Android音频架构
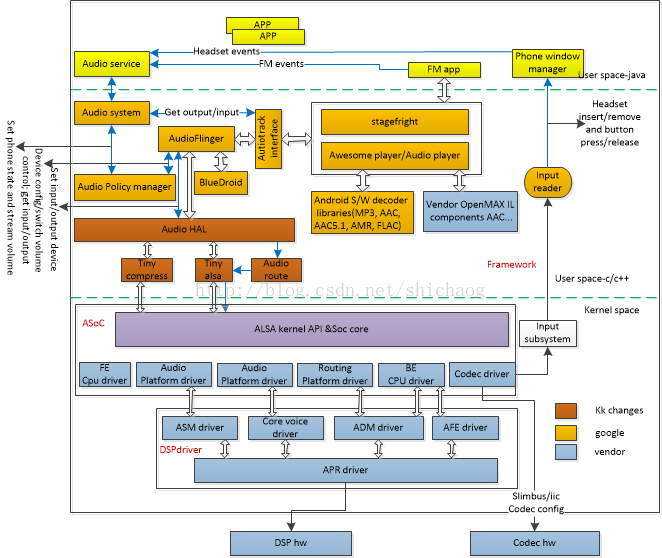 主要分为四个层次: 1.最底层是硬件层; 2.在这之上的是驱动层,这一层一般codec芯片会给一个基本的驱动示例; 3.在这之上是Linux的框架层,ALSA, 4.这之上是安卓audio管理层;
主要分为四个层次: 1.最底层是硬件层; 2.在这之上的是驱动层,这一层一般codec芯片会给一个基本的驱动示例; 3.在这之上是Linux的框架层,ALSA, 4.这之上是安卓audio管理层;
+
ALSA System on Chip(ASoC)
ASoC 驱动将一个audio子系统分成四个部分: Machine driver, Platform driver, CPU driver以及Codec driver。
Machine 驱动
- 将平台,CPU以及codec驱动绑定在一块
- 实现在kernel/sound/soc/msm/
- 定义前端FE和后端BE,DAI(digital audio interface) links
platform 驱动
- 包括了平台相关的音频数据流的传输和路由的控制
- 被区分成FE和BE两个平台驱动
FE
- Audio -例化PCM播放和采集,将播放的pcm数据从用户空间传递给DSP,采集是逆过程,高通使用ASM接口,实现于kernel/sound/soc/msm-pcm-q6.c
- Voice-初始化和销毁语音电话建立,实现与kernel/sound/soc/msm-pcm-voice-v2.c
- VoIP-初始化和销毁MVS接口在DSP和用户空间互传数据。kernel/sound/soc/msm-pcm-voip-v2.c
- Compress offload-Compress offload 播放数据传输到DSP。kernel/sound/soc/msm-compress-q6-v2.c
BE
- Routing-audio 通路选择,kernel/sound/soc/msm-pcm-routing-v2.c
CPU driver
分为FE和BE CPU驱动
FE
- 提供了ALSA SoC framework需要的FE PCM设备信息,由平台驱动提供的ASoC framework和音频路由表可以指示PCM 播放/采集。
- FE CPU DAI实现于kernel/sound/soc/msm/msm-dai-fe.c
BE
- 根据初始化的PCM播放和采集配置DSP AFE模块对应的audio 音频端口
- 定义了BE CPU DAI实现于kernel/sound/soc/msm/qdsp6v2/msm-dai-q6-v2.c
Framework层
- Audio Hardware Abstraction Layer(AHAL)-使用tinyalsa将AudioFlinger调用映射到ASOC驱动
- tinyalsa-kernel ASoC驱动接口,AHAL使用,提供了stream和设备管理需要的基本PCM和Mixer控制API
- Audio Route-该模块从XML文件读取ALSA mixer控制器,并根据AHAL设置mixer控制器。
- Multimedia framework -stageFright1)使用标准音频格式的播放和采集;2)和编解码库以及OpenMAX IL组件通信,实现音频编解码
- Audio service 1)运行时服务,由system server启动,service manager管理;2)注册intents,当接收到来自不同应用(HDMI,Bluetooth)的信息后通知Audio系统
- Audio Flinger 1)通过libaudio, 蓝牙A2DP管理所有音频输入/输出设备, 2)将多个audio stream合成单一PCM,混合的output输出源被路由给输出设备 3)music stream播放的音量控制
- Audio Policy Manager(APM) 1)定义了多个音频源并发的管理策略 2)设置场景(电话,音乐,系统音,通知) 3)定义了音频类型(语音,播放,ring)在何种设备上播放(Bluetooth, speaker, headset)
- APM的职责如下 1)管理各种输入/输出设备接口 2)管理各种输入/输出设备, mic/speaker/headphone/headset/A2DP以及Bluetooth SCO 3)基于stream模式选择和定义合适的路由策略 4)管理每一个stream的音量
Audio Output Stream and Volume Control
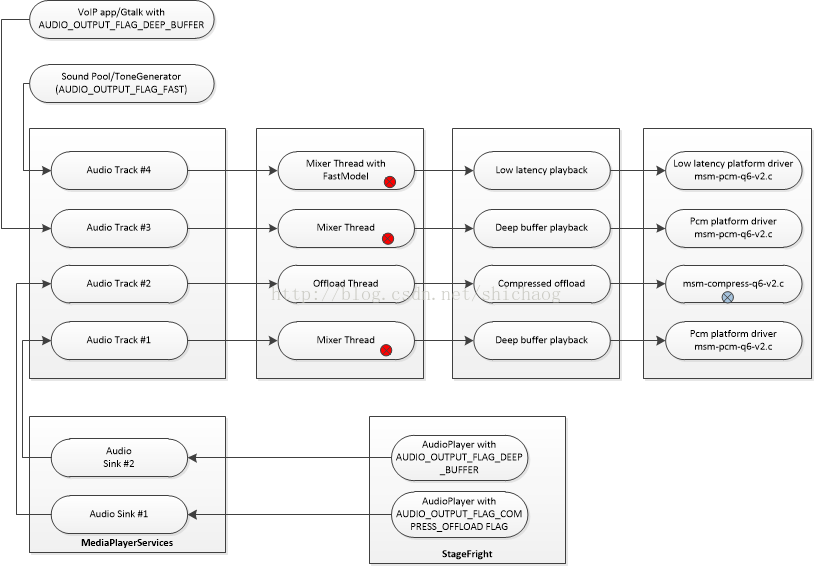
- 缺省的音频输出(primary output)使用AudioFlinger中的Mixer线程,音量和音效将在Flinger中使用
- Lowlatency输出使用AudioFlinger中的快速mixer,音量控制在Flinger中
