Twitter API: Door To Social Media Analysis I
个人博客地址在 https://mengjiexu.com/post/door-to-twitter-analysis-i/
文章目录
- Motivation
- Get Access To Twitter API v2
- What Can Twitter API v2 Do?
- Data Objects
- Fields of Tweet Object
- Fields of User Object
- Summary and Upcoming Posts
- References
Motivation
In the last few decades, a series of papers published in top accounting journals have repeatedly proved that Twitter data could empower very fascinating research ideas. To give readers an intuition about the potential of Twitter data, I would roughly show three directions and their relative examples which I have deepest impression through my limited personal reading experience.
Wisdom of crowds
Bartov, Faurel, and Mohanram (2018, TAR) found opinions of individuals tweeted just prior to a firm’s earnings announcement can predict its earnings and announcement returns. Similarly, Tang (2018, JAR) showed the customer responses towards a firm’s products in Twitter obtain a siginificant predictive power for the upcoming firm sales.
Information dissemination
Blankespoor, Miller, and White (2013, TAR) illustrated that firms who disseminate their earnings announcements via Twitter besides traditional dissemination channels (e.g., SEC EDGAR, business press, firm websites, etc) have higher maket visibility (e.g., bigger liquidity around earnings announcements, greater market depths, etc), which is especially crucial for samll and medium enterprises. Based on this idea, Jung, Naughton, Tahoun, and Wang (2018, TAR) showed that firms strategically use social media like Twitter as an extra information dissemination channel. Specifically, they found firms are less likely to disseminate their earnings in Twitter if they are underperforming.
Risk management
Lee, Hutton, and Shu (2015, JAR) noticed that the very special feature of Twitter, compared to traditional information dissemination intermediaries, is that firms can communicate quickly and directly with their stakeholders via their Twitter accounts. Utilizing this interactive feature, the authors found that firms who directly communicate with stakeholders in Twitter after the outbreak of crisis (e.g., product recall) experience attenuated negative market reaction.
Having made clear about the potential of Twitter data, in this blogpost I will briefly introduce some necesary background information which lays a base for efficiently obtaining a tailored dataset using Twitter API v2. A sample project which replicates the Tweets extraction process of Bartov, Faurel, and Mohanram (2018, TAR) will be discussed in the next blogpost.
Get Access To Twitter API v2
To make any request to the Twitter API, you must first apply for a developer account and have your use case approved. Twitter offers generous free academic developer accounts which provides qualified academic researchers access to elevated access and enhanced functionality (compared to standard version), including access to the full-archive search endpoint, a higher monthly Tweet cap (e.g., 10,000,000 tweets per month), and enhanced filtering capabilities with the filtered stream and recent search endpoint. One can apply for an academic developer account via this link. To make sure the account will be properly used, Twitter might require you to porvide the following information:
- Your full name as it is appears on your institution’s documentation
- Links to webpages that help establish your identity; provide one or more of the following:
- A link to your profile in your institution’s faculty or student directory
- A link to your Google Scholar profile
- A link to your research group, lab or departmental website where you are listed
- In English, describe your methodology for analyzing Twitter data, Tweets, and/or Twitter users. Minimum 200 characters.
- In other words, what types of analyses do you intend to perform with Twitter data? This should be more descriptive of your tactics than the question above.
- Will your research present Twitter data individually or in aggregate?
- Think of it as presenting individual Tweets or users vs. aggregate statistics or models.
To maintain a well-functioning developer community and also avoid potential litigation risks, please do not forget to check the multiple policies you need to comply, the restricted uses of your Twitter API account, and the speed limit of requests.
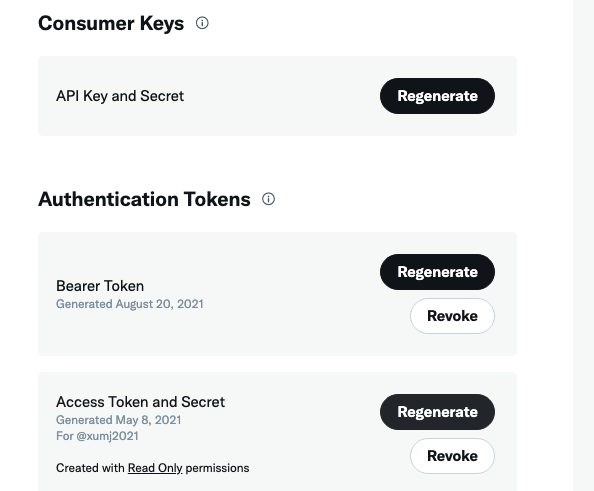
The dashboard of the developer portal is as follows. Click the little sign I have circled in Figure 1, you will have the various tokens showed in Figure 2.
