LTE上行链路反馈MCS(计算MCS、调制阶数、编码速率、频谱效率关系表格)
计算MCS、调制阶数、编码速率、频谱效率关系表格
参考网址:http://4g-lte-world.blogspot.tw/2012/12/transport-block-size-code-rate-protocol.html
参考网址:http://blog.richliu.com/2013/10/22/1545/
(1)前提:

因此,efficiency可简化为下式:

TBS=传输块的大小(表7.1.7.2.1-1)
CRC=附加的用于检错的比特数量=24
RE=分给PDSCH或PUSCH信道的Resource elaments数量(认为全部RE中,有90%用于共享信道)
Bits per RE=调制阶数
(2)举例
若eNB根据CQI分配该PUSCH传输的配置为:MCS index=20,2个RB。则有:
1)表7.1.7.1-1,TBS index=18
2)表7.1.7.2.1-1 计算TBS(传输块大小,单位bits)

3)计算code rate

Bits per RE=调制阶数=(MCS index=20)6阶=6

4)计算efficiency

(3)
计算RB数=12时,MCS
对应表
|
MCS index |
modulation |
code rate×1024 |
efficiency |
|
0 |
QPSK |
99.329806 |
0.194003527 |
|
1 |
QPSK |
126.4197531 |
0.24691358 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
153.5097002 |
0.299823633 |
|
3 |
QPSK |
198.659612 |
0.388007055 |
|
4 |
QPSK |
243.8095238 |
0.476190476 |
|
5 |
QPSK |
297.989418 |
0.582010582 |
|
6 |
QPSK |
352.1693122 |
0.687830688 |
|
7 |
QPSK |
424.4091711 |
0.828924162 |
|
8 |
QPSK |
478.5890653 |
0.934744268 |
|
9 |
QPSK |
532.7689594 |
1.040564374 |
|
10 |
16QAM |
266.3844797 |
1.040564374 |
|
11 |
16QAM |
297.989418 |
1.164021164 |
|
12 |
16QAM |
343.1393298 |
1.340388007 |
|
13 |
16QAM |
388.2892416 |
1.51675485 |
|
14 |
16QAM |
442.4691358 |
1.728395062 |
|
15 |
16QAM |
496.64903 |
1.940035273 |
|
16 |
16QAM |
514.7089947 |
2.010582011 |
|
17 |
64QAM |
343.1393298 |
2.010582011 |
|
18 |
64QAM |
367.2192828 |
2.151675485 |
|
19 |
64QAM |
415.3791887 |
2.433862434 |
|
20 |
64QAM |
451.4991182 |
2.645502646 |
|
21 |
64QAM |
487.6190476 |
2.857142857 |
|
22 |
64QAM |
523.7389771 |
3.068783069 |
|
23 |
64QAM |
565.8788948 |
3.315696649 |
|
24 |
64QAM |
609.5238095 |
3.571428571 |
|
25 |
64QAM |
657.6837155 |
3.85361552 |
|
26 |
64QAM |
681.7636684 |
3.994708995 |
|
27 |
64QAM |
705.8436214 |
4.135802469 |
|
28 |
64QAM |
826.2433862 |
4.841269841 |
参考文章附于此处
(1)CQI and MCS
LTE UE 會使用 CQI (Channel Quality Indicator) 動態調整 MCS 以降低傳輸錯誤率.
UE 測量 PRB (Physical Resource Block)的接收功率和干擾得到 SINR 值, 在 BLER 值不超過 10%. 將測量值轉換成 CQI. eNodeB 會根據 CQI 值選擇最合適的 MCS.
CQI 報告是由 eNodeB 主動發起, 可以是定時或是不定時.
不同的 CQI Index 有不同的 Code Rate.
如下表
|
CQI |
Modulation |
Bits/Symbol |
REs/PRB |
N_RB |
MCS |
TBS |
Code Rate |
|
1 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
0 |
536 |
0.101449 |
|
2 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
0 |
536 |
0.101449 |
|
3 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
2 |
872 |
0.162319 |
|
4 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
5 |
1736 |
0.318841 |
|
5 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
7 |
2417 |
0.442210 |
|
6 |
QPSK |
2 |
138 |
20 |
9 |
3112 |
0.568116 |
|
7 |
16QAM |
4 |
138 |
20 |
12 |
4008 |
0.365217 |
|
8 |
16QAM |
4 |
138 |
20 |
14 |
5160 |
0.469565 |
|
9 |
16QAM |
4 |
138 |
20 |
16 |
6200 |
0.563768 |
|
10 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
20 |
7992 |
0.484058 |
|
11 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
23 |
9912 |
0.600000 |
|
12 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
25 |
11448 |
0.692754 |
|
13 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