- Compress offload播放使用Audio Flinger中的compress offload线程,音量和音效在DSP中。
- VoIP播放在AudioFlinger中的mixerThread,Volume和echo cancelation由DSP完成。
设备和流管理
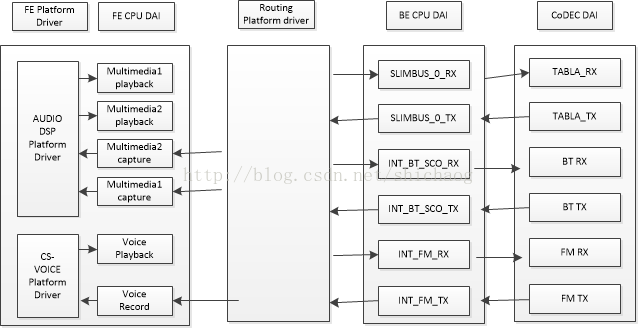
Frontend DAI
- 对用户空间作为PCM设备可见
- 可以将Audio路由到多个BE DAI
- Routing由用户空间mixer控制
- PCM由ALSA直接控制
- 定义与msm-dai-fe.c
static struct snd_soc_dai_driver msm_fe_dais[]={.playback = {.stream_name = "Multimedia1 Playback",.aif_name = "MM_DL1",.rates
...}}
当front DAI使能时,AIF将会被使能。
代码分布
用户空间和audio相关的代码
/hardware/qcom/audio/hal/msm8974 – Contains the audio Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)-related code
/external/tinyalsa/ – Contains the code related to tinymix, tinyplay, and tinycap
/hardware/qcom/audio/mm-audio – Contains the implementation of QTI OMX components for the audio encoder and decoders
/frameworks/av/media/libstagefright/ – Contains the source code for Google’s Stagefright implementation
/frameworks/av/media/libmediaplayerservice/nuplayer - Contains the source code for Google’s nuplayer implementation
/frameworks/av/services/audioflinger/ – Contains the source code for AudioFlinger that manages audio streams from the user space
/vendor/qcom/proprietary/mm-audio/ – Contains the code related to the Audio Calibration Database (ACDB) driver, parsers for DTS and AC3, surround sound, SVA, etc
/external/bluetooth/bluedroid/ – Contains the code related to Bluetooth® (BT) A2DP used in a QTI platform
/external/bluetooth/bluedroid/audio_a2dp_hw/ – Contains the A2DP audio HAL implementation
/hardware/libhardware/modules/usbaudio/ – Contains the USB HAL implementation for a USB dock use case
/hardware/qcom/audio/hal/audio_extn/:
audio_extn.c – Implements the wrapper function for audio extension features, such as FM, Dolby, Compress capture, HFP, SVA (listen), speaker protection, SSR, USB audio over headset
usb.c – Contains the HAL implementation for USB playback and record over the headset
compress_capture.c – Contains the HAL implementation for Compress capture
dolby.c – Contains the HAL implementation for the Dolby postprocessing feature
fm.c – Contains the HAL implementation for the FM playback and recording feature