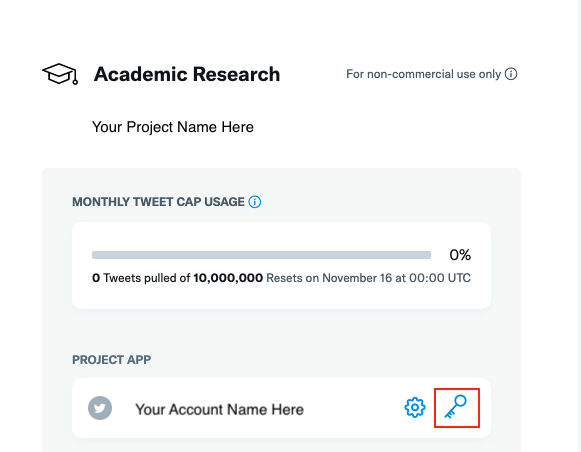
Twitter defines the different tokens as following:
Think of the API key as the user name that represents your App when making API requests. It helps us verify who you are.
Our API Key Secret is like a password and helps verify your API Key.
Bearer Token is an Access Token used in authentication that allows you to pull specific data.
For the safety of your developer account, you might not want to have the tokens explicitly displayed in your codes. In such case, you could basically set the tokens as the enviornment variables in your terminal and just cite the environment variables when writing codes.
(base) mengjiexu@MacBook-von-mengjie ~ % vim ~/.zsh_profile
export CONSUMER_KEY='<Your API Key>'
export CONSUMER_SECRET='<Your API Key>'
export BEARER_TOKEN=$BEARER_TOKEN:'<Your Bearer Token>'
(base) mengjiexu@MacBook-von-mengjie ~ % source ~/.zsh_profile
What Can Twitter API v2 Do?
According to the official manual, one can achieve the following functions via Twitter API v2.
| Category | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tweets | Tweet lookup | Look up Tweets by ID. |
| Search Tweets | Query the most recent seven days or the full-archive of Tweets, and receive a full-fidelity response. The full-archive search endpoint is currently only available via the Academic Research product track. | |
| Tweet counts | Retrieve a count of Tweets from either the last seven days or from the full-archive that matches a query. The full-archive Tweet counts endpoint is currently only available via the Academic Research product track. | |
| Timelines | Retrieve a timeline of either the Tweets composed by a specified Twitter account, or the mentions of a specified Twitter account. | |
| Filtered stream | Filter the complete stream of real-time public Tweets. | |
| Sampled stream | Stream a sample of new Tweets as they are published, across ~1% of all public Tweets in real-time. | |
| Retweets | Retrieve a list of accounts that have Retweeted a Tweet, or Retweet or undo a Retweet of a Tweet. | |
| Likes | Retrieve a list of users who liked a Tweet, retrieve a list of Tweets that a user has liked, or like and unlike a Tweet. | |
| Hide replies | Hide or unhide a reply to a Tweet. | |
| Users | User lookup | Look up users by name or ID. |
| Follows | Retrieve an account’s followers, retrieve a list of who an account is following, or follow and unfollow a user. | |
| Blocks | Retrieve a list of users that an account has blocked, or block and unblock a user. | |
| Mutes | Retrieve a list of users that an account has muted, or mute and unmute a user | |
| Spaces | Lookup Spaces | Lookup a Space using IDs or a creator’s username |
| Search Spaces | Search for a Space using a keyword | |
| Compliance | Batch compliance | Batch upload dataset to understand what action is needed to ensure that your datasets reflect the current state of the content on Twitter. |
Twitter also provides a series of sample codes to realize those functions using various programming languages (e.g., Java, Node.js, Python, R, Ruby). The codes are public available at Twitter Developer’s Github Repositories. I will introduce the most frequently used functions that researchers would use in the subsequent blogposts.
Data Objects
Before we move to the sample project, it’s necessary to make clear which data is available. According to the official manual, there are three primary types (Tweet, User, Space) of objects and three expanded ones (Media, Place, Poll). Each of them has a series of fields ready for requests.
Those objects are:
- Tweet object - Tweets are the basic building block of all things Twitter. The Tweet object has a long list of ‘root-level’ fields, such as
id,text, andcreated_at. Tweet objects are also the ‘parent’ object to several child objects includinguser,media,poll, andplace. Use the field parametertweet.fieldswhen requesting these root-level fields on the Tweet object. - User object - The user object contains Twitter user account metadata describing the referenced user. The user object is the primary object returned in the User Lookup endpoint. When requesting additional user fields on this endpoint, simply use the fields parameter
user.fields. - Space object - Spaces allow expression and interaction via live audio conversations. The Space data dictionary contains relevant metadata about a Space; all the details are updated in real time.