27 |
12576 |
0.760870 |
|
14 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
28 |
14688 |
0.888406 |
|
15 |
64QAM |
6 |
138 |
20 |
28 |
14688 |
0.88840 |
MCS
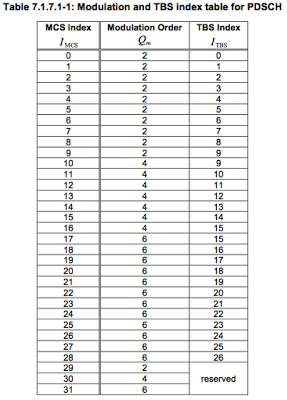
Table 7.1.7.1-1: Modulation and TBS index table for PDSCH
| MCS Index | Modulation Order | TBS Index |
| 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 |
| 6 | 2 | 6 |
| 7 | 2 | 7 |
| 8 | 2 | 8 |
| 9 | 2 | 9 |
| 10 | 4 | 9 |
| 11 |
4 |
10 |
| 12 | 4 | 11 |
| 13 | 4 | 12 |
| 14 | 4 | 13 |
| 15 | 4 | 14 |
| 16 | 4 | 15 |
| 17 | 6 | 15 |
| 18 | 6 | 16 |
| 19 | 6 | 17 |
| 20 | 6 | 18 |
| 21 | 6 | 19 |
| 22 | 6 | 20 |
| 23 | 6 | 21 |
| 24 | 6 | 22 |
| 25 | 6 | 23 |
| 26 | 6 | 24 |
| 27 | 6 | 25 |
| 28 | 6 | 26 |
| 29 | 2 | reserved |
| 30 | 4 | |
| 31 | 6 |
TBS Index (部份)
Table 7.1.7.2.1-1: Transport block size table (dimension 27×110)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
|
0 |
16 |
32 |
56 |
88 |
120 |
152 |
176 |
208 |
224 |
256 |
|
1 |
24 |
56 |
88 |
144 |
176 |
208 |
224 |
256 |
328 |
344 |
|
2 |
32 |
72 |
144 |
176 |
208 |
256 |
296 |
328 |
376 |
424 |
|
3 |
40 |
104 |
176 |
208 |
256 |
328 |
392 |
440 |
504 |
568 |
|
4 |
56 |
120 |
208 |
256 |
328 |
408 |
488 |
552 |
632 |
696 |
|
5 |
72 |
144 |
224 |
328 |
424 |
504 |
600 |
680 |
776 |
872 |
|
6 |
328 |
176 |
256 |
392 |
504 |
600 |
712 |
808 |
936 |
1032 |
|
7 |
104 |
224 |
328 |
472 |
584 |
712 |
840 |
968 |
1096 |
1224 |
|
8 |
120 |
256 |
392 |
536 |
680 |
808 |
968 |
1096 |
1256 |
1384 |
|
9 |
136 |
296 |
456 |
616 |
776 |
936 |
1096 |
1256 |
1416 |
1544 |
|
10 |
144 |
328 |
504 |
680 |
872 |
1032 |
1224 |
1384 |
1544 |
1736 |
|
11 |
176 |
376 |
584 |
776 |
1000 |
1192 |
1384 |
1608 |
1800 |
2024 |
|
12 |
208 |
440 |
680 |
904 |
1128 |
1352 |
1608 |
1800 |
2024 |
2280 |
|
13 |
224 |
488 |
744 |
1000 |
1256 |
1544 |
1800 |
2024 |
2280 |
2536 |
|
14 |
256 |
552 |
840 |
1128 |
1416 |
1736 |
1992 |
2280 |
2600 |
2856 |
|
15 |
280 |
600 |
904 |
1224 |
1544 |
1800 |
2152 |
2472 |
2728 |
3112 |
|
16 |
328 |
632 |
968 |
1288 |
1608 |
1928 |
2280 |
2600 |
2984 |
3240 |
|
17 |
336 |
696 |
1064 |
1416 |
1800 |
2152 |
2536 |
2856 |
3240 |
3624 |
|
18 |
376 |
776 |
1160 |
1544 |
1992 |
2344 |
2792 |
3112 |
3624 |
4008 |
|
19 |
408 |
840 |
1288 |
1736 |
2152 |
2600 |
2984 |
3496 |
3880 |
4264 |
|
20 |
440 |
904 |
1384 |
1864 |
2344 |
2792 |
3240 |
3752 |
4136 |
4584 |
|
21 |
488 |
1000 |
1480 |
1992 |
2472 |
2984 |
3496 |
4008 |
4584 |
4968 |
|
22 |
520 |
1064 |
1608 |
2152 |
2664 |
3240 |
3752 |
4264 |
4776 |
5352 |
|
23 |
552 |
1128 |
1736 |
2280 |
2856 |
3496 |
4008 |
4584 |
5160 |
5736 |
|
24 |
584 |
1192 |
1800 |
2408 |
2984 |
3624 |
4264 |
4968 |
5544 |
5992 |
|
25 |
616 |
1256 |
1864 |
2536 |
3112 |
3752 |
4392 |
5160 |
5736 |
6200 |
|
26 |
712 |
1480 |
2216 |
2984 |
3752 |
4392 |
5160 |
5992 |
6712 |
7480 |
依公式
Transport block size is 776 bits for ITBS = 18 and NPRB=2
code rate = (TBS + CRC) / (RE x Bits per RE)
code rate = (776 + 24) / (302 * 6 ) = 0.4
詳情請見
http://4g-lte-world.blogspot.tw/2012/12/transport-block-size-code-rate-protocol.html
以下引用自書LTE 關鍵技術與無線性能
覺得整理的還不錯




