绝缘子工作温度_在温度下工作
绝缘子工作温度
One of the hypotheses that the scientific community is working on is the option that the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus is less transmissible in the presence of a warm and humid climate, a possibility that could reduce the incidence of COVID-19 disease as the spring progresses, the summer months get closer and it becomes warmer. For the time being, this is only a hypothesis, since although there are preliminary studies that point in that direction, there is still not enough scientific evidence to say that the virus survives worse in heat and that the pandemic could be attenuated by the arrival of higher temperatures or a more humid climate.
科学界正在研究的一种假设是,在温暖潮湿的气候下,SARS-CoV-2冠状病毒的传播可能性较小,这种可能性可能会降低SpringSpringCOVID-19疾病的发病率进展,夏季越来越近,天气变得越来越暖和。 暂时,这只是一个假设,因为尽管有朝着这个方向进行的初步研究,但仍然没有足够的科学证据表明该病毒在高温下生存较差,并且流行病可能会随着流感的到来而减弱。更高的温度或更潮湿的气候。
Some respiratory viruses, such as influenza, are known to spread more during the cold-climate months, and the other known coronavirus generally survives worse in higher temperatures and greater humidity than in colder or drier environments. There are some reasons for the seasonality of viruses in temperate regions, but the information is still lacking as to whether this theory can be applied to the new coronavirus.
已知某些呼吸道病毒(例如流行性感冒)在寒冷气候月份传播更多,而另一种冠状病毒通常在较高温度和较高湿度下的生存能力较寒冷或干燥的环境差。 温带地区病毒的季节性存在某些原因,但仍缺乏有关该理论是否可以应用于新冠状病毒的信息。
数据概述: (Data Overview :)
The rising average temperature of Earth’s climate system, called global warming, is driving changes in rainfall patterns, extreme weather, arrival of seasons, and more. Collectively, global warming and its effects are known as climate change. While there have been prehistoric periods of global warming, observed changes since the mid-20th century have been unprecedented in rate and scale. So a dataset on the temperature of major cities of the world will help analyze the same. Also weather information is helpful for a lot of data science tasks like sales forecasting, logistics etc. The data is available for research and non-commercial purposes only.
地球气候系统的平均温度升高,称为全球变暖,正在推动降雨方式,极端天气,季节到来等等的变化。 总体而言,全球变暖及其影响被称为气候变化。 尽管有史前的全球变暖时期,但自20世纪中叶以来观察到的变化在速度和规模上都是空前的。 因此,有关世界主要城市温度的数据集将有助于对此进行分析。 此外,天气信息对于许多数据科学任务(例如销售预测,物流等)很有帮助。数据仅可用于研究和非商业目的。
执照 : (license :)
Content : Daily level average temperature values is present in city_temperature.csv file
内容:city_temperature.csv文件中存在每日平均温度水平值
致谢: (Acknowledgements :)
University of Dayton for making this dataset available in the first place!
代顿大学首先使该数据集可用!
The data contributor :
数据贡献者:
资料准备 (Data Preparing)
1.导入所需的库 (1. Importing the required libraries)
import pandas as pdimport numpy as npimport seaborn as snsimport matplotlib as mplimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# !pip install plotly# !pip install chart_studioimport plotly.tools as tlsimport plotly as pyimport plotly.graph_objs as gofrom plotly.offline import download_plotlyjs, init_notebook_mode, plot, iplotfrom chart_studio import plotly as pyfrom plotly.offline import iplot%matplotlib inline2.将数据加载到数据框中+浏览数据 (2. Loading the data into the data frame + Exploring The Data)
气象数据和来源的简要说明 (Brief description of weather data and sources)
This archive contains files of average daily temperatures for 157 U.S. and 167 international cities. Source data for these files are from the Global Summary of the Day (GSOD) database archived by the National Climatic Data Center (NCDC). The average daily temperatures posted on this site are computed from 24 hourly temperature readings in the Global Summary of the Day (GSOD) data.