hfp.c – Contains the HAL implementation for the hands-free profile feature where the MSM™ chipset can be used as as a BT headset device
listen.c – Contains the HAL implementation for the Snapdragon™ Voice Activation (SVA) feature
spkr_protection.c – Contains the HAL implementation for the speaker protection feature
ssr.c – Contains the HAL implementation for the surround sound recording feature/vendor/qcom/proprietary/wfd/mm/source/framework/src/ – Contains the Wi-Fi Display (WFD) frameworks-related code; WFDMMSourceAudioSource.cpp configures the RT Proxy port via ALSA APIs and gets the PCM data from the audio layer
/system/core/include/system/ – Contains audio.h and audio_policy.h that contain enum definitions and inline functions used all over the code for audio in the user space
/frameworks/base/media/java/android/media/ – Contains .java files for audio that expose APIs that can be called by Android™ applications written in Java
内核空间代码
<APSS_BUILD>/kernel/sound/soc/msm/ – Contains the msm8994.c machine driver
<APSS_BUILD>/kernel/sound/soc/msm/qdsp6v2 – Contains the source code for the platform drivers, Frontend (FE), and Backend (BE) DAI driver, QDSP drivers for AFE, ADM, and ASM, voice driver, etc.
<APSS_BUILD>/kernel/sound/soc/soc-*.c – All the soc-*.c files provide information on the ALSA SOC framework
<APSS_BUILD>/kernel/drivers/slimbus/ – Contains the source for the SLIMbus driver
<APSS_BUILD>/kernel/arch/arm/mach-msm/qdsp6v2/ – Contains the drivers for DSP-based encoders and decoders, code for the ADSP loader, APR driver, Ion memory driver, and other utility files
<APSS_BUILD>//LINUX/android/kernel/arch/arm/boot/dts – Contains msm8994-*.dtsi files that contain MSM8994-specific information;board-specific information on the MSM8994;GPIO management ; audio-related customization is available in files such as msm8994.dtsi, msm8994-mtp.dtsi, and msm8994-cdp.dtsi
<APSS_BUILD>/LINUX/android//kernel/sound/soc/codecs/ – Contains the source code for the codec driver for WCD9330; codec driver-related source files are wcd9330.c, wcd9xxx-mbhc.c, wcd9xxx-resmgr.c, wcd9xxx-common.c, etc.
