, if avail */PrintStream newStderr = null;if (descriptors != null && descriptors.length >= 3) {newStderr = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(descriptors[2]));}int pid = -1;FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null;FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null;try {【2-2-8】在这里将【2-2-7】中readArgumentList方法返回的字符串数组args封装到Arguments类型的parsedArgs对象中;parsedArgs = new Arguments(args);if (parsedArgs.abiListQuery) {return handleAbiListQuery();}if (parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities != 0 || parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities != 0) {throw new ZygoteSecurityException("Client may not specify capabilities: " +"permitted=0x" + Long.toHexString(parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities) +", effective=0x" + Long.toHexString(parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities));}applyUidSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);applyInvokeWithSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);int[][] rlimits = null;if (parsedArgs.rlimits != null) {rlimits = parsedArgs.rlimits.toArray(intArray2d);}if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {FileDescriptor[] pipeFds = Os.pipe2(O_CLOEXEC);childPipeFd = pipeFds[1];serverPipeFd = pipeFds[0];Os.fcntlInt(childPipeFd, F_SETFD, 0);}/*** In order to avoid leaking descriptors to the Zygote child,* the native code must close the two Zygote socket descriptors* in the child process before it switches from Zygote-root to* the UID and privileges of the application being launched.** In order to avoid "bad file descriptor" errors when the* two LocalSocket objects are closed, the Posix file* descriptors are released via a dup2() call which closes* the socket and substitutes an open descriptor to /dev/null.*/int [] fdsToClose = { -1, -1 };FileDescriptor fd = mSocket.getFileDescriptor();if (fd != null) {fdsToClose[0] = fd.getInt$();}fd = ZygoteInit.getServerSocketFileDescriptor();if (fd != null) {fdsToClose[1] = fd.getInt$();}fd = null;//【2-2-9】调用forkAndSpecialize方法创建应用程序进程;参数为parsedArgs中存储的应用进程启动参数,返回值pid;pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids,parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo,parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, parsedArgs.instructionSet,parsedArgs.appDataDir);} catch (ErrnoException ex) {logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Invalid zygote arguments", ex);} catch (ZygoteSecurityException ex) {logAndPrintError(newStderr,"Zygote security policy prevents request: ", ex);}try {if (pid == 0) {// in childIoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);serverPipeFd = null;//【2-2-10】代码逻辑在新创建的子进程中时调用handleChildProc来处理应用程序进程;handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);// should never get here, the child is expected to either// throw ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().return true;} else {// in parent...pid of < 0 means failureIoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);childPipeFd = null;//【2-2-11】return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);}} finally {IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);}}
【2-2-10】处调用的handleChildProc方法,其所在源码目录为:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
/*** Handles post-fork setup of child proc, closing sockets as appropriate,* reopen stdio as appropriate, and ultimately throwing MethodAndArgsCaller* if successful or returning if failed.** @param parsedArgs non-null; zygote args* @param descriptors null-ok; new file descriptors for stdio if available.* @param pipeFd null-ok; pipe for communication back to Zygote.* @param newStderr null-ok; stream to use for stderr until stdio* is reopened.** @throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller on success to* trampoline to code that invokes static main.*/private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {/*** By the time we get here, the native code has closed the two actual Zygote* socket connections, and substituted /dev/null in their place. The LocalSocket* objects still need to be closed properly.*/closeSocket();ZygoteInit.closeServerSocket();if (descriptors != null) {try {Os.dup2(descriptors[0], STDIN_FILENO);Os.dup2(descriptors[1], STDOUT_FILENO);Os.dup2(descriptors[2], STDERR_FILENO);for (FileDescriptor fd: descriptors) {IoUtils.closeQuietly(fd);}newStderr = System.err;} catch (ErrnoException ex) {Log.e(TAG, "Error reopening stdio", ex);}}if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);}// End of the postFork event.Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(),pipeFd, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);} else {【2-2-12】调用RuntimeInit的zygoteInit方法;RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,parsedArgs.remainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);}}