该档案库包含美国157个和167个国际城市的平均每日温度文件。 这些文件的源数据来自国家气候数据中心(NCDC)存档的全球每日摘要(GSOD)数据库。 该站点上发布的平均每日温度是根据“每日全球摘要”(GSOD)数据中24小时的温度读数计算得出的。
The data fields in each file posted on this site are: month, day, year, average daily temperature (F). We use “-99” as a no-data flag when data are not available.
在此站点上发布的每个文件中的数据字段为:月,日,年,日平均温度(F)。 当数据不可用时,我们将“ -99”用作无数据标志。
! rm -f daily-temperature-of-major-cities.zip! rm -f city_temperature.csv! kaggle datasets download -d sudalairajkumar/daily-temperature-of-major-cities! unzip daily-temperature-of-major-cities.zipWarning: Your Kaggle API key is readable by other users on this system! To fix this, you can run 'chmod 600 /home/oscar/.kaggle/kaggle.json'Downloading daily-temperature-of-major-cities.zip to /home/oscar/Documentos/PYTHON/world_temperature100%|██████████████████████████████████████| 12.9M/12.9M [00:00<00:00, 15.5MB/s]100%|██████████████████████████████████████| 12.9M/12.9M [00:00<00:00, 22.8MB/s]Archive: daily-temperature-of-major-cities.zip inflating: city_temperature.csv2.将数据加载到数据框中+浏览数据 (2. Loading the data into the data frame + Exploring The Data)
df = pd.read_csv("city_temperature.csv", low_memory=False)df.head()
转换华氏到摄氏 (Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius)
def fahr_to_celsius(temp_fahr): """Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius Return Celsius conversion of input""" temp_celsius = (temp_fahr - 32) * 5 / 9 return temp_celsiusdf["AvgTemperature"] = round(fahr_to_celsius(df["AvgTemperature"]),2)df.head()
len(df.Country.unique())125# df.tail()#df.shape#df.info()3.删除重复的行 (3. Dropping the duplicate rows)
df = df.drop_duplicates()df.shape(2885612, 8)df.count()Region 2885612Country 2885612State 1436807City 2885612Month 2885612Day 2885612Year 2885612AvgTemperature 2885612dtype: int644.处理缺失或空值 (4. Dealing with the missing or null values)
check missing values (Nan) in every column
检查每列中的缺失值(Nan)
for col in df.columns: print("The " + col + " contains Nan" + ":" + str((df[col].isna().any())))The Region contains Nan:FalseThe Country contains Nan:FalseThe State contains Nan:TrueThe City contains Nan:FalseThe Month contains Nan:FalseThe Day contains Nan:FalseThe Year contains Nan:FalseThe AvgTemperature contains Nan:Falsecheck missing values (Zeros) in every column
检查每列中的缺失值(零)
for col in df.columns: # check missing values (Zeros) in every column print("The " + col + " contains 0" + ":" + str((df[col] == 0 ).any()))df = df[df.Day != 0]df.head()The Region contains 0:FalseThe Country contains 0:FalseThe State contains 0:FalseThe City contains 0:FalseThe Month contains 0:FalseThe Day contains 0:TrueThe Year contains 0:FalseThe AvgTemperature contains 0:True
df = df[(df.Year!=200) & (df.Year!=201)]# df.head()we don’t have missing values. Our data is ready
我们没有缺失的价值观。 我们的数据已经准备好
探索性数据分析:EDA (Exploratory Data Analysis : EDA)
1.各地区平均气温 (1. Average Temperture in every region)
Average_Temperture_in_every_region = df.groupby("Region")["AvgTemperature"].mean().sort_values()[-1::-1]Average_Temperture_in_every_region = Average_Temperture_in_every_region.rename({ "South/Central America & Carribean":"South America", "Australia/South Pacific":"Australia"})Average_Temperture_in_every_regionRegionMiddle East 20.213581Asia 16.982514South America 16.772604Australia 16.211585North America 12.926734Africa 12.012884Europe 8.273087Name: AvgTemperature, dtype: float64plt.figure(figsize = (12,8))plt.bar(Average_Temperture_in_every_region.index,Average_Temperture_in_every_region.values)plt.xticks(rotation = 10,size = 15)plt.yticks(size = 15)plt.ylabel("Average_Temperture",size = 15)plt.title("Average Temperture in every region",size = 20)plt.show()
