Spring 框架 AOP 的总结
一:帝国之军-AOP
1:案例分析
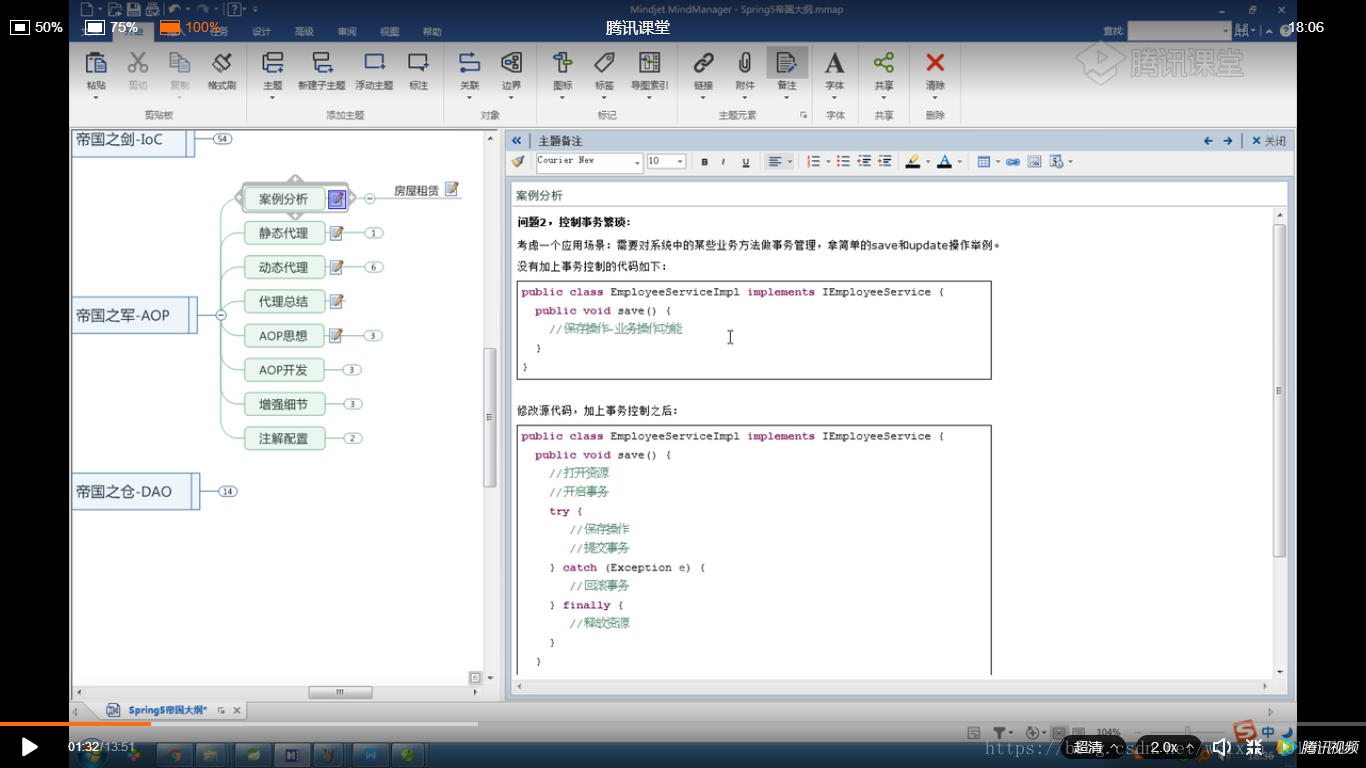上诉问题:在我们的业务层中每一个业务方法都的处理事务(频繁的try-cache),在设计上存在两个很严重问题:1):责任不分离,业务方法只需要关系如何完成业务功能,不需要去关心事务管理/日志管理/权限管理等.2):代码结构重复,在开发中不要重复代码,重复就意味着维护成本增大.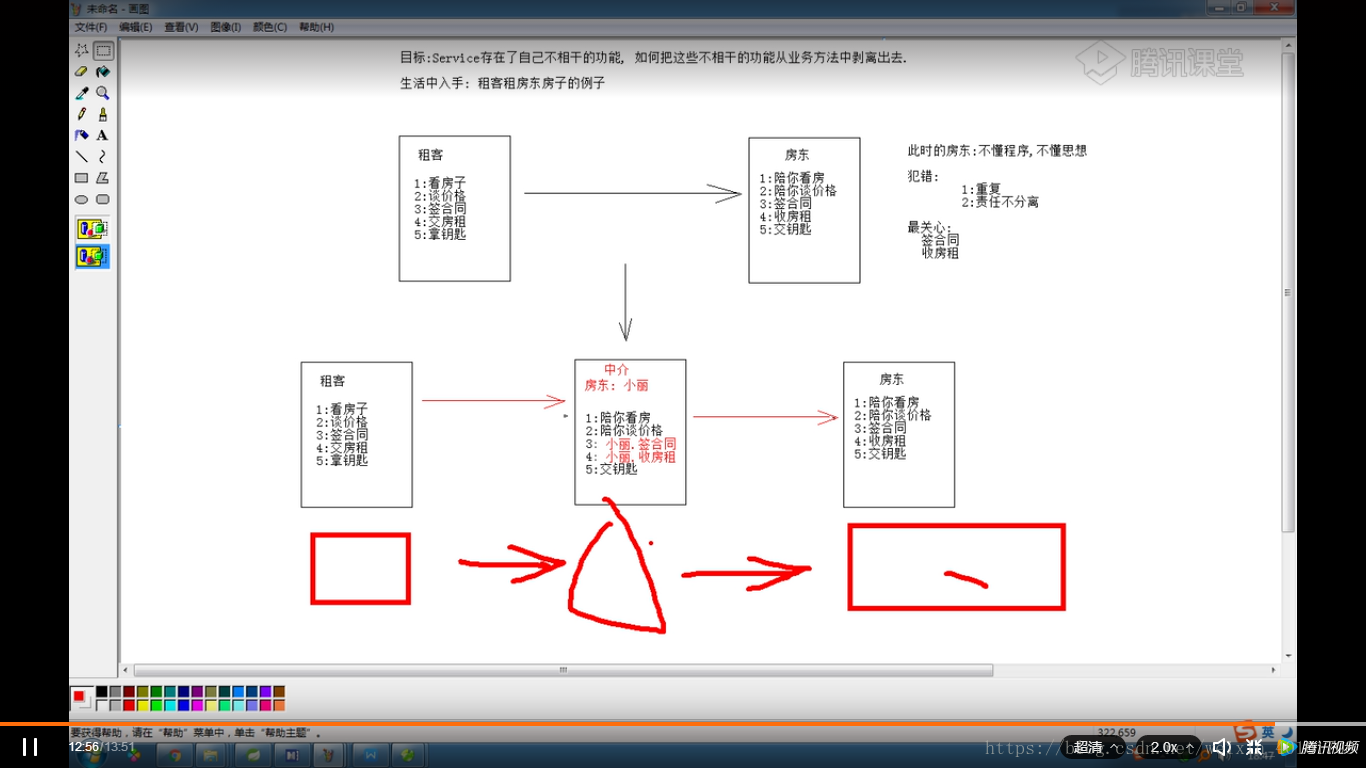2.静态代理
代理模式:客户端直接使用的都是代理对象,不知道真实对象是谁,此时代理对象可以在客户端和真是对象之间起到中介的作用1:代理对象完全包含真是对象,客户端使用的都是代理对象的方法,和真是对象没有直接关系;2:代理模式的职责:把不是真是对象该做的事情从真实对象上撇开--职责清晰;静态代理:在程序运行前就已经存在代理类的字节码文件,代理对象和真是对象的关系在运行前就确定了.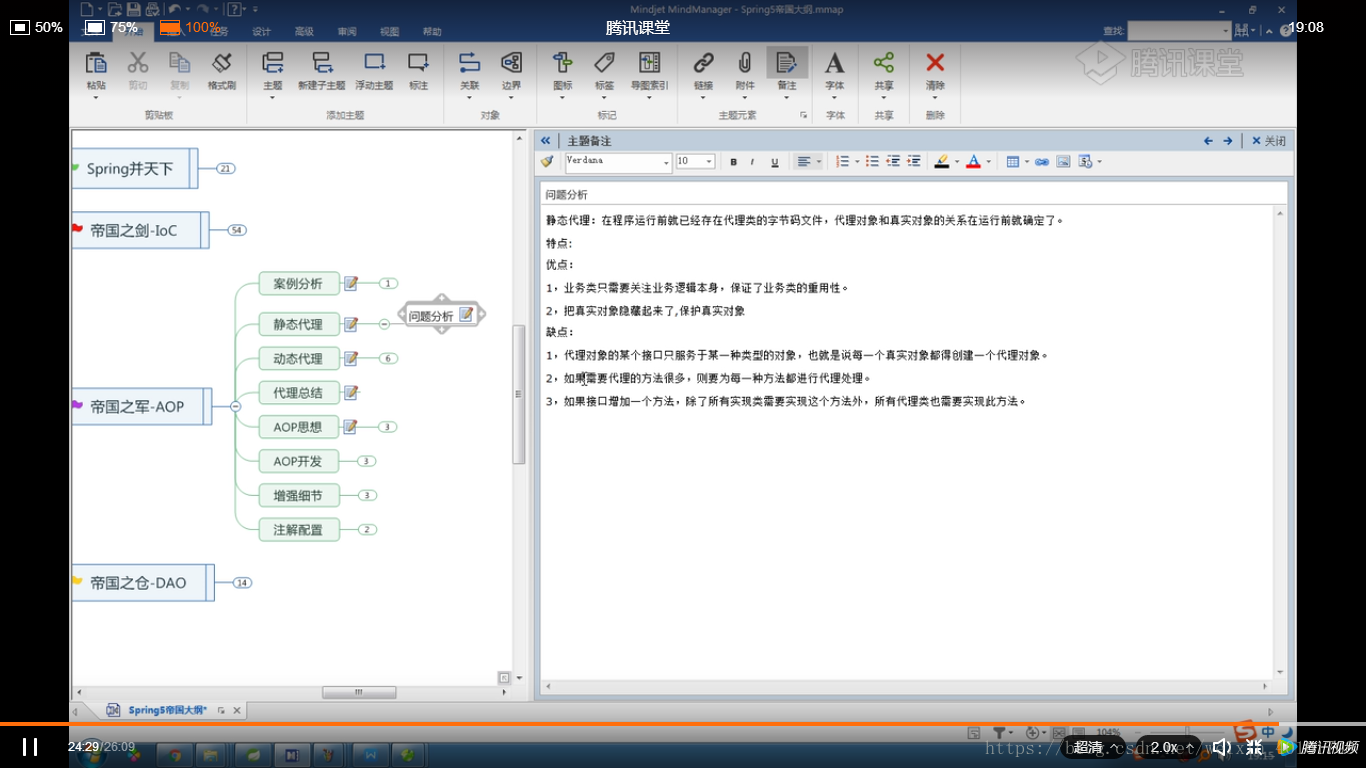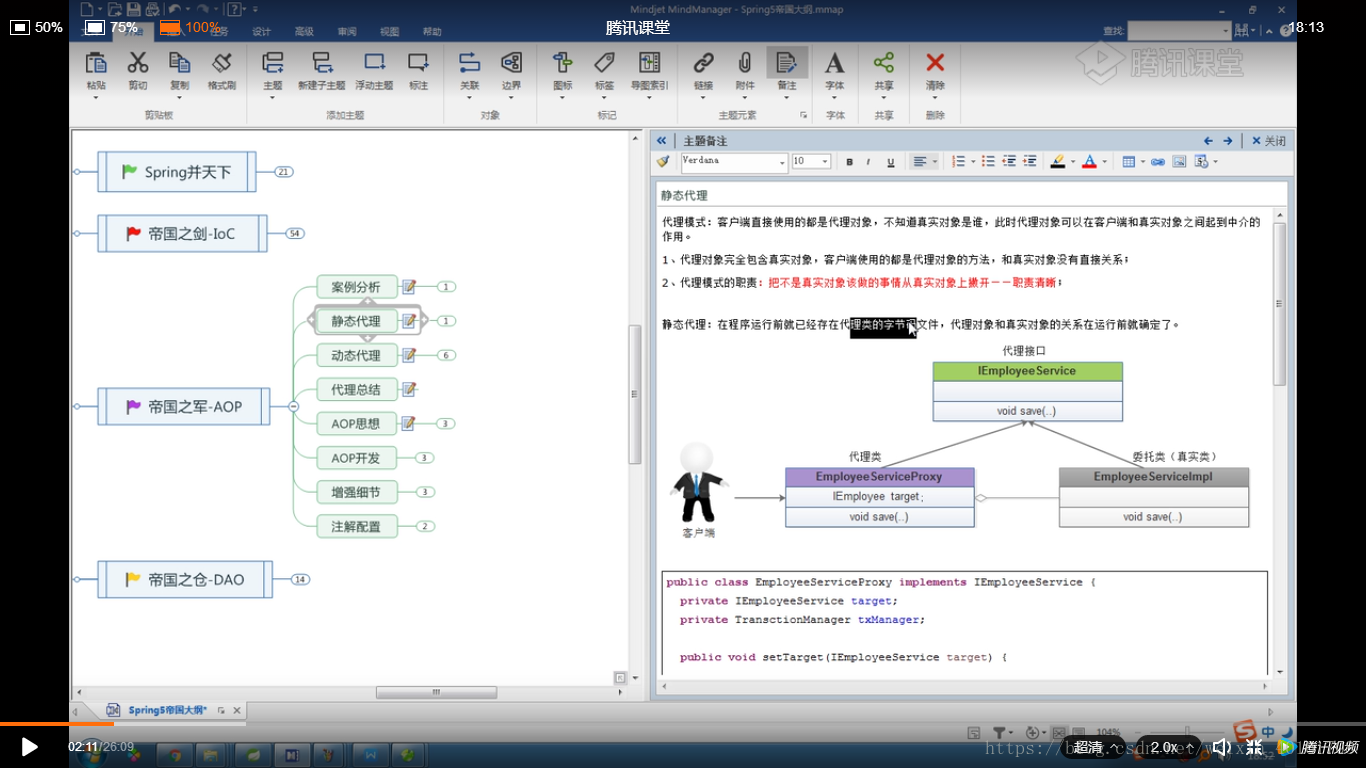//静态代理类
public class EmployeeServiceProxy implements IEmployeeService{private IEmployeeService target;//真是对象/委托对象private TransactionManager txManager;//事务管理器public void setTarget(IEmployeeService target) {this.target = target;}public void setTxManager(TransactionManager txManager) {this.txManager = txManager;}public void save(Employee emp) {txManager.begin();try {target.save(emp);txManager.commit();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();txManager.rollback();}}public void update(Employee emp) {txManager.begin();try {target.update(emp);txManager.commit();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();txManager.rollback();}}
}App
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration
public class App {@Autowired//@Qualifier("employeeServiceProxy")//因为代理类实现于接口,而接口还有一个imp类,xml配置文件的时候必须要标明,可以使用Qualifier标注,也可以跟下面一样内部<bean>表示private IEmployeeService service;@Testpublic void testSave() throws Exception {System.out.println(service.getClass());//查看对象的真实类型service.save(new Employee());}@Testpublic void testUpdate() throws Exception {service.update(new Employee());}
}App-Context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" ><bean id="employeeDAO" class="cn.wolfcode.dao.imp.IEmployeeDAOImpl"/><bean id="transactionManager" class="cn.wolfcode.tx.TransactionManager"/><!-- 代理对象 --><bean id="employeeServiceProxy" class="cn.wolfcode.proxy.EmployeeServiceProxy"><property name="txManager" ref="transactionManager"/><property name="target" ><bean class="cn.wolfcode.service.IEmployeeServiceImpl"><property name="dao" ref="employeeDAO"></property></bean></property></bean></beans>3.动态代理
动态代理:动态代理是在程勋运行期间有JVM通过反射等机制动态的生成的,所以不存在代理类的字节码文件,代理对象和真实对象的关系是在程序运行时期才确定的.如何实现动态代理:1):针对有接口:使用JDK动态代理2):针对无接口:使用CGLIB或Javassist组件①JDK动态代理
