java 7 的新特性
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
二进制前缀0b或者0B
Java 7 中,整数类型(byte, short, int以及long) 可以使用二进制数系来表示。要指定一个二进制字面量,可以给二进制数字添加前缀 0b 或者 0B。
public static void main(String[] args) {byte a = 0b11;short b = 0b11;int c = 0b11;long d = 0b11;System.out.println(a);System.out.println(b);System.out.println(c);System.out.println(d);
}
字面常量数字的下划线
用下划线连接整数提升其可读性,自身无含义,不可用在数字的起始和末尾。
public static void main(String[] args)
{long a = 2_147_483_648L;int b =0b0001_0010_0110;System.out.println(a);System.out.println(b);
}
捕获多个异常
单个catch中捕获多个异常类型(用|分割)并通过改进的类型检查重新抛出异常)。
Java 7之前的版本
try{......
}catch (IOException ex) {logger.error(ex);throw new MyException(ex.getMessage());
catch (SQLException ex) {logger.error(ex);throw new MyException(ex.getMessage());
}catch (Exception ex) {logger.error(ex);throw new MyException(ex.getMessage());
}
Java 7 的版本
try{......
}catch(IOException | SQLException | Exception ex){logger.error(ex);throw new MyException(ex.getMessage());
}
【摘自】 http://www.importnew.com/7015.html
try-with-resources
不需要使用finally来保证打开的流被正确关闭。
传统的资源关闭方式
为了确保外部资源一定要被关闭,通常关闭代码被写入finally代码块中,当然我们还必须注意到关闭资源时可能抛出的异常,于是变有了下面的经典代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {FileInputStream inputStream = null;try {inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("E:\\test.txt"));...} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);} finally {if (inputStream != null) {try {inputStream.close();//关闭资源时可能抛出的异常} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);}}}
}
Java 7 的资源关闭方式
将外部资源的句柄对象的创建放在try关键字后面的括号中,当这个try-catch代码块执行完毕后,Java会确保外部资源的close方法被调用。
public static void main(String[] args) {try (FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("E:\\test.txt"))) {...} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);}
}
【摘自】 https://www.cnblogs.com/itZhy/p/7636615.html
switch 支持String类型
在Java 7 之前,switch 只能支持 byte、short、char、int 这几个基本数据类型和其对应的封装类型。switch后面的括号里面只能放int类型的值,但由于byte,short,char类型,它们会 自动 转换为int类型(精精度小的向大的转化),所以它们也支持 。
注意: 对于精度比int大的类型,比如long、float,doulble,不会自动转换为int,如果想使用,就必须强转为int,如(int)float。
Java 7 后,整形、枚举类型、boolean和字符串都可以。
public class TestString {static String string = "123";public static void main(String[] args) {switch (string) {case "123":System.out.println("123");break;case "abc":System.out.println("abc");break;default:System.out.println("defauls");break;}}
}
【摘自】 https://www.cnblogs.com/lchzls/p/6711222.html
泛型实例化类型自动推断
Java 7 以前的版本
Map<String, String> myMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
Java 7 的版本
Map<String, String> myMap = new HashMap<>(); //注意后面的"<>"
在这条语句中,编译器会根据变量声明时的泛型类型自动推断出实例化HashMap时的泛型类型。再次提醒一定要注意new HashMap后面的<>,只有加上这个<>才表示是自动类型推断。
【摘自】 https://blog.csdn.net/u011240877/article/details/47702745
Files工具类和Path接口
java 7 引入了 FIles 类和 Path 接口。他们两封装了用户对文件的所有可能的操作,相比于之前的File类来说,使用起来方便很多。但是其实一些本质的操作还是很类似的。主要需要知道的是,Path表示路径可以使文件的路径也可以是目录的路径,Files中所有成员都是静态方法,通过路径实现了对文件的基本操作。
Files的简介
Files类是非常好用的io操作工具类,它提供了很多方法进行一些常用的io操作,例如文件复制,移动,删除,读取文件内容,写入文件内容等 。这里对Files不再赘述,读者可查阅相关的文档:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/nio/file/Files.html
Path和File的对比
1. 在错误处理方面
java.io.File类里面很多方法失败时没有异常处理,或抛出异常,例如:
public static void main(String[] args) { File file = new File("H://afile"); //This path does not exsit in file system.if(!file.delete()){System.out.println("删除失败");}