2.每个地区平均温度随时间的增长 (2. Growth of the average Temperture in every region over time)
Change the index to date
将索引更改为日期
datetime_series = pd.to_datetime(df[['Year','Month', 'Day']])df['date'] = datetime_seriesdf = df.set_index('date')df = df.drop(["Month","Day","Year"],axis = 1)# df.head()region_year = ['Region', pd.Grouper(freq='Y')]df_region = df.groupby(region_year).mean()# df_region.head()plt.figure(figsize = (15,8))for region in df["Region"].unique(): plt.plot((df_region.loc[region]).index,df_region.loc[region]["AvgTemperature"],label = region) plt.legend()plt.title("Growth of the average Temperture in every region over time",size = 20)plt.xticks(size = 15)plt.yticks(size = 15)plt.show()
3.平均温度(地球)的增长 (3. Growth of the average Temperture (Earth))
df_earth = df.groupby([pd.Grouper(freq = "Y")]).mean()# df_earth.head()plt.figure(figsize = (12,8))plt.plot(df_earth.index,df_earth.values,marker ="o")plt.xticks(size =15)plt.ylabel("average Temperture",size = 15)plt.yticks(size =15)plt.title("Growth of the average Temperture (Earth)",size =20)plt.show()
3.世界上最热的城市 (3. The hotest Cities in The world)
top_10_hotest_Cities_in_The_world = df.groupby("City").mean().sort_values(by = "AvgTemperature")[-1:-11:-1]top_10_hotest_Cities_in_The_world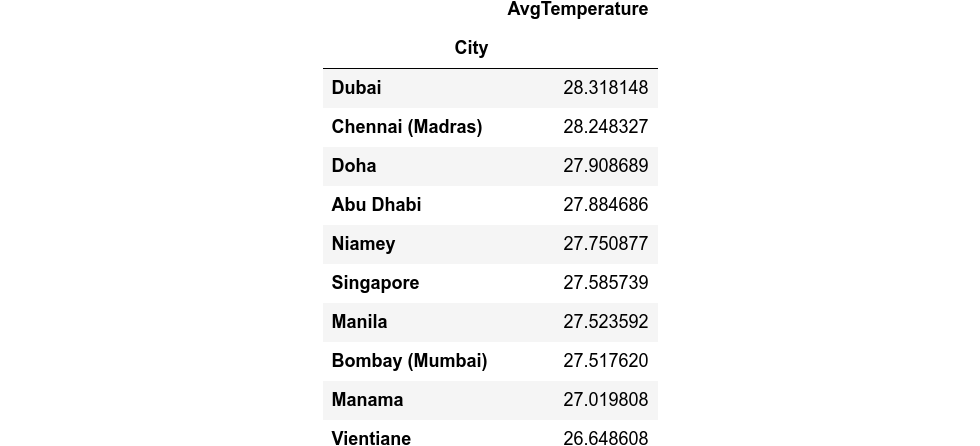
plt.figure(figsize = (12,8))plt.barh(top_10_hotest_Cities_in_The_world.index,top_10_hotest_Cities_in_The_world.AvgTemperature)<BarContainer object of 10 artists>
4.世界上最热的城市中温度的增长 (4. The Growth of the Temperture in the hotest Cities in The world)
city_year = ['City', pd.Grouper(freq='Y')]df_city = df.groupby(city_year).mean()# df_city.head()plt.figure(figsize = (12,8))for city in top_10_hotest_Cities_in_The_world.index: plt.plot(df_city.loc[city].index,df_city.loc[city].AvgTemperature,label = city)plt.legend()plt.yticks(size = 15)plt.xticks(size = 15)plt.ylabel("Average Temperature",size = 15)plt.title("The Growth of the Temperture in the hotest Cities in The world",size = 20)plt.show()
5.世界上最热的国家 (5. The hotest Countries in The world)
hotest_Countries_in_The_world = df.groupby("Country").mean().sort_values(by = "AvgTemperature")# hotest_Countries_in_The_world.tail()plt.figure(figsize = (12,8))plt.bar(hotest_Countries_in_The_world.index[-1:-33:-1],hotest_Countries_in_The_world.AvgTemperature[-1:-33:-1])plt.yticks(size = 15)plt.ylabel("Avgerage Temperature",size = 15)plt.xticks(rotation = 90,size = 12)plt.title("The hotest Countries in The world",size = 20)plt.show()
7.世界平均温度¶ (7. The Average Temperature around the world¶)
when using plotly we need codes of countries Data of Codes:
当使用密谋时,我们需要国家代码代码数据:
! rm -f wikipedia-iso-country-codes.csv ! rm -f countries-iso-codes.zip! kaggle datasets download -d juanumusic/countries-iso-codes! unzip countries-iso-codes.zipWarning: Your Kaggle API key is readable by other users on this system! To fix this, you can run 'chmod 600 /home/oscar/.kaggle/kaggle.json'Downloading countries-iso-codes.zip to /home/oscar/Documentos/PYTHON/world_temperature 0%| | 0.00/4.16k [00:00<?, ?B/s]100%|███████████████████████████████████████| 4.16k/4.16k [00:00<00:00, 879kB/s]Archive: countries-iso-codes.zip inflating: wikipedia-iso-country-codes.csvcode = pd.read_csv("wikipedia-iso-country-codes.csv") # this is for the county codescode= code.set_index("English short name lower case")# code.head()I changed some countries name in the code data frame so they become the same as our main data frame index