domain
public class Employee {}dao
public interface IEmployeeDAO {void save(Employee emp);void update(Employee emp);
}impl
public class IEmployeeDAOImpl implements IEmployeeDAO{public void save(Employee emp) {System.out.println("保存员工");System.out.println("保存成功");}public void update(Employee emp) {System.out.println("修改员工");throw new RuntimeException("故意错误");}
}service
public interface IEmployeeService {void save(Employee emp);void update(Employee emp);
}impl
public class IEmployeeServiceImpl implements IEmployeeService{private IEmployeeDAO dao;public void setDao(IEmployeeDAO dao) {this.dao = dao;}public void save(Employee emp) {dao.save(emp);}public void update(Employee emp) {dao.update(emp);}
}tx
//模拟事务管理器:
public class TransactionManager {public void begin(){System.out.println("开启事务");}public void commit(){System.out.println("提交事务");}public void rollback(){System.out.println("回滚事务");}
}//事务的增强操作
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class TransactionManagerAdvice implements InvocationHandler{private Object targer;//真实对象(对谁做增强)private TransactionManager txManager;//事务管理器(模拟)public void setTxManager(TransactionManager txManager) {this.txManager = txManager;}public void setTarger(Object targer) {this.targer = targer;}//创建一个代理对象public <T> T getProxyObject(){return (T)Proxy.newProxyInstance(targer.getClass().getClassLoader(),//类加载器,一般跟上真实对象的类加载器S targer.getClass().getInterfaces(),//真实对象实现的接口(JDK动态代理必须要求真是对象有接口)this);//如何做事务增强的对象}//如何为真实对象的方法做增强的具体操作public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {if(method.getName().startsWith("get")|| method.getName().startsWith("list")){return method.invoke(targer, args);//调用真实对象的方法}Object obj = null;txManager.begin();try {//-----------------------------------------------------obj = method.invoke(targer, args);//调用真实对象的方法//-----------------------------------------------------txManager.commit();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();txManager.rollback();}return obj;}
}
App
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration
public class App {@Autowiredprivate TransactionManagerAdvice advice;//代理对象:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy19@Testpublic void testSave() throws Exception {//获取代理对象IEmployeeService proxy = advice.getProxyObject();proxy.save(new Employee());}@Testpublic void testUpdate() throws Exception {//获取代理对象IEmployeeService proxy = advice.getProxyObject();proxy.update(new Employee());}
}App-Context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" ><bean id="employeeDAO" class="cn.wolfcode.dao.imp.IEmployeeDAOImpl"/><bean id="transactionManager" class="cn.wolfcode.tx.TransactionManager"/><bean id="employeeService" class="cn.wolfcode.service.impl.IEmployeeServiceImpl"><property name="dao" ref="employeeDAO"></property></bean><!-- 代理对象 --><!-- 配置一个事务增强的类 --><bean id="transactionManagerAdvice" class="cn.wolfcode.tx.TransactionManagerAdvice"><property name="targer" ref="employeeService"></property><property name="txManager" ref="transactionManager" /></bean>
</beans>②:CGLIB动态代理
domain
public class Employee {}dao
public interface IEmployeeDAO {void save(Employee emp);void update(Employee emp);
}
impl
public class IEmployeeDAOImpl implements IEmployeeDAO{public void save(Employee emp) {System.out.println("保存员工");System.out.println("保存成功");}public void update(Employee emp) {System.out.println("修改员工");throw new RuntimeException("故意错误");}
}
service.impl
public class EmployeeServiceImpl{private IEmployeeDAO dao;public void setDao(IEmployeeDAO dao) {this.dao = dao;}public void save(Employee emp) {dao.save(emp);}public void update(Employee emp) {dao.update(emp);}
}tx
public class TransactionManager {public void begin(){System.out.println("开启事务");}public void commit(){System.out.println("提交事务");}public void rollback(){System.out.println("回滚事务");}
}@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class TransactionManagerAdvice implements org.springframework.cglib.proxy.InvocationHandler{private Object target;//真实对象(对谁做增强)private TransactionManager tx;//事务管理器(模拟)public void setTarget(Object target) {this.target = target;}public void setTx(TransactionManager tx) {this.tx = tx;}//创建一个代理对象public <T> T getProxyObject(){Enhancer enhencer = new Enhancer();enhencer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());//将继承与哪一个类,去做增强enhencer.setCallback(this);//创建增强的对象return (T) enhencer.create();//创建代理对象}//如何为真实对象的方法做增强的具体操作public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {Object obj = null;tx.begin();try {obj = method.invoke(target, args);tx.commit();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();tx.rollback();}return obj;}