【2-2-12】处调用的RuntimeInit的zygoteInit方法,其所在源码目录为:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
/*** The main function called when started through the zygote process. This* could be unified with main(), if the native code in nativeFinishInit()* were rationalized with Zygote startup.<p>** Current recognized args:* <ul>* <li> <code> [--] <start class name> <args>* </ul>** @param targetSdkVersion target SDK version* @param argv arg strings*/public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "RuntimeInit");redirectLogStreams();commonInit();//【2-2-13】在新创建的应用程序进程中创建Binder线程池;nativeZygoteInit();//【2-2-14】调用RuntimeInit的applicationInit方法;applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);}
【2-2-14】处调用的RuntimeInit的applicationInit方法,其所在源码目录为:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);// We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid// holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed.VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);final Arguments args;try {args = new Arguments(argv);} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {Slog.e(TAG, ex.getMessage());// let the process exitreturn;}// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main//【2-2-15】调用invokeStaticMain方法,其中args.startClass参数指的是参数android.app.ActivityThread。invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
【2-2-15】处调用的RuntimeInit的invokeStaticMain方法,其所在源码目录为:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
/*** Invokes a static "main(argv[]) method on class "className".* Converts various failing exceptions into RuntimeExceptions, with* the assumption that they will then cause the VM instance to exit.** @param className Fully-qualified class name* @param argv Argument vector for main()* @param classLoader the classLoader to load {@className} with*/private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {Class<?> cl;try {//【2-2-16】通过反射获得android.app.ActivityThread类;cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {throw new RuntimeException("Missing class when invoking static main " + className,ex);}Method m;try {//【2-2-17】获得ActivityThread的main方法;m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {throw new RuntimeException("Missing static main on " + className, ex);} catch (SecurityException ex) {throw new RuntimeException("Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);}int modifiers = m.getModifiers();if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {throw new RuntimeException("Main method is not public and static on " + className);}/** This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting* up the process.*///【2-2-18】将【2-2-17】获得的main方法传入MethodAndArgsCaller类的构造方法中;这里抛出的MethodAndArgsCaller异常会被Zygote的main方法捕获;throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);}
【2-2-18】这里采用抛出异常而不是直接调用ActivityThread的main方法,其原理和Zygote处理SystemServer是一样的,这种抛出异常的处理会清除所有的设置过程需要的堆栈帧,并让ActivityThread的main方法看起来像应用程序进程的入口方法。
再看下ZygoteInit.java的main方法是如何捕获MethodAndArgsCaller异常的,参照注释【2-2-19】捕获到MethodAndArgsCaller异常时调用run方法,其中MethodAndArgsCaller是ZygoteInit的内部类;
/*** Helper exception class which holds a method and arguments and* can call them. This is used as part of a trampoline to get rid of* the initial process setup stack frames.*/public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exceptionimplements Runnable {/** method to call */private final Method mMethod;/** argument array */private final String[] mArgs;public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {mMethod = method;mArgs = args;}public void run() {try {//【2-2-20】mMethod指的是ActivityThread的main方法,调用了mMethod的main方法后ActivityThread的main方法会被动态调用,应用程序进程就进入ActivityThread的main方法中mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {Throwable cause = ex.getCause();if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {throw (RuntimeException) cause;} else if (cause instanceof Error) {throw (Error) cause;}throw new RuntimeException(ex);}}}