我在代码数据框中更改了一些国家/地区名称,因此它们与我们的主要数据框索引相同
This is important when merging the two data framescode = code.rename(index={"United States Of America": "US", "Côte d'Ivoire": "Ivory Coast", "Korea, Republic of (South Korea)": "South Korea", "Netherlands": "The Netherlands", "Syrian Arab Republic": "Syria", "Myanmar": "Myanmar (Burma)", "Korea, Democratic People's Republic of": "North Korea", "Macedonia, the former Yugoslav Republic of": "Macedonia", "Ecuador": "Equador", "Tanzania, United Republic of": "Tanzania", "Serbia": "Serbia-Montenegro"})# code.head()Now we do the merging between the code data frame and our data
现在,我们在代码数据框和我们的数据之间进行合并
hott = pd.merge(hotest_Countries_in_The_world,code,left_index = True , right_index = True , how = "left")hott.head()
data = [dict(type="choropleth", autocolorscale=False, locations=hott["Alpha-3 code"], z=hott["AvgTemperature"], text=hott.index, colorscale="reds", colorbar=dict(title="Temperture"))]layout = dict(title="The Average Temperature around the world", geo=dict(scope="world", projection=dict(type="equirectangular"), showlakes=True, lakecolor="rgb(66,165,245)",),)fig = dict(data = data,layout=layout)#iplot(fig,filename = "d3-choropleth-map")
8.全球12个月的平均温度变化 (8. Variation of the mean Temperature Over The 12 months around the world)
Variation_world = df.groupby(df.index.month).mean()Variation_world = Variation_world.rename(index={1: "January", 2: "February", 3: "March", 4: "April", 5: "May", 6: "June", 7: "July", 8: "August", 9: "September", 10: "October", 11: "November", 12: "December"})plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))sns.barplot(x=Variation_world.index, y= 'AvgTemperature',data=Variation_world,palette='Set2')plt.title('AVERAGE MEAN TEMPERATURE OF THE WORLD',size = 15)plt.xticks(size = 10)plt.yticks(size = 12)plt.xlabel("Month",size = 12)plt.ylabel("AVERAGE MEAN TEMPERATURE",size = 10)plt.show()
9.在世界上最热的国家/地区中,过去12个月的平均温度变化:阿拉伯联合酋长国 (9. Variation of the mean Temperature Over The 12 months in the hottest country in the world: United Arab Emirates)
Variation_UAE = df.loc[df["Country"] == "United Arab Emirates"].groupby( df.loc[df["Country"] == "United Arab Emirates"].index.month).mean()Variation_UAE = Variation_UAE.rename(index={1: "January", 2: "February", 3: "March", 4: "April", 5: "May", 6: "June", 7: "July", 8: "August", 9: "September", 10: "October", 11: "November", 12: "December"})plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))sns.barplot(x=Variation_UAE.index, y= 'AvgTemperature',data=Variation_UAE,palette='Set2')plt.title('Variation of the mean Temperature Over The 12 months in the United Arab Emirates',size = 20)plt.xticks(size = 10)plt.yticks(size = 12)plt.xlabel("Month",size = 12)plt.ylabel("AVERAGE MEAN TEMPERATURE",size = 12)plt.show()