- Media object - Media refers to any image, GIF, or video attached to a Tweet. The media object is not a primary object on any endpoint, but can be found and expanded in the Tweet object.
- Place objects - The place tagged in a Tweet is not a primary object on any endpoint, but can be found and expanded in the Tweet resource.
- Poll object - A poll included in a Tweet is not a primary object on any endpoint, but can be found and expanded in the Tweet object.
For research purposes, the most frequently used objects are Tweet object and User object. Thus, I will display the field lists of these two objects here. One could also find more detailed information about those fields in the official manual.
Fields of Tweet Object
| Field value | Type | How it can be used |
|---|---|---|
| id (default) | string | Use this to programmatically retrieve a specific Tweet. |
| text (default) | string | Keyword extraction and sentiment analysis/classification. |
| attachments | object | Understanding the objects returned for requested expansions |
| author_id | string | Hydrating User object, sharing dataset for peer review |
| context_annotations | array | Entity recognition/extraction, topical analysis |
| conversation_id | string | Use this to reconstruct the conversation from a Tweet. |
| created_at | date (ISO 8601) | This field can be used to understand when a Tweet was created and used for time-series analysis etc. |
| entities | object | Entities are JSON objects that provide additional information about hashtags, urls, user mentions, and cashtags associated with a Tweet. Reference each respective entity for further details. |
| geo | object | Determine if a Tweet is related to a named location with corresponding geo coordinates. |
| in_reply_to_user_id | string | Use this to determine if this Tweet was in reply to another Tweet. |
| lang | string | Classify Tweets by spoken language. |
| non_public_metrics | object | Use this to determine the total number of impressions generated for the Tweet. |
| organic_metrics | object | Use this to measure organic engagement for the Tweet. |
| possibly_sensitive | boolean | Studying circulation of certain types of content. |
| promoted_metrics | object | Use this to measure engagement for the Tweet when it was promoted. |
| public_metrics | object | Use this to measure Tweet engagement. |
| referenced_tweets | array | This field can be used to understand conversational aspects of retweets etc. |
| reply_settings | string | This field allows you to determine whether conversation reply settings have been set for the Tweet and if so, what settings have been set. |
| source | string | Determine if a Twitter user posted from the web, mobile device, or other app. |
| withheld | object | When present, contains withholding details for withheld content. |
Fields of User Object
| Field value | Type | How it can be used |
|---|---|---|
| id (default) | string | Use this to programmatically retrieve information about a specific Twitter user. |
| name (default) | string | |
| username (default) | string | |
| created_at | date (ISO 8601) | Can be used to determine how long a someone has been using Twitter |
| description | string | |
| entities | object | Entities are JSON objects that provide additional information about hashtags, urls, user mentions, and cashtags associated with the description. Reference each respective entity for further details. |
| location | string | |
| pinned_tweet_id | string | Determine the Tweet pinned to the top of the user’s profile. Can potentially be used to determine the user’s language. |
| profile_image_url | string | Can be used to download this user’s profile image. |
| protected | boolean | |
| public_metrics | object | Can potentially be used to determine a Twitter user’s reach or influence, quantify the user’s range of interests, and the user’s level of engagement on Twitter. |
| url | string | A URL provided by a Twitter user in their profile. This could be a homepage, but is not always the case. |
| verified | boolean | Indicates whether or not this Twitter user has a verified account. A verified account lets people know that an account of public interest is authentic. |
| withheld | object |
Summary and Upcoming Posts
In this blogpost, I have introduced the necessary background information about Twitter API v2. To give the readers a big picture about how Twitter API can serve for one’s research project, I will replicate the Tweets extraction process of Bartov, Faurel, and Mohanram (2018, TAR) aforementioned in the next blogpost.
References
Bartov, Eli, Lucile Faurel, and Partha S. Mohanram. “Can Twitter help predict firm-level earnings and stock returns?.” The Accounting Review 93.3
Blankespoor, Elizabeth, Gregory S. Miller, and Hal D. White. “The role of dissemination in market liquidity: Evidence from firms’ use of Twitter™.” The Accounting Review 89.1 (2014): 79-112.
Jung, Michael J., et al. “Do firms strategically disseminate? Evidence from corporate use of social media.” The Accounting Review 93.4 (2018): 225-252.
Lee, Lian Fen, Amy P. Hutton, and Susan Shu. “The role of social media in the capital market: Evidence from consumer product recalls.” Journal of Accounting Research 53.2 (2015): 367-404.