到注释【2-2-20】处,应用程序进程就创建完成了并运行了主线程的管理类ActivityThread。
2.3 启动线程池
在2.2节的注释【2-2-13】处调用了ZygoteInit的nativeZygoteInit方法创建了应用程序进程的Binder线程池,很明显nativeZygoteInit是一个JNI方法,其对应的函数是com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit,其所在的源码目录为:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
static void com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{//【2-3-1】gCurRuntime是AndroidRuntime类型的指针,它创建于AndroidRuntime初始化时(参考注释【2-3-2】);gCurRuntime->onZygoteInit();
}
AndroidRuntime::AndroidRuntime(char* argBlockStart, const size_t argBlockLength) :mExitWithoutCleanup(false),mArgBlockStart(argBlockStart),mArgBlockLength(argBlockLength)
{SkGraphics::Init();// There is also a global font cache, but its budget is specified by// SK_DEFAULT_FONT_CACHE_COUNT_LIMIT and SK_DEFAULT_FONT_CACHE_LIMIT.// Pre-allocate enough space to hold a fair number of options.mOptions.setCapacity(20);assert(gCurRuntime == NULL); // one per process//【2-3-2】AppRuntime继承自AndroidRuntime,AppRuntime创建时就会调用AndroidRuntime的构造函数,gCurRuntime就会被初始化,它指向AppRuntime;的onZygoteInit函数gCurRuntime = this;
}
在注释【3-2-1】处调用了AppRuntime的onZygoteInit函数,其在源码目录:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp中
virtual void onZygoteInit(){sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\n");【2-3-3】调用ProcessState的startThreadPool函数启动Binder线程池;proc->startThreadPool();}
注释【2-3-3】处调用ProcessState的startThreadPool函数启动Binder线程池; 其在源码目录:~/LineageOS/frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp中
void ProcessState::startThreadPool()
{AutoMutex _l(mLock);//【2-3-4】if (!mThreadPoolStarted) {//【2-3-5】设置mThreadPoolStarted为true;mThreadPoolStarted = true;//【2-3-6】调用spawnPooledThread函数创建线程池中第一个线程(线程池主线程);spawnPooledThread(true);}
}
注释【2-3-6】处调用ProcessState的spawnPooledThread函数启动Binder线程池; 其在源码目录:~/LineageOS/frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp中
void ProcessState::spawnPooledThread(bool isMain)
{if (mThreadPoolStarted) {String8 name = makeBinderThreadName();ALOGV("Spawning new pooled thread, name=%s\n", name.string());//【2-3-7】Binder线程其实是一个PoolThread;sp<Thread> t = new PoolThread(isMain);【2-3-8】调用PoolThread的run函数启动第一个新的线程;t->run(name.string());}
}
注释【2-3-7】处Binder线程其实是一个PoolThread类:
class PoolThread : public Thread
{
public:PoolThread(bool isMain): mIsMain(isMain){}protected:virtual bool threadLoop(){//【2-3-8】IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool(mIsMain);return false;}const bool mIsMain;
};
PoolThread类继承了Thread类,在注释【2-3-8】处调用了IPCThreadState的joinThreadPool函数,将当前线程注册到Binder驱动程序中,那么我创建的线程就加入了Binder线程池中,新创建的应用程序进程就支持Binder进程间通信了,只需要创建爱你当前进程的Binder对象,并将它注册到ServiceManager中就可以实现Binder进程间通信,而不必关系进程间是如何通过Binder通信的。
2.4 创建信息循环
到注释【2-2-20】处,应用程序进程就创建完成了并运行了主线程的管理类ActivityThread的main方法(ActivityThread类用于管理当前应用程序进程的主线程),其所在源码目录:~/LineageOS/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java中
public static void main(String[] args) {Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);Environment.initForCurrentUser();// Set the reporter for event logging in libcoreEventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter());// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificatesfinal File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");//【2-3-9】创建主线程消息循环Looper;Looper.prepareMainLooper();//【2-3-10】创建ActivityThread对象thread;ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();thread.attach(false);//【2-3-11】派单Handler类型的sMainThreadHandler是否为null;if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {//【2-3-12】获取创建的主线程H类,赋给sMainThreadHandler,此H类继承自Handler,是ActivityThread的内部类,用于处理线程的消息循环;sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();}if (false) {Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(newLogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));}// End of event ActivityThreadMain.Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);//【2-3-13】调用Looper的loop方法,Looper开始处理消息;Looper.loop();throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");}
由此可看出,系统在应用程序进程启动完成后,就会创建一个消息循环,应用程序进程上的应用程序就可以使用消息处理机制了。
Enjoy it ^_^
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/XiaoMaPedro/blog/3045009
[日更-2019.4.26、27、28] cm-14.1 Android系统启动过程分析(四)-应用程序进程启动过程...相关推荐
- [日更-2019.5.2、3、4] 关于JVM的概略分析
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 声明 上一篇写了[日更-2019.4.29.30] 关于JVM.Dalvik.ART的基础分析 ,本篇就单独对JVM进行一下分 ...