Ref.
3GPP 36.213 : 最主要的 Document.
http://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_CQI.html
(2)Transport Block Size and Code rate
Since the size of transport block is not fixed, often a question comes to mind as to how transport block size is calculated in LTE.
Back Ground
If we only consider "Uplink direction" and we assume that the UE is already attached to the network, then data is first received by PDCP (Packet data compression protocol) layer. This layer performs compression and ciphering / integrity if applicable. This layer will pass on the data to the next layer i.e. RLC Layer which will concatenate it to one RLC PDU.
RLC layer will concatenate or segment the data coming from PDCP layer into correct block size and forward it to the MAC layer with its own header. Now MAC layer selects the modulation and coding scheme configures the physical layer. The data is now in the shape of transport block size and needed to be transmitted in 1ms subframe.
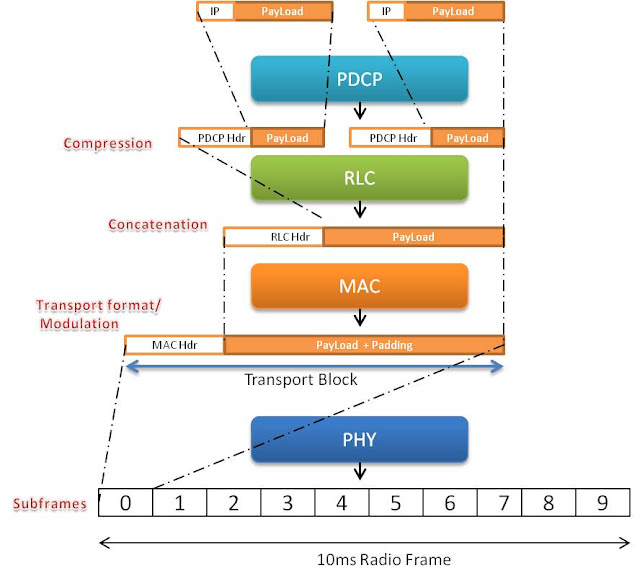
Transport Block size

