匿名函数python_基于python内置函数与匿名函数详解
内置函数
Built-in Functions
abs()
dict()
help()
min()
setattr()
all()
dir()
hex()
next()
slice()
any()
divmod()
id()
object()
sorted()
ascii()
enumerate()
input()
oct()
staticmethod()
bin()
eval()
int()
open()
str()
bool()
exec()
isinstance()
pow()
super()
bytes()
float()
iter()
print()
tuple()
callable()
format()
len()
property()
type()
chr()
frozenset()
list()
range()
vars()
classmethod()
getattr()
locals()
repr()
zip()
compile()
globals()
map()
reversed()
__import__()
complex()
hasattr()
max()
round()
bytearray()
filter()
issubclass()
pow()
super()
delattr()
hash()
memoryview()
set
截止到python版本3.6.2,现在python一共为我们提供了68个内置函数。它们就是python提供给你直接可以拿来使用的所有函数。
内置函数分类
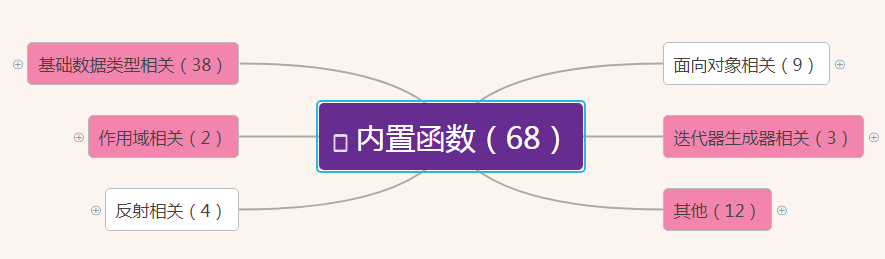
作用域相关

基于字典的形式获取局部变量和全局变量
globals()——获取全局变量的字典
locals()——获取执行本方法所在命名空间内的局部变量的字典
其他

输入输出相关
input()输入
s = input("请输入内容 : ") #输入的内容赋值给s变量
print(s) #输入什么打印什么。数据类型是str
print输出
def print(self, *args, sep=' ', end='\n', file=None): # known special case of print
"""
print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='\n', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
file: 默认是输出到屏幕,如果设置为文件句柄,输出到文件
sep: 打印多个值之间的分隔符,默认为空格
end: 每一次打印的结尾,默认为换行符
flush: 立即把内容输出到流文件,不作缓存
"""
f = open('tmp_file','w')
print(123,456,sep=',',file = f,flush=True)
from time import sleep
for i in range(0,101,2):
sleep(0.1)
str="*"*(i//2)
print('\r%s%%:%s'%(i,str),end="",flush=True)
数据类型相关
type(s)返回s的数据类型
s="abc"
print(type(s))#
内存相关
id(s) s是参数,返回一个变量的内存地址
hash(s) s是参数,返回一个可hash变量的哈希值,不可hash的变量被hash之后会报错。
l1=[1,2,3]
l2=(1,2,3)
print(hash(l2))#2528502973977326415
print(hash(l1))#TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
hash函数会根据一个内部的算法对当前可hash变量进行处理,返回一个int数字。
*每一次执行程序,内容相同的变量hash值在这一次执行过程中不会发生改变。
hash函数会根据一个内部的算法对当前可hash变量进行处理,返回一个int数字。
*每一次执行程序,内容相同的变量hash值在这一次执行过程中不会发生改变。
文件操作相关
open() 打开一个文件,返回一个文件操作符(文件句柄)
操作文件的模式有r,w,a,r+,w+,a+ 共6种,每一种方式都可以用二进制的形式操作(rb,wb,ab,rb+,wb+,ab+)
可以用encoding指定编码.
模块操作相关
__import__导入一个模块
os = __import__('os')
print(os.path.abspath('.'))
帮助方法
help(s) s为函数名
help(str)
#输出
class str(object)
| str(object='') -> str
| str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str
|
| Create a new string object from the given object. If encoding or
| errors is specified, then the object must expose a data buffer
| that will be decoded using the given encoding and error handler.
| Otherwise, returns the result of object.__str__() (if defined)
| or repr(object).
| encoding defaults to sys.getdefaultencoding().
| errors defaults to 'strict'.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __add__(self, value, /)
| Return self+value.
|
| __contains__(self, key, /)
| Return key in self.
|
| __eq__(self, value, /)
| Return self==value.
|
| __format__(...)
| S.__format__(format_spec) -> str
|
| Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec.
|
| __ge__(self, value, /)
| Return self>=value.