}App
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration
public class App {@Autowiredprivate TransactionManagerAdvice advice;//代理对象:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy19//CGLIB代理对象:class cn.wolfcode.service.impl.IEmployeeServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$8db50f30@Testpublic void testSave() throws Exception {EmployeeServiceImpl proxy = advice.getProxyObject();proxy.save(new Employee());}@Testpublic void testUpdate() throws Exception {EmployeeServiceImpl proxy = advice.getProxyObject();proxy.update(new Employee());}
}
App-Context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" ><bean id="employeeDAO" class="cn.wolfcode.dao.imp.IEmployeeDAOImpl"/><bean id="employeeService" class="cn.wolfcode.service.impl.EmployeeServiceImpl"><property name="dao" ref="employeeDAO"></property></bean><bean id="transactionManager" class="cn.wolfcode.tx.TransactionManager"></bean><!-- 代理对象 --><!-- 配置一个事务增强的类 --><bean id="transactionManagerAdvice" class="cn.wolfcode.tx.TransactionManagerAdvice"><property name="target" ref="employeeService"></property><property name="tx" ref="transactionManager"></property></bean></beans>③:拦截器的原理和日志记录
拦截器跟Filter过滤器很相似:Filter就是对请求和响应做拦截.Filter: WEB领域的概念,只能针对请求和响应做增强,离不开servlet-api.jarIntegerceptor: 整个Java领域的概念,不仅可以运用到service层,还可以用到Web层.domain
public class Employee {}
dao
public interface IEmployeeDAO {void save(Employee emp);void update(Employee emp);
}
imp
public class IEmployeeDAOImpl implements IEmployeeDAO{public void save(Employee emp) {System.out.println("保存员工");System.out.println("保存成功");}public void update(Employee emp) {System.out.println("修改员工");throw new RuntimeException("故意错误");}
}
service
public class IEmployeeServiceImpl{private IEmployeeDAO dao;public void setDao(IEmployeeDAO dao) {this.dao = dao;}public void save(Employee emp) {dao.save(emp);}public void update(Employee emp) {dao.update(emp);}
}
log
public class LogUtil {public void writeLog(String className,String methodName){System.out.println(new Date().toLocaleString()+"调用了"+className+"类中的"+methodName+"方法");}
}
//日志增强