10.每个区域几个月内的平均温度变化 (10. Variation of mean Temperature over the months for each region)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 18))i = 1 # this is for the subplotfor region in df.Region.unique(): # this for loop make it easy to visualize every region with less code region_data = df[df['Region'] == region] final_data = region_data.groupby(region_data.index.month).mean()[ 'AvgTemperature'].sort_values(ascending=False) final_data = pd.DataFrame(final_data) final_data = final_data.sort_index() final_data = final_data.rename(index={1: "January", 2: "February", 3: "March", 4: "April", 5: "May", 6: "June", 7: "July", 8: "August", 9: "September", 10: "October", 11: "November", 12: "December"}) plt.subplot(4, 2, i) sns.barplot(x=final_data.index, y='AvgTemperature', data=final_data, palette='Paired') plt.title(region, size=10) plt.xlabel(None) plt.xticks(rotation=90, size=9) plt.ylabel("Mean Temperature", size=11) i += 1
- The Average Temperature in Spain西班牙的平均温度
Average_Temperature_Spain = df.loc[df["Country"] == "Spain"].groupby("City").mean()Average_Temperature_Spain.head()
Average_Temperature_USA = df.loc[df["Country"] == "US"].groupby("State").mean().drop(["Additional Territories"], axis = 0)# Average_Temperature_USA.head()we need to add the code to this data for visualization
我们需要向该数据添加代码以进行可视化
! rm -f state-areas.csv! rm -f state-population.csv! rm -f state-abbrevs.csv! rm -f usstates-dataset.zip! kaggle datasets download -d giodev11/usstates-dataset! unzip usstates-dataset.zipWarning: Your Kaggle API key is readable by other users on this system! To fix this, you can run 'chmod 600 /home/oscar/.kaggle/kaggle.json'Downloading usstates-dataset.zip to /home/oscar/Documentos/PYTHON/world_temperature 0%| | 0.00/18.4k [00:00<?, ?B/s]100%|██████████████████████████████████████| 18.4k/18.4k [00:00<00:00, 2.38MB/s]Archive: usstates-dataset.zip inflating: state-abbrevs.csv inflating: state-areas.csv inflating: state-population.csvusa_codes = pd.read_csv('state-abbrevs.csv')# Duplicate columnsusa_codes['State'] = usa_codes['state']# Set new indexusa_codes =usa_codes.set_index("State")# Rename columnsusa_codes.rename(columns={'abbreviation': 'Code', 'state': 'State'}, inplace=True)Average_Temperature_USA = pd.merge(Average_Temperature_USA, usa_codes,how = "left",right_index = True,left_index = True)Average_Temperature_USA.head()
data_usa = [dict(type="choropleth", autocolorscale=False, locations=Average_Temperature_USA["Code"], z=Average_Temperature_USA["AvgTemperature"], locationmode="USA-states", text=Average_Temperature_USA.index, colorscale="reds", colorbar=dict(title="Temperture"))]layout_usa = dict(title="The Average Temperature in the USA states", geo=dict(scope="usa", projection=dict(type="albers usa"), showlakes=True, lakecolor="rgb(66,165,245)",),)fig_usa = dict(data = data_usa,layout=layout_usa)#iplot(fig_usa,filename = "d3-choropleth-map")
12,1995年至2020年美国平均气温 (12.Average Temperature in USA from 1995 to 2020)
Temperature_USA_year = df.loc[df["Country"] == "US"].groupby(pd.Grouper(freq = "Y")).mean()#Temperature_USA_year.head()plt.figure(figsize = (12,8))sns.barplot(x = Temperature_USA_year.index.year,y = "AvgTemperature",data = Temperature_USA_year)plt.yticks(size = 12)plt.xticks(size = 12,rotation = 90)plt.xlabel(None)plt.ylabel("Avgerage Temperature",size = 12)plt.title("Average Temperature in USA from 1995 to 2020",size = 15)plt.show()
结论 (Conclusion)
Displaying the data via plots can be an effective way to quickly present the data.