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __getitem__(self, key, /)
| Return self[key].
|
| __getnewargs__(...)
|
| __gt__(self, value, /)
| Return self>value.
|
| __hash__(self, /)
| Return hash(self).
|
| __iter__(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| __le__(self, value, /)
| Return self<=value.
|
| __len__(self, /)
| Return len(self).
|
| __lt__(self, value, /)
| Return self
|
| __mod__(self, value, /)
| Return self%value.
|
| __mul__(self, value, /)
| Return self*value.n
|
| __ne__(self, value, /)
| Return self!=value.
|
| __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
|
| __repr__(self, /)
| Return repr(self).
|
| __rmod__(self, value, /)
| Return value%self.
|
| __rmul__(self, value, /)
| Return self*value.
|
| __sizeof__(...)
| S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes
|
| __str__(self, /)
| Return str(self).
|
| capitalize(...)
| S.capitalize() -> str
|
| Return a capitalized version of S, i.e. make the first character
| have upper case and the rest lower case.
|
| casefold(...)
| S.casefold() -> str
|
| Return a version of S suitable for caseless comparisons.
|
| center(...)
| S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> str
|
| Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is
| done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
|
| count(...)
| S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in
| string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are
| interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| encode(...)
| S.encode(encoding='utf-8', errors='strict') -> bytes
|
| Encode S using the codec registered for encoding. Default encoding
| is 'utf-8'. errors may be given to set a different error
| handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
| a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and
| 'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with
| codecs.register_error that can handle UnicodeEncodeErrors.
|
| endswith(...)
| S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
|
| Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise.
| With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
| With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
| suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
|
| expandtabs(...)
| S.expandtabs(tabsize=8) -> str
|
| Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
| If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed.
|
| find(...)
| S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
| such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
| arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| Return -1 on failure.
|
| format(...)
| S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> str
|
| Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs.
| The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
|
| format_map(...)
| S.format_map(mapping) -> str
|
| Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from mapping.
| The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
|
| index(...)
| S.index(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
| such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
| arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| Raises ValueError when the substring is not found.
|
| isalnum(...)
| S.isalnum() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric
| and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
|
| isalpha(...)
| S.isalpha() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic
| and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
|
| isdecimal(...)
| S.isdecimal() -> bool
|
| Return True if there are only decimal characters in S,
| False otherwise.
|
| isdigit(...)
| S.isdigit() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are digits
| and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
|
| isidentifier(...)
| S.isidentifier() -> bool
|
| Return True if S is a valid identifier according
| to the language definition.
|
| Use keyword.iskeyword() to test for reserved identifiers
| such as "def" and "class".
|
| islower(...)
| S.islower() -> bool
|
| Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is
| at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
|
| isnumeric(...)
| S.isnumeric() -> bool
|
| Return True if there are only numeric characters in S,
| False otherwise.
|
| isprintable(...)
| S.isprintable() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are considered
| printable in repr() or S is empty, False otherwise.
|
| isspace(...)
| S.isspace() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are whitespace
| and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
|
| istitle(...)
| S.istitle() -> bool
|
| Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one
| character in S, i.e. upper- and titlecase characters may only
| follow uncased characters and lowercase characters only cased ones.
| Return False otherwise.
|
| isupper(...)
| S.isupper() -> bool
|
| Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is
| at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
|
| join(...)
| S.join(iterable) -> str
|
| Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the
| iterable. The separator between elements is S.
|
| ljust(...)
| S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
|
| Return S left-justified in a Unicode string of length width. Padding is
| done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
|
| lower(...)
| S.lower() -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase.
|
| lstrip(...)
| S.lstrip([chars]) -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed.
| If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
|
| partition(...)
| S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
|
| Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it,
| the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not
| found, return S and two empty strings.
|
| replace(...)
| S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str
|
| Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring
| old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
| given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
|
| rfind(...)
| S.rfind(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
| such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
| arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| Return -1 on failure.
|
| rindex(...)
| S.rindex(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
| such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
| arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| Raises ValueError when the substring is not found.
|
| rjust(...)
| S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
|
| Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
| done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
|
| rpartition(...)
| S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
|
| Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return
| the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the
| separator is not found, return two empty strings and S.
|
| rsplit(...)
| S.rsplit(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings
|
| Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the
| delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and
| working to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
| splits are done. If sep is not specified, any whitespace string
| is a separator.
|
| rstrip(...)
| S.rstrip([chars]) -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
| If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
|
| split(...)
| S.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) -> list of strings
|
| Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the
| delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
| splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any
| whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are
| removed from the result.
|
| splitlines(...)
| S.splitlines([keepends]) -> list of strings
|
| Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries.
| Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends
| is given and true.
|
| startswith(...)
| S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
|
| Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
| With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
| With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
| prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
|
| strip(...)
| S.strip([chars]) -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing
| whitespace removed.
| If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
|
| swapcase(...)
| S.swapcase() -> str
|
| Return a copy of S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase
| and vice versa.