public class LogAdvice implements org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor{private Object target;//真实对象private LogUtil logUtil;public void setTarget(Object target) {this.target = target;}public void setLogUtil(LogUtil logUtil) {this.logUtil = logUtil;}//创建代理对象public <T> T getProxyObject(){/*Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());enhancer.setCallback(this);return (T) enhancer.create();*/return (T) Enhancer.create(target.getClass(),this);} @Overridepublic Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {logUtil.writeLog(method.getDeclaringClass().getName(),method.getName());Object ret = method.invoke(target,args);//调用真实对象的方法return ret;}
}
App
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration
public class App {@Autowiredprivate LogAdvice advice;//代理对象:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy19//CGLIB代理对象:class cn.wolfcode.service.impl.IEmployeeServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$8db50f30@Testpublic void testSave() throws Exception {IEmployeeServiceImpl proxy = advice.getProxyObject();proxy.save(new Employee());}@Testpublic void testUpdate() throws Exception {IEmployeeServiceImpl proxy = advice.getProxyObject();proxy.update(new Employee());}
}App-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" ><bean id="employeeDAO" class="cn.wolfcode.dao.imp.IEmployeeDAOImpl"/><bean id="logUtil" class="cn.wolfcode.log.LogUtil"/><bean id="employeeService" class="cn.wolfcode.service.impl.IEmployeeServiceImpl"><property name="dao" ref="employeeDAO"></property></bean><!-- 代理对象 --><!-- 配置一个事务增强的类 --><bean id="logAdvice" class="cn.wolfcode.log.LogAdvice"><property name="target" ref="employeeService"></property><property name="logUtil" ref="logUtil" /></bean>
</beans>4.代理总结
JDK动态代理总结:1:Java动态代理是使用java.lang.reflect包中的Proxy类与InvocationHandler接口这两个来完成的.2:要使用JDK动态代理,委托必须要定义接口.3:JDK动态代理将会拦截所有public的方法(因为只能调用接口中定义的方法),这样即使在接口中定义了方法,不用修改代码也会被拦截.4:动态代理的最小单位是类(所有类中的方法都会被处理),如果只想拦截一部分方法,可以在invoke方法中对要执行的方法名进行判断.CGLIB代理总结:1:CGLIB可以生成委托类的子类,并重写父类非final修饰的方法.2:要求类不能是final,要拦截的方法要是非final,非static, 非private的.3:动态代理的最小单位是类(所有类中的方法都会被处理).关于性能:JDK动态代理是基于实现接口的,CGLIB和Javassit是基于继承委托类的.从性能上考虑: Javassit > CGLIB > JDKStruts2的拦截器和Hibemate延迟加载对象,采用的是Javassit的方式.对接口创建代理优于对类创建代理,因为会产生更加松耦合的系统,也更符合面向接口编程规范.若委托对象实现了接口,优先选用JDK动态代理.若委托对象没有实现任何接口,使用Javassit和CGLIB动态代理.5.AOP思想