<APSS_BUILD>//LINUX/android/kernel/drivers/mfd/ – Contains the source code for the codec driver; wcd9xxx-core.c, wcd9xxx-slimslave.c, and wcd9xxx-irq.c are the codec driver-related files
AudioFlinger
创建
./frameworks/av/media/mediaserver/main_mediaserver.cpp:47 int main(int argc __unused, char** argv)48 {
...135: AudioFlinger::instantiate();139 AudioPolicyService::instantiate();140 SoundTriggerHwService::instantiate();147 ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();148 IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}
该文件所在目录的Android.mk文件将其编译成一个可执行程序mediaserver,该程序在/system/bin/mediaserver。
59 LOCAL_MODULE:= mediaserver60 LOCAL_32_BIT_ONLY := true61 62 include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE)
同时在init.rc文件有如下内容:
724 service media /system/bin/mediaserver
725 class main
726 user media
727 group audio camera inet net_bt net_bt_admin net_bw_acct drmrpc mediadrm qcom_diag
728 ioprio rt 4
也就是将mediaserver执行,即执行其中的main函数。
AudioFlinger的静态初始化
```
class AudioFlinger :
public BinderService<AudioFlinger>,
public BnAudioFlinger
/frameworks/native/include/binder/BinderService.h
33template<typename SERVICE>
34class BinderService
35{
36public:
37 static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false) {
38 sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
39 return sm->addService(
40 String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()),
41 new SERVICE(), allowIsolated);
42 }
43
44 static void publishAndJoinThreadPool(bool allowIsolated = false) {
45 publish(allowIsolated);
46 joinThreadPool();
47 }
48
49 static void instantiate() { publish(); }//调用的是这里的instantiate
50
51 static status_t shutdown() { return NO_ERROR; }
52
instantiate时,首先将AudioFlinger作为一个服务添加到ServiceManager中,此间会调用AudioFl的构造函数。
AudioFlinger::AudioFlinger(): BnAudioFlinger(),mPrimaryHardwareDev(NULL),mAudioHwDevs(NULL),mHardwareStatus(AUDIO_HW_IDLE),mMasterVolume(1.0f),mMasterMute(false),mNextUniqueId(1),mMode(AUDIO_MODE_INVALID),mBtNrecIsOff(false),mIsLowRamDevice(true),mIsDeviceTypeKnown(false),mGlobalEffectEnableTime(0),mSystemReady(false)
{}
这个构造函数基本上就是对以上变量的初始化。其实际的工作放在了onFirstRef方法中完成了。 BnAudioFlinger类由虚基类RefBase层继承而来,并且IserviceManager::addService的第二个参数是个强指针引用,所以在AudioFlinger被引用时,onFirstRef将被调用。
void AudioFlinger::onFirstRef()
{int rc = 0;Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);/* TODO: move all this work into an Init() function */char val_str[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = { 0 };if (property_get("ro.audio.flinger_standbytime_ms", val_str, NULL) >= 0) {uint32_t int_val;if (1 == sscanf(val_str, "%u", &int_val)) {mStandbyTimeInNsecs = milliseconds(int_val);ALOGI("Using %u mSec as standby time.", int_val);} else {mStandbyTimeInNsecs = kDefaultStandbyTimeInNsecs;ALOGI("Using default %u mSec as standby time.",(uint32_t)(mStandbyTimeInNsecs / 1000000));}}mPatchPanel = new PatchPanel(this);mMode = AUDIO_MODE_NORMAL;
}
ro.audio.flinger_standbytime_ms属性给用户调节stand_by时间,接下来其它进程可以通过servicemanager来访问,并通过createtrack以及openOutput等接口来驱使Audioflinger为其服务。
AudioFlinger和HAL的交互
<AudioFlinger.cpp>
static const char * const audio_interfaces[] = {AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_PRIMARY,AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_A2DP,AUDIO_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID_USB,
};
#define ARRAY_SIZE(x) (sizeof((x))/sizeof(((x)[0])))
在编译的时候,这三种设备分别被编译成audio.primary.xxx.so,audio.a2dp.xxx.so的形式,xxx表示具体的硬件平台,AP会调用AF的函数AudioFlinger::loadHwModule完成对应SO的加载。
audio_module_handle_t AudioFlinger::loadHwModule(const char *name)
{if (name == NULL) {return 0;}if (!settingsAllowed()) {return 0;}Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);return loadHwModule_l(name);//调用loadHwModule_l完成功能
}
loadHwModule_l的实现如下:
audio_module_handle_t AudioFlinger::loadHwModule_l(const char *name)
{audio_hw_device_t *dev;//加载对应的so库文件,通过dlsym的形式打开so文件,加载路径/system/lib/hw或者/vendor/lib/hw//最终会调用audio_hw_hal.cpp里面的legacy_adev_open来挂载一些钩子函数, int rc = load_audio_interface(name, &dev); mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_INIT; rc = dev->init_check(dev); mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;
audio_module_handle_t handle = nextUniqueId();mAudioHwDevs.add(handle, new AudioHwDevice(handle, name, dev, flags)); //将设备添加到AF的键值对里
}
在打开so对应的音频库之后,最终调用HAL层的open函数。