- [日更-2019.4.8、4.9、4.12、4.13] cm-14.1 Android系统启动过程分析(一)-init进程的启动、rc脚本解析、zygote启动、属性服务...
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 声明 前阶段在项目中涉及到了Android系统定制任务,Android系统定制前提要知道Android系统是如何启动的. 本文 ...
- 26.27.28.29.极区图(南丁格尔玫瑰图)、维恩图 (Venn diagram)、面状图(Area chart)、树地图
26.极区图(南丁格尔玫瑰图) 27.维恩图 (Venn diagram) 28.面状图(Area chart) 29.树地图 26.极区图(南丁格尔玫瑰图) 极区图(又名南丁格尔玫瑰图)呈放射延伸状 ...
- 小甲鱼python课后习题【26,27,28,29,30】
[学习笔记,仅供学习交流使用,知识源于鱼c论坛] 作业26: 测试题: 0.python的字典是否支持一键多值? 不支持,对相同的键再次赋值直接覆盖 >>> dict2 = {1 ...
- 26 27 28 副词
形容词标识状态,配be动词 happy sad cute 英 [kjuːt] 美 [kjʊt] adj. 可爱的:漂亮的:聪明的,伶俐的 比较级 cuter最高级 cutest heavy 英 ['h ...
- 2018年11月26日到2019年4月26日工作汇总
2018年11月26日到2019年4月26日工作汇总 2018年11月26日-2017年11月30日 上午:各种协议的填写,已经有关表单的培训 下午:对公司目前做的项目的培训,以及明确我当前的工作 部 ...
- 逆水寒捏脸服务器维护,《逆水寒》2019年3月28日更新公告
各位自在同门: 为了保证服务器的运行稳定和服务质量,<逆水寒>将于2019年3月28日早8:00停机进行维护工作,预计维护到上午10:00(挑灯看剑.虎啸龙吟.一生一世合并成的超级大服预计 ...
- 圖譜謎宮(2019年6月28日於鄂爾多斯)
圖譜謎宮(2019年6月28日) ◆◆◆◆◆◆ 導航: (1)A,K,V,T,B,H,Y,Z,N使用的數字是:3,1,4,1,5,9,2,6,5. (2)加入適當的負號構成6層圖譜. (3)謎宮答案左 ...
- 2017年8月5日 星期六 --出埃及记 Exodus 28:27
2017年8月5日 星期六 --出埃及记 Exodus 28:27 Make two more gold rings and attach them to the bottom of the shou ...
最新文章
- C++ 检测内存泄露
- 【mybatis】mybatis中 返回map集合
- 文件目录表(FDT)及其结构
- js /jquery停止事件冒泡和阻止浏览器默认事件
- java.sql.SQLException: ORA-00923: FROM keyword not
- 阿里面试官问你准备在阿里待几年, 怎么回答?
- Omi框架学习之旅 - 通过对象实例来实现组件通讯 及原理说明
- bool查询原理 es_ES系列之原理copy_to用好了这么香
- mysql8安装步骤及排坑
- origin画图_3分钟浏览,Origin绘图中的12个经典问题集锦,早看早知道,躲坑没烦恼!!!...
- 手机黑圆点怎么打_手机能「打快板」是怎么回事?浅谈手机的光学防抖
- eNSP检测不到网卡信息——WinPacp
- 团队开发——冲刺1.e
- 飘刃 0.1.1 发布,速度碾压 Vue-CLI 的轻量级 Vue 项目构建工具
- MaxDEA如何计算DEA-Malmquist指数
- 【OS笔记 4】操作系统的组织结构(层次结构、微内核结构)虚拟机的概念
- Iconfont 替代品网站 图标网站推荐
- 2020年裸辞的人,真的待业了一整年吗?
- 智能分析的所见即所得——基于Lambda架构的实时数据引擎
- 计算机操作系统-磁盘存储器