1.AOP思想和重要术语
AOP(Aspect oritention Programming):把一个个的横切关注点放到某个模块中去,称之为切面.那么每一个的切面都能影响业务的某一种功能,切面的目的就是功能增强,如日志切面就是一个横切关注点,应用中许多方法需要做日志记录,只需要插入日志的切面即可. Joinpoint: 连接点,被拦截到需要被增强的方法 WHERE 去哪里做增强操作 Pointcut: 切入点,需要为哪些包中的哪些类中的哪些方法.Joinpoint的集合. WHERE:去哪些地方做增强. Advice: 增强(通知),当拦截到Joinpoint之后,在方法执行的某一个时机(when),做怎么样的增强操作(what). Aspect: 切面 Pointcut + Advice 去哪些地方+在什么时候,做说明增强 Target: 目标对象,被代理的目标对象 Weaving: 织入,把 Advice 加到 Target 上之后,创建出Proxy对象的过程. Proxy: 一个类被AOP织入增强后,产生的代理类.方法执行的时机:前置增强, 后置增强, 异常增强, 最终增强, 环绕增强①:Pointcut表达式
AOP的规范本应该由SUN公司提出,但是被AOP联盟捷足先登,AOP联盟制定AOP规范,首先就要解决一个问题,怎么表示切入点,也就是在哪些方法上增强(where).AspectJ是一个面向切面的框架,Aspect切入点语法如下(表示在哪些包下的哪些类的哪些方法上做切入增强):翻译成中文:execution(<修饰符>? <返回类型> <声明类型>? <方法名>(<参数>) <异常>?)举例 :public static Class java.Class.forName(String className)throws ClassNotFoundException通配符:* :匹配任何部分,只能表示一个单词.. :可用于全限定名中和方法参数中,分别表示子包和0到N个参数2.AOP开发
①:依赖
依赖的jar:spring-aop-版本.RELEASE.jarcom.springsource.org-aopalliance-1.0.0.jar Spring5以后不需要拷贝,纳入了aop包中com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar②:AOP各种增强
before:前置增强 被增强方法执行之前执行 权限控制日志记录等after-returning:后置增强 正常执行完毕后执行 提交事务/统计分析数据结果等after-throwing:异常增强 被增强方法出现异常时执行 回滚事务/记录日志的日常信息after:最终增强 无论是否有异常,最终都要执行的增强操作 释放资源等around:环绕增强 可以自定义在被增强方法的什么时机执行(返回一个Object,参数ProceedingJoinPoint) 缓存,性能日志,权限,事务管理获取被增强方法的信息,并可以传递给增强方法:Spring AOP: Joinpoint类 连接点, 访问被增强方法的真是对象,代理对象,方法参数等等可以做前置,后置,异常,最终增强方法的参数,第一个参数ProceedingJoinpoint:是Joinipoint的子类,只用于环绕增强,作为一个参数,还可以调用真实对象中被增强的方法:如何获取增强方法里的异常信息, 增强方法里的参数JoinPoint,以及如何在环绕增强里面调用真实方法?
//模拟事务管理器:
public class TransactionManager {public void begin(JoinPoint po){System.out.println("代理对象: "+po.getThis().getClass());System.out.println("目标对象: "+po.getTarget().getClass());System.out.println("被增强方法参数: "+Arrays.toString(po.getArgs()));System.out.println("当前连接点签名: "+po.getSignature());System.out.println("当前连接点类型: "+po.getKind());System.out.println("开启事务");}public void commit(JoinPoint po){System.out.println("提交事务");}public void rollback(JoinPoint po,Throwable tx){System.out.println("回滚事务"+" 方法的错误信息: "+tx.getMessage());}public void after(JoinPoint po){System.out.println("释放资源");}public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint po){Object ret = null;System.out.println("开启事务");try {ret = po.proceed();//调用真实对象的方法,取的一个返回值,查询有返回值System.out.println("提交事务");} catch (Throwable e) {System.out.println("回滚事务 错误信息:"+e.getMessage());} finally {System.out.println("释放资源");}return ret;}