static inline int audio_hw_device_open(const struct hw_module_t* module,struct audio_hw_device** device)
{return module->methods->open(module, AUDIO_HARDWARE_INTERFACE,(struct hw_device_t**)device);
}
open函数里会将若干需要的钩子函数添加到audio_hw_device_t表示的结构体里。
AudioFlinger在播放流程中的行为
status_t AudioFlinger::openOutput(audio_module_handle_t module,audio_io_handle_t *output,audio_config_t *config,audio_devices_t *devices,const String8& address,uint32_t *latencyMs,audio_output_flags_t flags)
{
//判断要打开的设备参数是否合法if (*devices == AUDIO_DEVICE_NONE) {return BAD_VALUE;}Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
//创建playback线程sp<PlaybackThread> thread = openOutput_l(module, output, config, *devices, address, flags);if (thread != 0) {*latencyMs = thread->latency();// notify client processes of the new output creationthread->ioConfigChanged(AUDIO_OUTPUT_OPENED);// the first primary output opened designates the primary hw deviceif ((mPrimaryHardwareDev == NULL) && (flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_PRIMARY)) {ALOGI("Using module %d has the primary audio interface", module);mPrimaryHardwareDev = thread->getOutput()->audioHwDev;AutoMutex lock(mHardwareLock);mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_SET_MODE;mPrimaryHardwareDev->hwDevice()->set_mode(mPrimaryHardwareDev->hwDevice(), mMode);mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;}return NO_ERROR;}return NO_INIT;
}
sp<AudioFlinger::PlaybackThread> AudioFlinger::openOutput_l(audio_module_handle_t module,audio_io_handle_t *output,audio_config_t *config,audio_devices_t devices,const String8& address,audio_output_flags_t flags)
{
//根据key-value找到相应的audio interfaceAudioHwDevice *outHwDev = findSuitableHwDev_l(module, devices);if (outHwDev == NULL) {return 0;}audio_hw_device_t *hwDevHal = outHwDev->hwDevice();if (*output == AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE) {*output = nextUniqueId();}mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_OUTPUT_OPEN;// FOR TESTING ONLY:// This if statement allows overriding the audio policy settings// and forcing a specific format or channel mask to the HAL/Sink device for testing.if (!(flags & (AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD | AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT))) {// Check only for Normal Mixing modeif (kEnableExtendedPrecision) {// Specify format (uncomment one below to choose)//config->format = AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_FLOAT;//config->format = AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_24_BIT_PACKED;//config->format = AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_32_BIT;//config->format = AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_8_24_BIT;// ALOGV("openOutput_l() upgrading format to %#08x", config->format);}if (kEnableExtendedChannels) {// Specify channel mask (uncomment one below to choose)//config->channel_mask = audio_channel_out_mask_from_count(4); // for USB 4ch//config->channel_mask = audio_channel_mask_from_representation_and_bits(// AUDIO_CHANNEL_REPRESENTATION_INDEX, (1 << 4) - 1); // another 4ch example}}AudioStreamOut *outputStream = NULL;status_t status = outHwDev->openOutputStream(&outputStream,*output,devices,flags,config,address.string());mHardwareStatus = AUDIO_HW_IDLE;if (status == NO_ERROR) {PlaybackThread *thread;if (flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_COMPRESS_OFFLOAD) {thread = new OffloadThread(this, outputStream, *output, devices, mSystemReady);ALOGV("openOutput_l() created offload output: ID %d thread %p", *output, thread);} else if ((flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT)|| !isValidPcmSinkFormat(config->format)|| !isValidPcmSinkChannelMask(config->channel_mask)) {thread = new DirectOutputThread(this, outputStream, *output, devices, mSystemReady);ALOGV("openOutput_l() created direct output: ID %d thread %p ", *output, thread);//Check if this is DirectPCM, if soif (flags & AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT_PCM) {thread->mIsDirectPcm = true;}} else {thread = new MixerThread(this, outputStream, *output, devices, mSystemReady);ALOGV("openOutput_l() created mixer output: ID %d thread %p", *output, thread);}mPlaybackThreads.add(*output, thread);return thread;}return 0;
}From
Android音频架构相关推荐
- Android 音频架构
Android 音频架构定义了音频功能的实现方式,并指出实现中所涉及的相关源代码. 应用框架 应用框架包含应用代码,该代码可使用 android.media API 与音频硬件进行交互.在内部,此代码 ...