}
运行结果:
删除失败
java.io.File.delete()方法返回一个布尔值指示成功或失败但是没有失败原因。而java.nio.file.Files.delete(Path)会抛出:NoSuchFileException,DirectoryNotEmptyException,IOException,SecurityException,这样当删除一个文件失败时可以根据异常来查找失败原因。例如:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Path path = Paths.get("H://afile"); //This path does not exsit in file system. Files.delete(path);
}
运行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.nio.file.NoSuchFileException: H:\afileat sun.nio.fs.WindowsException.translateToIOException(Unknown Source)at sun.nio.fs.WindowsException.rethrowAsIOException(Unknown Source)at sun.nio.fs.WindowsException.rethrowAsIOException(Unknown Source)at sun.nio.fs.WindowsFileSystemProvider.implDelete(Unknown Source)at sun.nio.fs.AbstractFileSystemProvider.delete(Unknown Source)at java.nio.file.Files.delete(Unknown Source)at bin.main(bin.java:10
2. 读取文件属性相关
File类中读取文件属性都是一个方法返回一个属性值,而没有能够直接一次返回很多属性的方法,造成访问文件属性时效率的问题。例如:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("C:\\Users\\liutaigang\\Desktop\\java各个版本的新特性\\javacode\\test.txt"); System.out.println("isDirectory:" + file.isDirectory()); System.out.println("isHidden:" + file.isHidden()); System.out.println("canRead:" + file.canRead()); System.out.println("canWrite:" + file.canWrite()); System.out.println("lastModified:" + file.lastModified()); System.out.println("length:" + file.length()); }
打印结果:
isDirectory:false
isHidden:false
canRead:true
canWrite:true
lastModified:1534155733866
length:0
但是对于Java 7中可以批量读取文件属性,而且可以访问到文件更详细的属性。例如:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Users\\liutaigang\\Desktop\\java各个版本的新特性\\javacode\\test.txt"); Map<String, Object> map = Files.readAttributes(path, "*", LinkOption.NOFOLLOW_LINKS); for (String s : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(s + ":" + map.get(s)); };}
打印结果:
lastAccessTime:2018-08-13T10:22:13.866759Z
lastModifiedTime:2018-08-13T10:22:13.866759Z
size:0
creationTime:2018-08-13T10:22:13.866759Z
isSymbolicLink:false
isRegularFile:true
fileKey:null
isOther:false
isDirectory:false
【部分摘自】https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35326718/article/details/65447561
DirectoryStream
使用DirectoryStream,我们可以方便的使用for-each语句迭代出一个目录下的所有条目(包括文件和目录),也可以迭代出指定的文件。例如:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Path path = Paths.get("");//get files of alltry (DirectoryStream<Path> stream = Files.newDirectoryStream(path)) {for (Path entry: stream) {System.out.println(entry);}}System.out.println("=======================================================");//get the file that you needtry (DirectoryStream<Path> stream = Files.newDirectoryStream(path, "*.{c,h,class,java}")) {for (Path entry: stream) {System.out.println(entry);}}}
而在Java 7 之前,要在某个目录下获得指定后缀的文件,就有点繁琐了,例如:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File file = new File(".");File[] fs = file.listFiles();for (File f : fs) { if(f.isFile() && ( f.getName().endsWith(".c") || f.getName().endsWith(".h")|| f.getName().endsWith(".class")|| f.getName().endsWith(".java") )){System.out.println(f);}}}
【部分摘自】https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/nio/file/DirectoryStream.html
WatchService
Java 7 中新增WatchService可以监控文件的变动信息(监控到文件是修改,新增、删除等事件;)
其中注册事件需要的是:
StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY,//更新
StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_DELETE,//删除
StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_CREATE,//创建
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{String filePath = ("E:");// 获取文件系统的WatchService对象WatchService watchService = FileSystems.getDefault().newWatchService();Paths.get(filePath).register(watchService , StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_CREATE, StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY, StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_DELETE);//注册事件while(true){// 获取下一个文件改动事件WatchKey key = watchService.take();for (WatchEvent<?> event : key.pollEvents()) {System.out.println(event.context() +" --> " + event.kind());}// 重设WatchKeyboolean valid = key.reset();// 如果重设失败,退出监听if (!valid) break;}
}
当你在 E: 盘下新建一个目录,并改名为 “test” 后,再删除时,会有打印如下信息:
新建文件夹 --> ENTRY_CREATE
新建文件夹 --> ENTRY_DELETE
test --> ENTRY_CREATE
test --> ENTRY_DELETE
【摘自】http://www.cnblogs.com/hwaggLee/p/6552561.html
FileChannel通道获取
Java 7 的FileChannel类中新增了静态方法 open(),用于创建一个访问文件的通道。例如:
public static void main(String[] args) {try {Path file = Paths.get("E:\\test.txt");FileChannel channel = FileChannel.open(file, StandardOpenOption.READ);ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);channel.read(buffer);for(byte b : buffer.array()){System.out.print((char)b);}} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage());}}
【详情请看】https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/nio/channels/FileChannel.html
AsynchronousFileChannel
在 Java 7 中 ,AsynchronousFileChannel被添加到Java NIO。AsynchronousFileChannel使读取数据,使异步地读写文件成为可能。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {Path path = Paths.get("E:\\test.txt");AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(path, StandardOpenOption.READ);ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);long position = 0;Future<Integer> operation = fileChannel.read(buffer, position);//异步读取,不在主线程中while (true){if(operation.isDone())//在主线程中判断是否读取完成{buffer.flip();byte[] data = new byte[buffer.limit()];buffer.get(data);System.out.println(new String(data));buffer.clear();break;}else{System.out.println("loading...");}}}
如果使用传统的方法(java 7 之前)实现上述的功能,会比较复杂。请看示例:
/** 回调接口的定义,由需要异步回调的类实现*/public interface CallBack {// 当异步线程完成时,调用此方法public void Done();}
public class MainThread implements CallBack {private ReadThread readThread;public Boolean isDone = false;//异步线程的完成标识,false--未完成,true--已完成public MainThread(ReadThread readThread) {this.readThread = readThread;}public void readFile(){new Thread(new Runnable() {[@Override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)public void run() {readThread.readFileContent(MainThread.this);}}).start();}[@Override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)public void Done() {this.isDone = true;} }
public class ReadThread {private File file;private byte[] buf;public ReadThread(File file, byte[] buf){this.file = file;this.buf = buf;}public void readFileContent(CallBack callBack) {InputStream input = null;try {input = new FileInputStream(file);input.read(buf);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally{try {if(null != input) input.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}callBack.Done();//通知已完成}}
