It's all about buffers: zero-copy, mmap and Java NIO
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
Sep 10, 2016 in OS
There are use cases where data need to be read from source to a sink without modification. In code this might look quite simple: for example in Java, you may read data from one InputStream chunk by chunk into a small buffer (typically 8KB), and feed them into the OutputStream, or even better, you could create a PipedInputStream, which is basically just a util that maintains that buffer for you. However, if low latency is crucial to your software, this might be quite expensive from the OS perspective and I shall explain.
What happens under the hood
Well, here’s what happens when the above code is used:
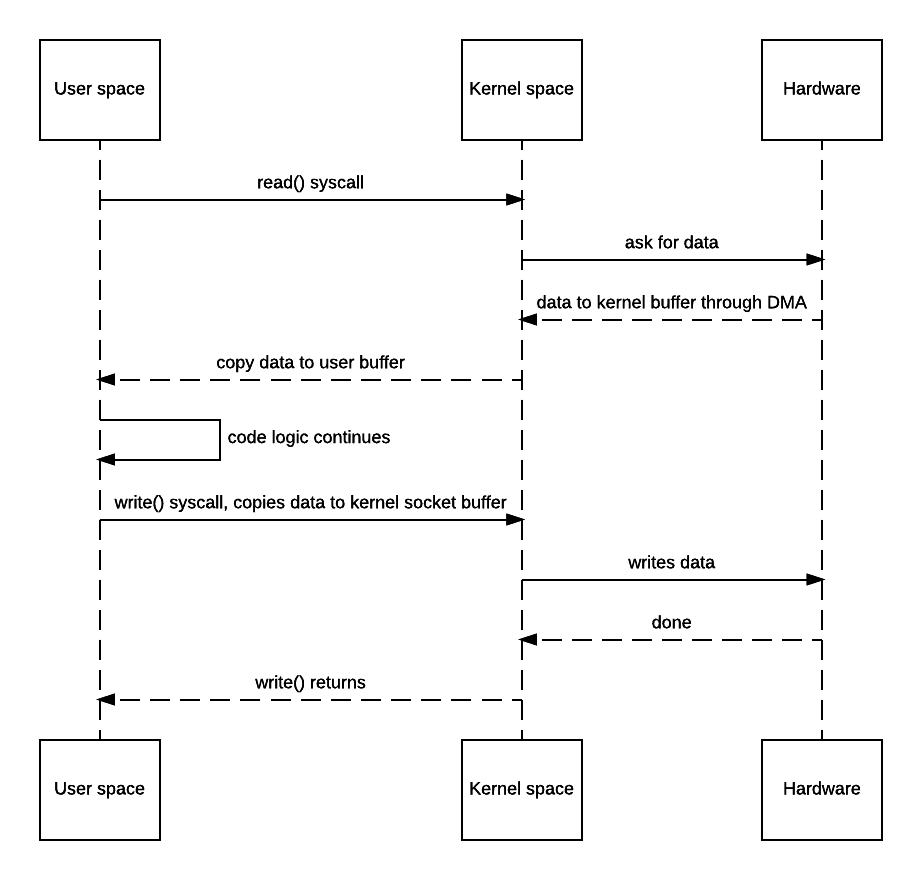
- JVM sends read() syscall.
- OS context switches to kernel mode and reads data into the input socket buffer.
- OS kernel then copies data into user buffer, and context switches back to user mode. read() returns.
- JVM processes code logic and sends write() syscall.
- OS context switches to kernel mode and copies data from user buffer to output socket buffer.
- OS returns to user mode and logic in JVM continues.
This would be fine if latency and throughput aren’t your service’s concern or bottleneck, but it would be annoying if you do care, say for a static asset server. There are 4 context switches and 2 unnecessary copies for the above example.
OS-level zero copy for the rescue
Clearly in this use case, the copy from/to user space memory is totally unnecessary because we didn’t do anything other than dumping data to a different socket. Zero copy can thus be used here to save the 2 extra copies. The actual implementation doesn’t really have a standard and is up to the OS how to achieve that. Typically *nix systems will offer sendfile(). Its man page can be found here. Some say some operating systems have broken versions of that with one of them being OSX link. Honestly with such low-level feature, I wouldn’t trust Apple’s BSD-like system so never tested there.