|
| title(...)
| S.title() -> str
|
| Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with title case
| characters, all remaining cased characters have lower case.
|
| translate(...)
| S.translate(table) -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S in which each character has been mapped
| through the given translation table. The table must implement
| lookup/indexing via __getitem__, for instance a dictionary or list,
| mapping Unicode ordinals to Unicode ordinals, strings, or None. If
| this operation raises LookupError, the character is left untouched.
| Characters mapped to None are deleted.
|
| upper(...)
| S.upper() -> str
|
| Return a copy of S converted to uppercase.
|
| zfill(...)
| S.zfill(width) -> str
|
| Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field
| of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods defined here:
|
| maketrans(x, y=None, z=None, /)
| Return a translation table usable for str.translate().
|
| If there is only one argument, it must be a dictionary mapping Unicode
| ordinals (integers) or characters to Unicode ordinals, strings or None.
| Character keys will be then converted to ordinals.
| If there are two arguments, they must be strings of equal length, and
| in the resulting dictionary, each character in x will be mapped to the
| character at the same position in y. If there is a third argument, it
| must be a string, whose characters will be mapped to None in the result.
在控制台执行help()进入帮助模式。可以随意输入变量或者变量的类型。输入q退出
或者直接执行help(o),o是参数,查看和变量o有关的操作。。。
和调用相关
callable(s),s是参数,看这个变量是不是可调用。
如果s是一个函数名,就会返回True
def func():pass
print(callable(func))#True
print(callable(123))#Flase
查看参数所属类型的所有内置方法
dir() 默认查看全局空间内的属性,也接受一个参数,查看这个参数内的方法或变量
dir(list)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort']
和数字相关
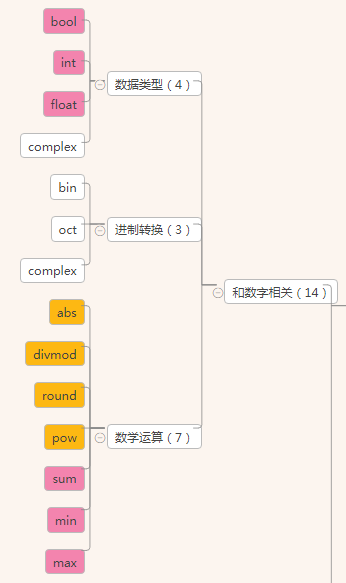
数字——数据类型相关:bool,int,float,complex
数字——进制转换相关:bin,oct,hex
数字——数学运算:abs,divmod,min,max,sum,round,pow
和数据结构相关

序列——列表和元组相关的:list和tuple
序列——字符串相关的:str,format,bytes,bytearry,memoryview,ord,chr,ascii,repr
ret=bytearray('xiaozhangmen',encoding='utf-8')
print(ret)#bytearray(b'xiaozhangmen')
ret = memoryview(bytes('你好',encoding='utf-8'))
print(len(ret))
print(bytes(ret[:3]).decode('utf-8'))
print(bytes(ret[3:]).decode('utf-8'))
序列:reversed,slice
l=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
l.reverse()
print(l)#[6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
l=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
sli=slice(1,4,2)#slice看起来返回的是一个规则,拿到这个规则后再对列表进行操作
print(l[sli])#[2, 4]
数据集合——字典和集合:dict,set,frozenset
数据集合:len,sorted,enumerate,all,any,zip,filter,map
filter:使用指定方法过滤可迭代对象的元素
def is_odd(x):
return x % 2 == 1
print(filter(is_odd,[1,2,3,4,5,6]))#
print(list(filter(is_odd,[1,2,3,4,5,6])))#[1, 3, 5]
map:python中的map函数应用于每一个可迭代的项,返回的是一个结果list。如果有其他的可迭代参数传进来,map函数则会把每一个参数都以相应的处理函数进行迭代处理。map()函数接收两个参数,一个是函数,一个是序列,map将传入的函数依次作用到序列的每个元素,并把结果作为新的list返回。
def pow(x):
return x**2
print(map(pow,[0,1,2,3]))#
print(list(map(pow,[0,1,2,3])))#[0, 1, 4, 9]
匿名函数
匿名函数:为了解决那些功能很简单的需求而设计的一句话函数
匿名函数格式:
函数名 = lambda 参数 :返回值
#参数可以有多个,用逗号隔开
#匿名函数不管逻辑多复杂,只能写一行,且逻辑执行结束后的内容就是返回值
#返回值和正常的函数一样可以是任意数据类型
匿名函数实例
#如把下面函数改为匿名函数
def add(x,y):
return x+y
add1=lambda x,y:x+y
print(add(1,2))
print(add1(1,2))
面试题笔记:
现有两个元组(('a'),('b')),(('c'),('d')),请使用python中匿名函数生成列表[{'a':'c'},{'b':'d'}]
#答案一
test = lambda t1,t2 :[{i:j} for i,j in zip(t1,t2)]
print(test(t1,t2))
#答案二
print(list(map(lambda t:{t[0]:t[1]},zip(t1,t2))))
#还可以这样写
print([{i:j} for i,j in zip(t1,t2)])
1.下面程序的输出结果是:
d = lambda p:p*2
t = lambda p:p*3
x = 2
x = d(x)
x = t(x)
x = d(x)
print x
2.现有两元组(('a'),('b')),(('c'),('d')),请使用python中匿名函数生成列表[{'a':'c'},{'b':'d'}]
3.以下代码的输出是什么?请给出答案并解释。
def multipliers():
return [lambda x:i*x for i in range(4)]
print([m(2) for m in multipliers()])
请修改multipliers的定义来产生期望的结果。
以上这篇基于python内置函数与匿名函数详解就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
匿名函数python_基于python内置函数与匿名函数详解相关推荐
- Python内置的字符串处理函数整理
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> Python内置的字符串处理函数整理 27 May 2011 16:30 Friday by 小屋 标签: 函数 字符串 Py ...