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {File file = new File("E:\\test.txt");byte[] buf = new byte[1024];ReadThread readThread = new ReadThread(file, buf);MainThread mainThread = new MainThread(readThread);mainThread.readFile();//等待异步线程完成while(true){if(mainThread.isDone){for(byte b : buf){System.out.print((char)b);}break;}else{System.out.println("loading...");}}}}
【部分摘自】
https://www.jianshu.com/p/b38f8c596193
https://blog.csdn.net/wanglha/article/details/51383245
NetworkChannel接口
NetworkChannel是 Java 7 中新增的NIO.2中的接口,ServerSocketChannel,SocketChannel和DatagramChannel 都实现了这个接口。NetworkChannel加入让我们对channel控制的更细腻,可以对本地网卡做详细的检索。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {SelectorProvider provider = SelectorProvider.provider();try {NetworkChannel socketChannel = provider.openSocketChannel();SocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(3080);socketChannel = socketChannel.bind(address);Set<SocketOption<?>> socketOptions = socketChannel.supportedOptions();System.out.println(socketOptions.toString());socketChannel.setOption(StandardSocketOptions.IP_TOS, 3);System.out.println(socketChannel.getOption(StandardSocketOptions.IP_TOS));Boolean keepAlive = socketChannel.getOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_KEEPALIVE);System.out.println(keepAlive);} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage());}}
【部分摘自】https://www.cnblogs.com/pony1223/p/8186229.html?utm_source=debugrun&utm_medium=referral
新增Fork/Join框架
什么是Fork/Join框架
java 7 加入了并行计算的框架Fork/Join,Fork/Join采用的是分治法。所谓分治法就是将一个大任务切分成N个小任务并行执行,并最终聚合结果。 在实际情况中,很多时候我们都需要面对经典的“分治”问题。要解决这类问题,主要任务通常被分解为多个任务块(分解阶段),其后每一小块任务被独立并行计算。一旦计算任务完成,每一块的结果会被合并或者解决(解决阶段) 。
请看图:
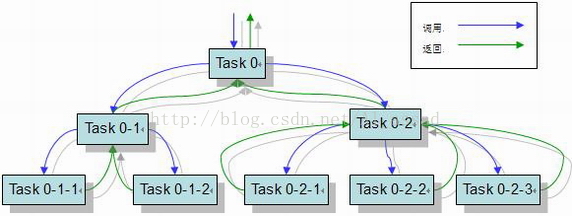
Fork/Join框架的核心类
1. ForkJoinPool
这个类实现了ExecutorService接口和工作窃取算法(Work-Stealing Algorithm)。它管理工作者线程,并提供任务的状态信息,以及任务的执行信息。
2. ForkJoinTask
这个类是一个在ForkJoinPool中执行的任务的基类。ForkJoinTask 提供了在一个任务里执行 fork() 和 join() 操作的机制和控制任务状态的方法。通常,为了实现Fork/Join任务,需要实现它的子类:RecursiveAction、RecursiveTask。
- RecursiveAction:用于任务没有返回结果的场景。
- RecursiveTask:用于任务有返回结果的场景。
它们的继承(实现)关系图: 
简单的例子
在这个例子中,会使用ExecutorService的方法和Fork/Join的方法来共同实现一个任务——1~1000的累加和。
1. Java 7 之前——ExecutorService
public class ExecutorServiceCalculator {private int parallism;private ExecutorService pool;public ExecutorServiceCalculator() {parallism = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); // 获取CPU的核心数pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(parallism);}private class SumTask implements Callable<Integer> {private Integer[] numbers;private int from;private int to;public SumTask(Integer[] numbers, int from, int to) {this.numbers = numbers;this.from = from;this.to = to;}[@Override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)public Integer call() throws Exception {int total = 0;for (int i = from; i <= to; i++) {total += numbers[i];}return total;}}/*** 计算入口* [@param](https://my.oschina.net/u/2303379) numbers 用于计算的数组* [@return](https://my.oschina.net/u/556800) 最终的计算结果*/public int sumUp(Integer[] numbers) {List<Future<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();// 把任务分解为 n 份,交给 n 个线程处理int part = numbers.length / parallism;for (int i = 0; i < parallism; i++) {int from = i * part;int to = (i == parallism - 1) ? numbers.length - 1 : (i + 1) * part - 1;results.add(pool.submit(new SumTask(numbers, from, to)));}// 把每个线程的结果相加,得到最终结果int total = 0;for (Future<Integer> f : results) {try {total += f.get();} catch (Exception ignore) {}}return total;}/*** 当所有线程任务完成时,关闭计算器(Calculator)*/public void shutDown(){this.pool.shutdown();};