With that, the diagram would be like this:
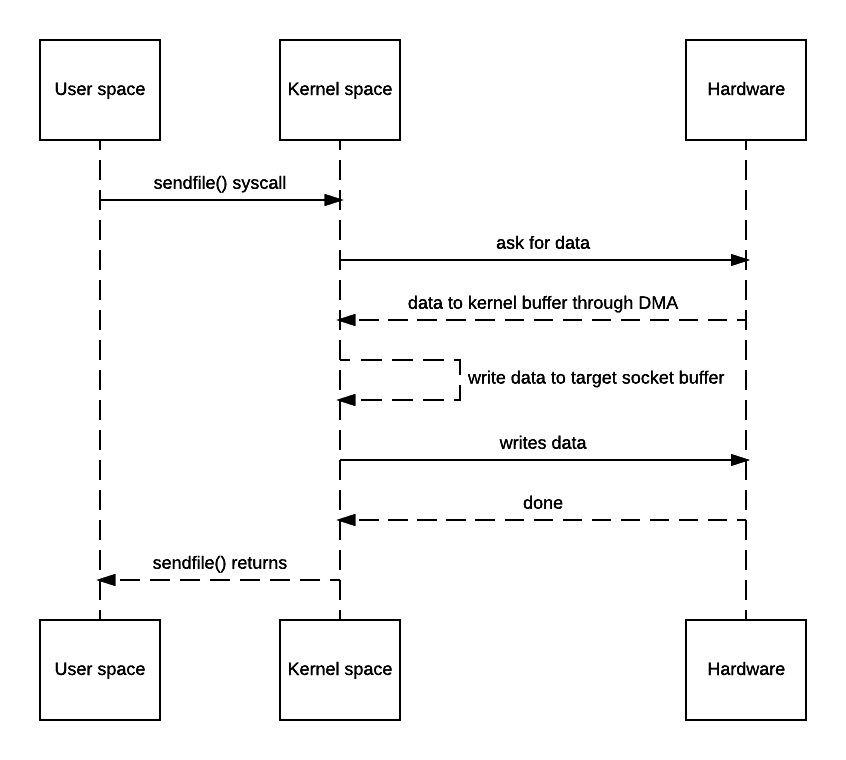
You may say OS still has to make a copy of the data in kernel memory space. Yes but from OS’s perspective this is already zero-copy because there’s no data copied from kernel space to user space. The reason why kernel needs to make a copy is because general hardware DMA access expects consecutive memory space (and hence the buffer). However this is avoidable if the hardware supports scatter-n-gather:
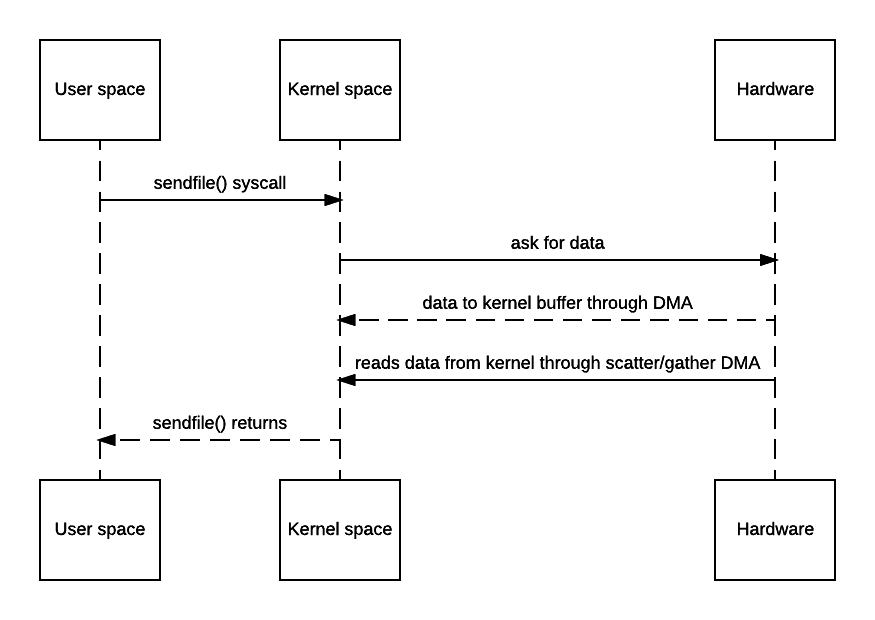
A lot of web servers do support zero-copy such as Tomcat and Apache. For example apache’s related doc can be found here but by default it’s off.
Note: Java’s NIO offers this through transferTo (doc).
mmap
The problem with the above zero-copy approach is that because there’s no user mode actually involved, code cannot do anything other than piping the stream. However, there’s a more expensive yet more useful approach - mmap, short for memory-map.