通过绘图显示数据是快速显示数据的有效方法。
I hope it will help you to develop your training.
我希望它能帮助您发展培训。
No matter what books or blogs or courses or videos one learns from, when it comes to implementation everything might look like “Out of Syllabus”
无论从中学到什么书,博客,课程或视频,到实施时,一切都可能看起来像“课程提纲”
Best way to learn is by doing!
最好的学习方法就是干!
Best way to learn is by teaching what you have learned!
最好的学习方法是教您所学的知识!
永不放弃! (Never give up!)
See you in Linkedin!
在Linkedin上见!
翻译自: https://medium.com/swlh/working-with-temperatures-6133baa35a7c
绝缘子工作温度
http://www.taodudu.cc/news/show-3106026.html
相关文章:
- signature=b5d482f98802c3bc661cc82639edaa27,Taro
- 中间件 | Redis - [数据类型 指令]
- Eclipse 10 hotest-keys
- python百度云盘搜索引擎_2016百度云网盘搜索引擎源码,附带Python爬虫+PHP网站+Xunsearch搜索引擎...
- 网盘搜索插件php源码,百度云网盘搜索引擎 PHP版 v1.0
- 校园网新闻搜索引擎
- 基于java的搜索引擎的设计与实现
- 搜索引擎的设计与实现
- 一文看懂-ElasticSearch全文搜索引擎
- ElasticSearch全文搜索引擎
- springboot+solr实现搜索引擎
- 《Spring Boot 实战派》--13.集成NoSQL数据库,实现Elasticsearch和Solr搜索引擎
- 【植物大战僵尸-3】种植物无CD
- 植物大战僵尸tv版显示无法连接服务器,打开植物大战僵尸提示网络异常或者连接不上...
- 植物大战僵尸2010年度版C语言修改阳光数
- Python实现植物大战僵尸
- 植物大战僵尸中文年度版
- 植物大战僵尸java 7723_植物大战僵尸BT版
- 植物大战僵尸2android最新版,手机植物大战僵尸2高清版下载官方-植物大战僵尸2高清版 安卓版v2.4.8-PC6手游网...
- 植物大战僵尸java版_植物大战僵尸:M8版 JAVA版下载
- 基于Java基础-面向对象实现植物大战僵尸简易版
- 植物大战僵尸java圣诞版,植物大战僵尸圣诞版-植物大战僵尸2圣诞节版v1.9.1 安卓版-腾牛安卓网...
- mac数据恢复easyrecovery mac版
- 如何恢复Linux中的误删文件
- 光盘修复问题大全
- 移动磁盘使用驱动器中的光盘之前需要格式化数据如何恢复
- 数据恢复技术揭秘
- 恢复服务器安装信息被破坏了,服务器存储瘫痪数据恢复成功案例-服务器数据恢复...
- EasyRecovery15数据恢复软件相关使用教程
- 5款光盘数据恢复软件帮你忙!
绝缘子工作温度_在温度下工作相关推荐
- 商用计算机低温工作,突破量子计算机瓶颈!超低温芯片能在接近绝对零度的温度下工作...
如何克服量子计算机运转时产生的超高热量仍是量子计算机研究当中的一大难题.日前,科学家开发出一种新型的低温计算机芯片,能够在接近绝对零度的理论温度极限下工作. 这种名为 Gooseberry 的低温系统 ...