}
public class Test {static final int TOTAL = 1000;public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorServiceCalculator esc = new ExecutorServiceCalculator();Integer[] numbers = new Integer[TOTAL];for(int i=0; i<TOTAL; i++){numbers[i] = Integer.valueOf(i+1);}int sum = 0;sum = esc.sumUp(numbers);esc.shutDown();System.out.println("ExecutorServiceCalculator's result :" + sum); }
}
2. java 7的版本 ——Fork/Join
public class ForkJoinCalculator {private ForkJoinPool pool;public ForkJoinCalculator() {pool = new ForkJoinPool();//会以Runtime.avaliableProcessors()方法的返回值作为并行线程数量参数}private class SumTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {private Integer[] numbers;private int from;private int to;private int threshold;//最小任务的计算量(临界值)public SumTask(Integer[] numbers, int from, int to, int threshold) {this.numbers = numbers;this.from = from;this.to = to;this.threshold = threshold;}[@Override](https://my.oschina.net/u/1162528)protected Integer compute() {// 当需要计算的数字小于threshold时,直接计算结果if (to - from < threshold) {int total = 0;for (int i = from; i <= to; i++) {total += numbers[i];}return total;// 否则,把任务一分为二,递归计算} else {int middle = (from + to) / 2;SumTask taskLeft = new SumTask(numbers, from, middle, threshold);SumTask taskRight = new SumTask(numbers, middle+1, to, threshold);taskLeft.fork();taskRight.fork();return taskLeft.join() + taskRight.join();}}}/*** 计算入口* [@param](https://my.oschina.net/u/2303379) numbers 用于计算的数组* @param threshold 最小任务的计算量(临界值)* @return 最终的计算结果* @throws InterruptedException* @throws ExecutionException*/public int sumUp(Integer[] numbers, int threshold) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {return pool.submit(new SumTask(numbers, 0, numbers.length-1, threshold)).get();}/*** 当所有线程任务完成时,关闭计算器(Calculator)*/public void shutDown(){this.pool.shutdown();}
}
public class Test {static final int TOTAL = 1000;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {ForkJoinCalculator fjc = new ForkJoinCalculator();Integer[] numbers = new Integer[TOTAL];for(int i=0; i<TOTAL; i++){numbers[i] = Integer.valueOf(i+1);}int sum = 0;sum = fjc.sumUp(numbers, 50);fjc.shutDown();System.out.println("ForkJoinCalculator's result :" + sum); }
}
【摘自】
https://blog.csdn.net/caicongyang/article/details/51180330
http://www.importnew.com/2279.html
https://blog.csdn.net/al_assad/article/details/60878486
http://blog.dyngr.com/blog/2016/09/15/java-forkjoinpool-internals/
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/u/3471006/blog/2998080
java 7 的新特性相关推荐
- Java SE 6 新特性 Instrumentation 新功能
系列内容: 此内容是该系列的一部分:Java SE 6 新特性 Instrumentation 简介 利用 Java 代码,即 java.lang.instrument 做动态 Instrumenta ...
- JDK 15 JAVA 15的新特性展望
文章目录 JEP 371: Hidden Classes JEP 372: 删除 Nashorn JavaScript Engine JEP 377: 新的垃圾回收器ZGC正式上线了 JEP 378: ...
- Atitit..jdk java 各版本新特性 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5(5.0) 1.6(6.0) 7.0 8.0 9.0 attilax 大总结...
Atitit..jdk java 各版本新特性 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5(5.0) 1.6(6.0) 7.0 8.0 9.0 attilax 大总结 1.1. Java的编年史2 ...