}
<!-- 1:what,做说明增强 --><bean id="txManager" class="cn.wolfcode.tx.TransactionManager" /><aop:config proxy-target-class="false"><aop:aspect ref="txManager"> <!-- 关联what --><!-- 2:where:在哪些语句中的哪些类中的哪些方法上做增强 --><aop:pointcut id="txPoint" expression="execution( * cn.wolfcode.service.*Service.*(..))"/><!-- 3:when:在方法执行的什么时机做增强 --><aop:before method="begin" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/> <aop:after-returning method="commit" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/><aop:after-throwing method="rollback" pointcut-ref="txPoint" throwing="tx"/><aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/><!-- <aop:around method="aroundMethod" pointcut-ref="txPoint"/> --></aop:aspect></aop:config>③:使用注解开发AOP
@Component
@Aspect //配置一个切面
public class TransactionManager {@Pointcut("execution( * cn.wolfcode.service.impl.*.*(..))")public void txPoint(){}//@Before("txPoint()")public void begin(JoinPoint po){System.out.println("开启事务");}//@AfterReturning("txPoint()")public void commit(JoinPoint po){System.out.println("提交事务");}//@AfterThrowing(value="txPoint()",throwing="tx")public void rollback(JoinPoint po,Throwable tx){System.out.println("回滚事务"+" 方法的错误信息: "+tx.getMessage());}//@After("txPoint()")public void after(JoinPoint po){System.out.println("释放资源");}@Around("txPoint()")public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint po){Object ret = null;System.out.println("开启事务");try {ret = po.proceed();//调用真实对象的方法,取的一个返回值,查询有返回值System.out.println("提交事务");} catch (Throwable e) {System.out.println("回滚事务 错误信息:"+e.getMessage());} finally {System.out.println("释放资源");}return ret;}
}
<!-- DI注解解析器 --><context:annotation-config/><!-- IoC注解解析器--><context:component-scan base-package="cn.wolfcode"/><!-- AOP注解解析器 --><!-- 当有接口的时候自动使用JDK代理, 没有接口的时候自动使用CGLIB代理 AOP的本质是动态代理 --><aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="false"/>Spring 框架 AOP 的总结相关推荐
- spring框架 AOP核心详解
AOP称为面向切面编程,在程序开发中主要用来解决一些系统层面上的问题,比如日志,事务,权限等待,Struts2的拦截器设计就是基于AOP的思想,是个比较经典的例子. 一 AOP的基本概念 (1)Asp ...