- Android音频架构工程师开篇引言
Android音频架构师 目的 风格 受众 文章结构 更新进度 目的 写这样一个专栏的初衷,是因为本人在2019年上半年入职目前这家公司,最初入职的职位是驱动工程师,一开始从事的内容也都是驱动这一块的 ...
- Android音频架构概览
FROM:http://www.bobbog.com/archives/147 ============================ 一.架构图 二.MediaServer初始化 所有的media ...
- Android 音频(Audio)架构
一.概述 Android 的音频硬件抽象层 (HAL) 可将 android.media 中特定于音频的较高级别的框架 API 连接到底层音频驱动程序和硬件.本部分介绍了有关提升性能的实现说明和提示. ...
- Android P的音频架构(二)
Android P的音频策略分析 本文主要讲解AudioPolicy部分,对音频策略流程的分析,音频策略代码在frameworks\av\services\audiopolicy中. 相关定义: fr ...
- android 音频增益_参考级音频播放器!七彩虹发布Pocket HIFI U6:4999亲民价
作为国产HiFi音频的老牌厂商,七彩虹去年年中推出了新旗舰播放器Pocket HIFI U8,时隔一年U系旗下第二款参考级播放器又来了,型号为"Pocket HIFI U6",将于 ...
- Android系统架构图及简单的系统架构介绍
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> ndroid的系统架构和其操作系统一样,采用了分层的架构.从架构图看,android分为四个层,从高层到低层分别是应用程序层. ...
- Android系统架构基本模式解析
Android系统架构总共被分为四层,在这里大家就可以通过介绍对这四个层次进行一个深入的解读,以加深大家对这一系统的认识. 如今,大家面对市场中种类繁多的手机必然挑的眼花缭乱.不过,在智能手机占据主要 ...
- Android MediaRecorder架构详解
1. 简介 在android中录制音频有两种方式,MediaRecorder和AudioRecord.两者的区别如下: (1) MediaRecorder 简单方便,不需要理会中间录制过程,结束录制后 ...
最新文章
- 刚刚,生物学横扫诺贝尔3大奖,两名女性获奖!化学奖授予试管中的“进化论”...
- springmuvc如何设置jsp的input跳转_如何扩大私域流量?「上线了」跳转小程序来帮你...
- TCP/IP详解 笔记八
- 苹果挂端口方法_调音台变身直播声卡的方法
- 开发中常用到的通用 scss 模块
- python等比例压缩图片_python(PIL)图像处理(等比例压缩、裁剪压缩) 缩略(水印)图详解...
- 区块链教程Fabric1.0源代码分析configtx#genesis-兄弟连
- rk3399_android7.1音频通路相关说明
- MyEclipse中VSS的使用详解
- HttpClient 发送请求和参数
- ztree带有选项框的树形菜单使用
- 一阶惯性环节如何实现跟踪性能与滤波性能共存(三)
- 基于wincc的虚拟电梯设计_PLC基于WinCC的四层电梯监控系统设计+梯形图
- BIGEMAP如何将高程数据(等高线)转换成xi'an80或者beijing54坐标系
- 论傻瓜交换机接到有vlan的网管交换机为什么可以通信
- Steam Sdk接入
- 【包邮送书活动】20210928期-开奖通知
- OLLYDBG逆天 往事随风修改专版
- MRCP协议-提供语音识别(ASR)与语音合成服务(TTS)
- stack-es-标准篇-ElasticsearchClient-combined_fields