- 【小家java】java8新特性之---全新的日期、时间API(JSR 310规范),附SpringMVC、Mybatis中使用JSR310的正确姿势
[小家java]java5新特性(简述十大新特性) 重要一跃 [小家java]java6新特性(简述十大新特性) 鸡肋升级 [小家java]java7新特性(简述八大新特性) 不温不火 [小家java ...
- Java SE 6 新特性: 对脚本语言的支持 [VERY GOOD]
Java SE 6 新特性: 对脚本语言的支持 [VERY GOOD] Java SE 6 新特性: 对脚本语言的支持 Java SE 6 新特性: 对脚本语言的支持 邱 小侠 (qiuxiaox@c ...
- Java SE 8 新特性之旅 : Java开发世界的大变动
我很自豪的成为了adopt-OpenJDK的一员,像其他专业团队成员一样,但是我只刚加入了8个月,我们一同经历了Java SE 8 的开发.编译.编码.讨论--等等,直到JDK上线.Java SE 8 ...
- 【小家java】java9新特性(简述十大新特性) 褒贬不一
相关阅读 [小家java]java5新特性(简述十大新特性) 重要一跃 [小家java]java6新特性(简述十大新特性) 鸡肋升级 [小家java]java7新特性(简述八大新特性) 不温不火 [小 ...
- Java 8的新特性—终极版
前言: Java 8 已经发布很久了,很多报道表明Java 8 是一次重大的版本升级.在Java Code Geeks上已经有很多介绍Java 8新特性的文章,例如Playing with Java ...
- java编译器加上参数_java8 之 Java编译器的新特性
简介 毫无疑问,Java 8是Java自Java 5(发布于2004年)之后的最重要的版本.这个版本包含语言.编译器.库.工具和JVM等方面的十多个新特性.在本文中我们将学习这些新特性,并用实际的例子 ...
- 【小家java】java10新特性(简述十大新特性) 小步迭代
相关阅读 [小家java]java5新特性(简述十大新特性) 重要一跃 [小家java]java6新特性(简述十大新特性) 鸡肋升级 [小家java]java7新特性(简述八大新特性) 不温不火 [小 ...
最新文章
- 2021-11-10 YOLOX训练最新笔记总结(coco格式)
- java 之 解释器模式(大话设计模式)
- 深入浅出之-route命令实战使用指南
- 获取Table选中行数据(Table篇二)
- 创建一个springMVC项目总结
- NOIP2007 字符串的展开
- DVWA-暴力破解-对‘g0tmi1k’文章的学习笔记
- 【笔记】汇编..寄存器和地址的概述
- 监管大屏系统_“警视” 警务情指一体大屏可视化决策系统
- IE iframe不刷新的问题之完美解决
- JAVAWeb项目 微型商城项目-------(六)管理员登录
- 北京新文化运动纪念馆展出中国古代建筑经典模型
- win 7共享计算机改名,不用再去找软件 批量改名Win7一键搞定
- HackerRank - C语言 - Introduction - Playing With Characters
- SQL语句如何精准查找某一时间段的数据
- http post 415错误
- archlinux下网易云音乐netease-cloud-music部分问题
- 面包师问题--linux实现
- Unity 3D模型展示框架篇之框架运用
- 实战小米官网静态页面1:导航栏部分
热门文章
- db2 mysql oracle,五大主流数据库比较 DB2 Oracle MySQL SyBase SQLServer)
- 解决myeclipse里面git的更新(pull)操作问题
- 用AI实现隔墙“透视”,准确率达97%,这家中国公司研究入选CVPR
- 大小仅17KB!这个微型风格迁移模型太好玩了 | 代码+教程
- DeepMind去年亏损27亿元,同比扩大221%,谷歌说:继续烧
- 圣诞节吃饺子时,怎么给女票解释啥是AI?
- CV还要更热闹!旷视刚宣布4.6亿美元融资,商汤:新一轮年内完成
- springboot如何使用外部tomcat容器
- Linux系统下如何实现文件系统配额
- ECMAScript 6新特性介绍