- python for everybody作业和测试答案_【计算题】编写函数,模拟 Python 内置函数 reversed() 。...
[计算题]编写函数,模拟 Python 内置函数 reversed() . 更多相关问题 In California, there lives a pretty girl called Donna G ...
- Win7下的内置FTP组件的设置详解
Win7下的内置FTP组件的设置详解 在局域网中共享文件,FTP是比较方便的方案之一.Win7内部集成了FTP,只是设置起来颇费一番功夫.着文以记之. 一.安装FTP组件 由于Win7默认没有安装FT ...
- python基础编程:基于Python对象引用、可变性和垃圾回收详解
下面小编就为大家带来一篇基于Python对象引用.可变性和垃圾回收详解.小编觉得挺不错的,现在就分享给大家,也给大家做个参考.一起跟随小编过来看看吧 变量不是盒子 在示例所示的交互式控制台中,无法使用 ...
- pythonpass函数_有的python内置函数怎么就一个pass?
你看到的是pass,但可能现实并非如此. 火车上信号太差了,待我移动一下再续-- 先随便扯扯吧-- 既然提到Python内置函数的实现,就涉及到Python本身的实现方式了,也就是这个解释器是怎么实现 ...
- python内置函数调用_Python中函数的基本定义与调用及内置函数详解
前言 函数function是python编程核心内容之一,也是比较重要的一块.首先我们要了解Python函数的基本定义: 函数是什么? 函数是可以实现一些特定功能的小方法或是小程序.在Python中有 ...
- sort函数pythonreverse_Python基础 7 ---- Python内置sort和sorted函数
1 Python对数据的排序有两种方法,一种是容器内置的sort函数,另外一种利用sorted函数 2 对于sort函数我们不再进行讨论,只要研究一下sorted函数 3 sorted函数的原形sor ...
- python内置的读取文件函数_Python函数篇(3)-内置函数、文件处理(已更新)
1.内置函数 上一篇文章中,我重点写了reduce.map.filter3个内置函数,在本篇章节中,会补充其他的一些常规内置函数,并重点写max,min函数,其他没有说明的函数,会在后面写到类和面向对 ...
- python内置的数字运算函数_Python 内置函数1
abs(x)函数 返回绝对值 参数可以是:负数.正数.浮点数或者长整形 print(abs(-1.2)) # 结果1.2 cmp(x, y)函数 (python3已删) 中文说明: 比较两个对象x和y ...
最新文章
- 用大数据分析顾客会掏钱买你哪件商品
- java 打包的两种方式
- RTSP over UDP RTSP over TCP
- linux qt sql,linux qt联接sqlserver怎么配置服务器
- ios kvo 要引入_iOS中KVO的使用
- Lesson4 一阶方程代换法
- JavaSE基础 ——运算符
- 将pdm换成mysql表结构 报错_MySQL随机生成百万级别数据
- python连接高斯数据库_高斯数据库 (gaussDB) - 连接数据库(6)
- 阿里云os边缘应用程序的三个问题
- 我的世界服务器无限铁傀儡,我的世界刷铁教程 铁傀儡无限刷铁攻略
- 网站对接支付宝进行支付
- 自动备份android,Android自动备份错误
- POJ1655 树重心模板题
- 全球及中国停车信息系统行业研究及十四五规划分析报告
- tcp 阻塞与非阻塞
- 班长快速统计到班上同学信息(excel表格)
- NFS服务器的配置与管理
- STP怎么选根桥和根端口
- 输出用1、2、3、4四个数字,能组成多少个互不相同且无重复数字的三位数(C语言)