- 饱和气压与温度的关系_不同温度下空气中饱和水分含量及饱和蒸汽压
不同温度下空气中饱和水分含量及饱和蒸汽压 温度℃ 饱和水分含量g/m3 饱和蒸汽压Pa 温度℃ 饱和水分含量g/m3 饱和蒸汽压Pa 40 50.91 7368.624 -12 1.81 217.38 ...
- 电磁波波长越短能量越强_在同一温度下波长越短的电磁波辐射强度越大
展开全部 这句e5a48de588b662616964757a686964616f31333262366364话显然是不对的,楼上的人都在说单个光子的能量,当然是波长越短越大.可是这里说的是辐射强度, ...
- 低温工作笔记本计算机,为什么极低温度下不宜使用笔记本电脑?
原标题:为什么极低温度下不宜使用笔记本电脑? 夏季高温对笔记本的危害很多人都知道,那么冬季的低温对笔记本电脑有什么影响呢? 低温对笔记本电脑的影响 首先,低温可能损伤笔记本电脑的电池.笔记本电池的最佳 ...
- 传感器工作原理_荧光氧气传感器工作原理简介
冷发光是一种电子激发的物质在激发时发出的紫外线(UV).可见光(Vis)和红外线(IR)光.而光的吸收和发射之间的过程通常用一个能量级图来说明,即雅布朗斯基图.下面工采网小编通过光学原理给大家说说荧光 ...
- 关于Excel下通过VBA实现工作簿文件下工作表的合并
对于普通使用者而言,Excel是一个比较强大的数据处理工具.一般公司的普通职员常使用它来完成数据的录入分析,但是当面对处理经由多人按统一模板统计完成的录入数据分析时,数据将分散存放在多个.xlsx文件 ...
- 二极管温度补偿电路工作原理分析
众所周知,PN结导通后有一个约为0.6V(指硅材料PN结)的压降,同时PN结还有一个与温度相关的特性:PN结导通后的压降基本不变,但不是不变,PN结两端的压降随温度升高而略有下降,温度愈高其下降的量愈 ...
- Qt Creator在编辑模式下工作
Qt Creator在编辑模式下工作 在编辑模式下工作 使用编辑器工具栏 在打开的文件和符号之间导航 选择解析上下文 更改文字编码 选择行尾样式 分割编辑器视图 使用书签 转到符号定义或声明 重新解析 ...
- 苹果 CEO 库克:我每天晚上 9 点半睡觉,凌晨 4 点起床,希望员工重返线下工作...
整理 | 王晓曼 出品 | 程序人生 (ID:coder _life) 3月18日,据外媒报道,苹果CEO蒂姆·库克热切希望员工在疫情爆发后重返办公室,在接受<人物>(People)杂志采 ...
最新文章
- 使用system语句出现不明确问题
- cmd启动tomcat
- Qt-QTableWidget设置只能选中一行
- 正交多项式族(勒让德多项式跟切比雪夫多项式)理论
- 中国节能减排行业十四五运行现状及建设应用价值分析报告2021-2027年
- 工具类用得好,下班下的早
- 20220207-CTF-MISC-第11题--- base64隐写--附带脚本
- 灵魂拷问!细数Android开发者的艰辛历程,成功入职阿里
- linux多线程编程之互斥锁
- PSP记录个人项目耗时情况
- 有赞 插入html,有赞 前端工程师面试题
- cadlisp点选面积标注_一个在CAD中标注坐标的LISP
- 基于wincc的虚拟电梯设计_基于WinCC的电梯PLC控制仿真.doc
- font标签的size属性
- c++系列:关于MSVCR100.dll、MSVCR100d.dll、Msvcp100.dll、Msvcp100D.dll 故障查及解决方法
- java gef_GefExample GEF的例子,用于eclipse 学习,非常好的源码材料。 Java Develop 238万源代码下载- www.pudn.com...
- 赣州旅游职业学校学计算机,赣州旅游职业学校是公办的吗
- args 打印输出argparse.ArgumentParser()的所有选项和默认值
- 谈谈你对 MVC 模式的理解?
- MISAG与MIMAG:基因组质量评估标准