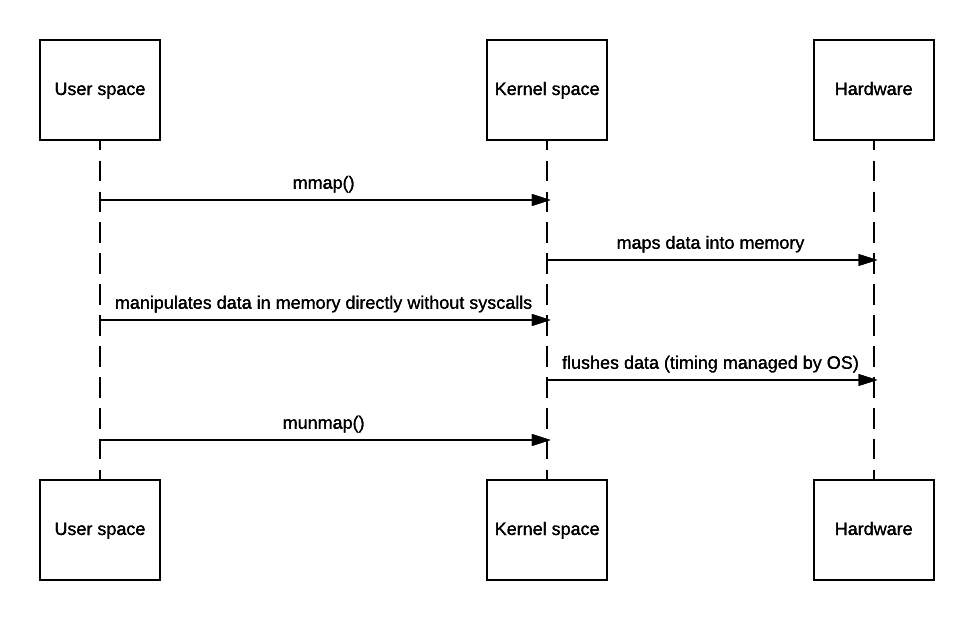
Mmap allows code to map file to kernel memory and access that directly as if it were in the application user space, thus avoiding the unnecessary copy. As a tradeoff, that will still involve 4 context switches. But since OS maps certain chunk of file into memory, you get all benefits from OS virtual memory management - hot content can be intelligently cached efficiently, and all data are page-aligned thus no buffer copying is needed to write stuff back.
However, nothing comes for free - while mmap does avoid that extra copy, it doesn’t guarantee the code will always be faster - depending on the OS implementation, there may be quite a bit of setup and teardown overhead (since it needs to find the space and maintain it in the TLB and make sure to flush it after unmapping) and page fault gets much more expensive since kernel now needs to read from hardware (like disk) to update the memory space and TLB. Hence, if performance is this critical, benchmark is always needed as abusing mmap() may yield worse performance than simply doing the copy.
The corresponding class in Java is MappedByteBuffer from NIO package. It’s actually a variation of DirectByteBuffer though there’s no direct relationship between classes. The actual usage is out of scope of this post.
NIO DirectByteBuffer
Java NIO introduces ByteBuffer which represents the buffer area used for channels. There are 3 main implementations of ByteBuffer:
HeapByteBufferThis is used when
ByteBuffer.allocate()is called. It’s called heap because it’s maintained in JVM’s heap space and hence you get all benefits like GC support and caching optimization. However, it’s not page aligned, which means if you need to talk to native code through JNI, JVM would have to make a copy to the aligned buffer space.DirectByteBufferUsed when
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect()is called. JVM will allocate memory space outside the heap space usingmalloc(). Because it’s not managed by JVM, your memory space is page-aligned and not subject to GC, which makes it perfect candidate for working with native code (e.g. when writing OpenGL stuff). However, you are then “deteriorated” to C programmer as you’ll have to allocate and deallocate memory yourself to prevent memory leak.MappedByteBufferUsed when
FileChannel.map()is called. Similar toDirectByteBufferthis is also outside of JVM heap. It essentially functions as a wrapper around OS mmap() system call in order for code to directly manipulate mapped physical memory data.
Conclusion
sendfile() and mmap() offer efficient, low-latency low-level solutions to data manipulation across sockets. Again, no code should assume these are silver bullets as real world scenarios may be complex and it might not be worth the effort to switch code to them if this is not the true bottleneck. For software engineering to get the most ROI, in most cases, it’s better to “make it right” and then “make it fast”. Without the guardrails offered by JVM, it’s easy to make software much more vulnerable to crashing (I literally mean crashing, not exceptions) when it comes to complicated logic.
Quick Reference
Efficient data transfer through zero copy - It also covers sendfile() performance comparison.