Now from the Table 7.1.7.2.1-1 the value of Transport block size is 776 bits for ITBS = 18 and NPRB=
Code Rate
In simple words, code rate can be defined as how effectively data can be transmitted in 1ms transport block or in other words, it is the ratio of actual amount of bits transmitted to the maximum amount of bits that could be transmitted in one transport block
code rate = (TBS + CRC) / (RE x Bits per RE)
where
TBS = Transport block size as we calculated from Table 7.1.7.2.1-1
CRC = Cyclic redundancy check i.e. Number of bits appended for error detection
RE = Resource elements assigned to PDSCH or PUSCH
Bits per RE = Modulation scheme used
While we know the values of TBS, CRC and bits per RE (modulation order), it is not easy to calculate the exact amount of RE used for PDSCH or PUSCH since some of the REs are also used by control channels like PDCCH, PHICH etc
In our case, lets assume that 10% of RE's are assigned for control channels then
TBS = 776
CRC = 24
RE = 2 (RB) x 12 (subcarriers) x 7 (assuming 7 ofdm symbols) x 2 (slots per subframe) x 0.9 (10% assumption as above) = 302 REs
Bits per RE = 6 (Modulation order from table 7.1.7.1-1)
So
code rate = (776 + 24) / (302 * 6 ) = 0.4
LTE上行链路反馈MCS(计算MCS、调制阶数、编码速率、频谱效率关系表格)相关推荐
- LTE QPSK 16QAM星座图、调制符号与bit序列映射关系
1. 星座图 在MATLAB中,constellation是一个系统对象,调用constellation可以计算和画出星座图. 语法: out = constellation(input); 返回星座 ...
- 程序阅读_全面详解LTE:MATLAB建模仿真与实现_自学笔记(1)调制与编码_程序阅读
程序阅读_全面详解LTE:MATLAB建模仿真与实现_自学笔记(1)调制与编码_程序阅读 在粗浅地掌握了LTE知识后,从今天开始对<全面详解LTE:MATLAB建模仿真与实现>一书的学习. ...
- matlab实现子载波分配,一种lte上行链路分步式动态子载波分配方法
一种lte上行链路分步式动态子载波分配方法 [技术领域] [0001] 本发明涉及移动通信技术资源分配领域,尤其是一种LTE上行链路动态子载波分 配方法. [背景技术] [0002] 目前LTE作为最 ...
- 4ask调制与解调的matlab_LTE中的调制和编码
LTE的调制方式 LTE中使用的调制方式包括QPSK.16QAM记忆64QAM.QPSK需要2bits数据来编码4中不同的调制符号:16QAM使用4bits二进制信号来编码16中不同的调制符号:64Q ...
- C++实现设计一个圆形类(Circle),和一个点类(Point), 计算并判断点和圆的位置关系
题目要求 设计一个圆形类(Circle),和一个点类(Point), 计算并判断点和圆的位置关系. 无分区版 : #include <iostream> using namespace s ...
- VOS中开启媒体转发功能后,计算几种常用编码所需占用的带宽量
VOS中开启媒体转发功能后,计算几种常用编码所需占用的带宽量 计算方法如下: 带宽 = 包长度 × 每秒包数 = 包长度 × (1 / 打包周期) =(Ethernet 头 + IP 头 + UDP ...
- 计算共表达蛋白编码基因
题目回顾 计算与差异表达lncRNA共表达的蛋白编码基因(同时用斯皮尔曼相关及皮尔森相关),比较两种方法得到的显著共表达蛋白编码基因列表的差异. 在计算共表达蛋白编码基因之前,我们已经得到了差异表达的 ...
- LTE上行链路学习笔记(1)
物理信道 LTE的上行物理信道对应于一组资源单元的集合,用于承载源自高层的消息.规范定义了如下的上行信道: 物理上行共享信道:PUSCH 物理上行控制信道:PUCCH 物理随机接入信道:PARCH 物 ...
- 无线通信——调制与编码
基础概念 载波:是一个特定频率的无线电波,载波需要被调制才能传输有效信号,如433M,900M,2.4G,5G等指的就是载波的频率 码片:一个载波周期对应一个码片,码片速率即为载波频率 符号(Symb ...
最新文章
- Spring Hibernate使用TransactionInterceptor声明式事务配置
- echarts的词云图表类型有哪些_数据可视化之常见12种图表类型分析
- 一步一步写算法(之 A*算法)
- 洛谷——P1317 低洼地
- XP-在恢复时返回到欢迎屏幕
- 计算机毕业设计ssm校园办公管理系统
- (2.1)【经典木马-冰河木马】详细介绍,原理、使用方法
- C++/Qt获取屏幕尺寸和放大比例
- matlab中一个显示根号的技巧
- 【PS功能学习】10:蒙版带你领略台前幕后的故事
- linux脚本while死循环,shell编程之while死循环
- Compile、Make和Build的区别
- 微软的现实困难:产品需要再次变“酷”
- 简单几行代码带你爬取王者荣耀皮肤
- 火狐浏览器打开发现是2345的网站-----解决方法
- 转区系统开放艾欧尼亚转入服务器,【英雄联盟】转区系统开放艾欧尼亚转入服务...
- Android图片加载框架 Glide 4 的用法
- wireshark数据包流量分析
- 在服务器系统Windows 2003安装Avira AntiVir小红伞免费个人版
- MAC visio的替代品Omnigraffle+激活许可证