Tang, Vicki Wei. “Wisdom of crowds: Cross‐sectional variation in the informativeness of third‐party‐generated product information on Twitter.” Journal of Accounting Research 56.3 (2018): 989-1034.
https://developer.twitter.com/en/docs/twitter-api/getting-started/getting-access-to-the-twitter-api
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7501678/set-environment-variables-on-mac-os-x-lion
https://github.com/twitterdev/Twitter-API-v2-sample-code
https://developer.twitter.com/en/docs/twitter-api/data-dictionary/object-model/
Twitter API: Door To Social Media Analysis I相关推荐
- 【论文翻译 假新闻检测综述 HICSS 2019】Can Machines Learn to Detect Fake News? A Survey Focused on Social Media
论文题目:Can Machines Learn to Detect Fake News? A Survey Focused on Social Media 论文来源:HICSS 2019,Procee ...
- [yzhpdh多读paper]Discovering Shifts to Suicidal Ideationfrom Mental Health Content in Social Media
这次介绍一下第一作者:来自佐治亚理工学院人机交互学院的副教授Munmun De Choudhury Munmun 通过分析 Reddit 网站半匿名互助社区的数据,研究哪些人群会经历心理疾病到自杀意念 ...
- 【Twitter API开发者账户协议必知】
Twitter API协议必知 中文 英文 中文 开发商协议 生效日期:2022年10月10日 本Twitter开发者协议(以下简称"协议")由您(个人或实体,以下简称" ...
- Day 1. Depressive Emotion Detection, Men Who Have Sex With Men, Social Media
Title: Depressive Emotion Detection and Behavior Analysis of Men Who Have Sex With Men via Social Me ...
- 由VMWorld2010想到的Social Media宣传
VMWorld2010会场归来,精彩的演讲.连轴转的采访和气势恢弘的展区仍然历历在目."管中窥豹,时见一斑",且将此行的一些所见所想记录下来,与各位分享. 抛开VMware发布的I ...
- 用css3实现Social Media Buttons
以前实现按钮一般都是用图片来实现的,特别是一些拥有质感的按钮,今天练习了一些相关方面的的例子,用css3来实现Social Media Buttons html代码如下 <div class=& ...
- 论文导读:Deep Attentive Learning for Stock Movement Prediction From Social Media Text and Company Correl
1. Introduction 股票走势受到多方面影响,没有了解相关信息的投资决策会面临金融风险以及金钱损失,而仔细考虑过的投资可以使收益增大.传统的方法依赖于时间序列,以及对股票的分析,比如利用历史 ...
- LOWKEY: LEVERAGING ADVERSARIAL ATTACKS TO PROTECT SOCIAL MEDIA USERS FROM FACIAL RECOGNITION
LOWKEY: LEVERAGING ADVERSARIAL ATTACKS TO PROTECT SOCIAL MEDIA USERS FROM FACIAL RECOGNITION LOWKEY: ...
- 【笔记】使用Twitter API V2进行数据爬取的经验总结
写在最前面:这篇笔记主要是基于自己使用API过程中遇到的问题以及不断的尝试形成的经验总结,所有内容都是一个字一个字敲的,所以还挺辛苦的.不过也正是因为这只是一些个人经验的归纳,所以对于API的函数和功 ...
最新文章
- KubeCon 北美前瞻|在 2020 最后,容器领域有哪些值得你关注的话题?
- 用代码,打造创意新世界!【Innovation 2021】网易应用创新开发者大赛正式开赛!
- Atitit截屏功能的设计解决方案
- 《零基础看得懂的C语言入门教程 》——(十)C语言的指针原来是这样
- Spring的核心模块解析
- eureka上的微服务不能通过服务名调用_掌门教育微服务体系 Solar | 阿里巴巴 Nacos 企业级落地上篇...
- Nginx作为web服务器的安装配置
- CentOS5.6系统中安装并使用USB无线网卡(配置成功) 转
- goolgle版本87.0乱码设置utf-8,附有charset插件
- 在所难免!我也阳了。。
- js如何判断闰年?整除的符号是什么?
- Linux性能分析工具总结
- 根据空间中不共面的四个点坐标,求构成任意四面体的内外球
- 使用神经网络实现葡萄酒数据集的分类分析
- 地面无人系统人机交互关键技术
- 国产电流传感器芯片CH701与ACS712的分析对比
- Polygon Cruncher(3D模型优化插件)v12.25版
- Java8 重复注解与类型注解
- ae导出gif插件_AE导出GIF动画的几种方式
- 高等几何——射影变换7