Getting started with new I/O (NIO)
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/fuckmylife0/blog/1554915
It's all about buffers: zero-copy, mmap and Java NIO相关推荐
- Google Protocol Buffers 2.3.0 for java 快速开始
Google Protocol Buffers 2.3.0 for java 快速开始 博客分类: Java JavaGoogleUbuntuLinux数据结构 Protocol Buffers是一个 ...
- copy所有的java文件到硬盘_将d:\java目录下的所有.java文件复制到d:\jad目录下,并将原来文件的扩展名从.java改为.jad...
listFiles方法接受一个FileFilter对象,这个FileFilter对象就是过虑的策略对象,不同的人提供不同的FileFilter实现,即提供了不同的过滤策略. //将d:\java目录下 ...
- Linux I/O原理和零拷贝Zero-copy技术全面揭秘
目录 导言 计算机存储器 物理内存 虚拟内存 静态重定位 存储器抽象 交换(swapping)技术 虚拟内存技术 用户态和内核态 Linux I/O I/O 缓冲区 I/O 模式 程序控制 I/O 中 ...
- Java NIO理解与使用
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> Netty的使用或许我们看着官网user guide还是很容易入门的.因为Java nio使用非常的繁琐,netty对Java ...
- Java NIO使用及原理分析(三)
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 转载自:李会军•宁静致远 在上一篇文章中介绍了缓冲区内部对于状态变化的跟踪机制,而对于NIO中缓冲区来说,还有很多的内容值的学 ...
- java直接调用复制文件,java中文件复制的4种方式,java文件的复制
java中文件复制的4种方式,java文件的复制 今天一个同事问我文件复制的问题,他一个100M的文件复制的指定目录下竟然成了1G多,吓我一跳,后来看了他的代码发现是自己通过字节流复制的,定义的字节数 ...
- 4种Java文件复制的方法
1.Java 复制文件 - 流 这是java中文件复制的常规方式.在这里,我们创建两个文件 - 源和目标.然后我们从源创建InputStream并使用OutputStream将其写入目标文件进行 ja ...
- java netty教程_明哥教学 - Netty简单入门教程
作为一个正在Java路上摸爬滚打的小菜鸡,之前在项目中也用过Netty,也因为Netty报名阿里的中间件大赛,但终究功力太浅,最终不了了之,最近工作中又遇到了Netty的小姐妹Mina.此时楼主觉得N ...
- 对于 Netty ByteBuf 的零拷贝(Zero Copy) 的理解
根据 Wiki 对 Zero-copy 的定义: "Zero-copy" describes computer operations in which the CPU does n ...
最新文章
- OpenGL学习(4)——纹理(补)
- oracle将213变成123,oracle 转换函数
- cygwin用命令安装软件_Cygwin本地安装版
- oracle index contention,Index Contention等待
- eclipse debug 重新指定源码
- Angular component的职责
- 使用Excel消费SAP C4C的OData service
- W3 Total Cache+Hacklog Remote Attachment Upyun
- Spark SQL External Data Sources JDBC官方实现写测试
- 图像处理技术上的空间域和空间频率域
- 一键分析你的上网行为, 看看你平时上网都在干嘛?
- 优达笔记-安然数据分析 异常值处理
- Android - Bootloader? root原理?Recovery? SuperSU?Magisk?Xposed?ROM包?这都啥玩意?
- 股票交易接口与各种路由器接口与连接方法
- 好玩的Canvas射箭小游戏
- 【Android 学习】之二维码扫描开发(闪光灯功能)
- 一个SAPer的网络日志-连载一-看,内部订单都能用来干啥
- 超神学院的宇宙天体计算机,正文 第一章:银河之力被一分为二
- python英汉互译-中汉英在线翻译
- 特步CIO:企业信息化建设的“解放战争”
热门文章
- linux小小输入法 不能中文,在centos 下安装小小输入法存在的问题
- pytorch指定用多张显卡训练_Pytorch中多GPU训练指北
- mysql验证配置_详解MySQL|教你一招如何自动验证 MySQL 配置正确性
- 用python批量创建docker_「docker实战篇」python的docker-docker镜像的创建使用dockerfile(3...
- python需要安装的库_使用python学习【机器学习】需要安装的库~
- python 测试mysql数据库_Python操作MySQL数据库----继续安装和测试
- java httpclient教程_HttpClient4.5.2 HTTP协议的请求和执行
- php str_replace多个参数,php str_replace()函数的用法,有那些参数?
- mysql启动错误1.69,MySQL无法启动例一
- win7mysql免安装版安装_win7下MySQL免安装版下载安装、配置与使用