- Spring框架AOP源码剖析
今天我要和大家分享的是 AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming)这个东西的源码剖析,作为多年的开发者,想必大家在面试的时候都被问过,你知道Spring框架AOP的底层实现机制吗 ...
- Spring框架 AOP面向切面编程(转)
一.前言 在以前的项目中,很少去关注spring aop的具体实现与理论,只是简单了解了一下什么是aop具体怎么用,看到了一篇博文写得还不错,就转载来学习一下,博文地址:http://www.cnbl ...
- Spring框架----AOP的概念及术语
1.什么是AOP AOP:全称是 Aspect Oriented Programming 即:面向切面编程 简单的说它就是把我们程序重复的代码抽取出来,在需要执行的时候,使用动态代理的技术,在不修改源 ...
- Spring框架-AOP
1.什么是AOP? 面向切面编程,可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率 通过不修改源代码方式,在主干功能里面添加新功能 2 ...
- Spring框架——AOP入门笔记以及个人总结
注:作者本人也是初学者,所以本文有些总结性见解可能存在问题,但是多数问题都是在上网查询过资料后总结的,如果有逻辑或者原理上的错误,或者见解不同,欢迎在评论区讨论!!! 目录 Spring的AOP 1. ...
- spring框架AOP的理解,程序高类聚的体现
本文主要介绍AOP思想,而不是Spring,Spring在本文只做为理解AOP的工具和例子,所以也不打算介绍Spring的Aspect.Join point.Advice.AOP proxy等概念,那 ...
- 08 Spring框架 AOP (一)
首先我们先来介绍一下AOP: AOP(Aspect Orient Programming),面向切面编程,是面向对象编程OOP的一种补充. 面向对象编程是从静态角度考虑程序的结构,面向切面编程是从动态 ...
- Spring框架AOP原理及实现
1.AOP思想 1.1 什么是AOP Aspect oritention programming(面向切面编程),把一个个的横切关注点(这些零散存在于业务方法中的功能代码,我们称之为横切面关注点)放到 ...
最新文章
- Python同步文件
- AC日记——积木大赛 洛谷 P1969
- eclipse 启动tomcat, java.lang.ClassNotFoundExcepti
- lower_bound和upper_bound算法
- 融资13亿后突然死亡!首款产品被苹果点赞,与谷歌竞赛的明星创业公司Anki倒闭...
- 【Robo 3T】MongoDB可视化工具-- Robo 3T使用教程
- 扒一扒那些叫欧拉的定理们(五)——平面几何欧拉定理的证明
- linux卸载小企鹅输入法,Linux(FC)小企鹅输入法的安装
- pycharm提示 进程已结束,退出代码 -1073740791 (0xC0000409)
- java 实现点击率_redis实现点击量/浏览量
- CRM实施阻力之独行侠作风
- inverted dropout(反向随机失活)正则化
- Python|Leetcode《306》|累加数
- 最全PLC输入输出各种回路接线
- 尚硅谷-SpringMVC篇
- STM32实战总结:HAL之FSMC控制TFT-LCD
- 小x与三角形 c语言 1秒,[2019年第一水] 小x与神牛
- HBase 2.0 API 初步窥探
- 通讯录怎么恢复?在 手机上检索找回已删除的电话号码的3种方式
- 基于HBuilder 开发 项目之微信支付
