Android6.0源码解读之ViewGroup点击事件分发机制
本篇博文是Android点击事件分发机制系列博文的第三篇,主要是从解读ViewGroup类的源码入手,根据源码理清ViewGroup点击事件分发原理,明白ViewGroup和View点击事件分发的关系,并掌握ViewGroup点击事件分法机制。特别声明的是,本源码解读是基于最新的Android6.0版本。
各位童鞋可以参考下面链接进行系统学习
(一)Android6.0触摸事件分发机制解读
(二)Android6.0源码解读之View点击事件分发机制
(三)Android6.0源码解读之ViewGroup点击事件分发机制
(四)Android6.0源码解读之Activity点击事件分发机制
ViewGroup事件分发中的三个重要方法的源码解析
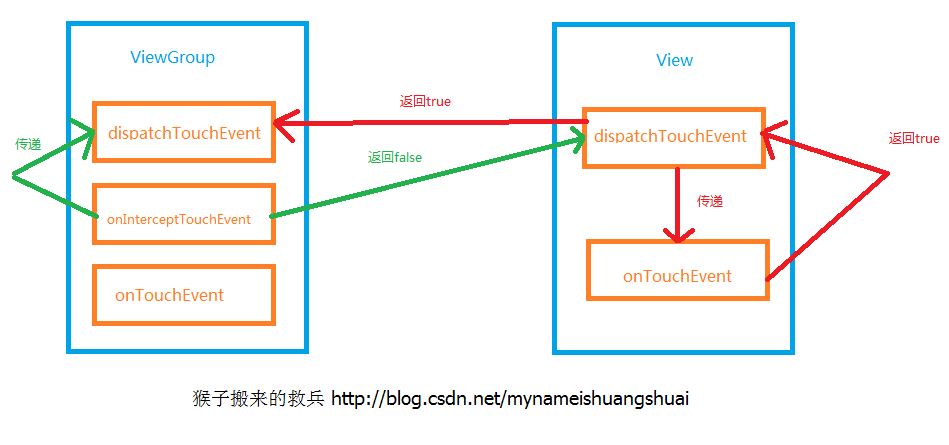
关于ViewGroup事件分发,我们重点需要解读dispatchTouchEvent、onInterceptTouchEvent和onTouchEvent三个方法。ViewGroup比View多了一个onInterceptTouchEvent拦截事件方法,该方法源码默认返回false,即ViewGroup默认不拦截任何事件。
(一)dispatchTouchEvent源码解析
/** * 重写了父类View的dispatchTouchEvent方法 */@Overridepublic boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(ev, 1);}// If the event targets the accessibility focused view and this is it, start// normal event dispatch. Maybe a descendant is what will handle the click.if (ev.isTargetAccessibilityFocus() && isAccessibilityFocusedViewOrHost()) {ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);}boolean handled = false;// 是否处理if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(ev)) {final int action = ev.getAction();final int actionMasked = action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK;// 手指按下去进行一些初始化的处理if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {// 当开启了一个新的手势触摸时,我要先去重置之前的状态// Throw away all previous state when starting a new touch gesture.// The framework may have dropped the up or cancel event for the previous gesture// due to an app switch, ANR, or some other state change.cancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev);// 取消、清理resetTouchState();// 重置}// Check for interception.final boolean intercepted;// 是否被拦截// 如果事件类型ACTION_DOWN或者mFirstTouchTarget不为空if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;if (!disallowIntercept) {// 当disallowIntercept为false时intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);// 这里是重点,它会调用onInterceptTouchEvent方法,当该方法为true时拦截,为false时不拦截// 所谓的拦截,是指按下去自身以及以后的后续事件move up,拦截下来给自己onTouch使用ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed} else {intercepted = false;}} else {// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down// so this view group continues to intercept touches.intercepted = true;}// If intercepted, start normal event dispatch. Also if there is already// a view that is handling the gesture, do normal event dispatch.if (intercepted || mFirstTouchTarget != null) {ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);}// Check for cancelation.final boolean canceled = resetCancelNextUpFlag(this)|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL;// Update list of touch targets for pointer down, if needed.final boolean split = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_SPLIT_MOTION_EVENTS) != 0;TouchTarget newTouchTarget = null;boolean alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = false;if (!canceled && !intercepted) {// 这里的canceled和intercepted都为false时,条件成立,也就是说不拦截// If the event is targeting accessiiblity focus we give it to the// view that has accessibility focus and if it does not handle it// we clear the flag and dispatch the event to all children as usual.// We are looking up the accessibility focused host to avoid keeping// state since these events are very rare.View childWithAccessibilityFocus = ev.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()? findChildWithAccessibilityFocus() : null;if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {// 按下去或多指触摸或者移动划过final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex(); // always 0 for downfinal int idBitsToAssign = split ? 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex): TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS;// Clean up earlier touch targets for this pointer id in case they// have become out of sync.removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToAssign);final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {// 如果子控件的个数不为0 且 newTouchTarget为空final float x = ev.getX(actionIndex);final float y = ev.getY(actionIndex);// Find a child that can receive the event.// Scan children from front to back.// 考虑到两个View交叉重合的情况,下面的先放进集合,但是按常理说我们手指先按到上面的,这里做了一个倒序final ArrayList<View> preorderedList = buildOrderedChildList();final boolean customOrder = preorderedList == null&& isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();final View[] children = mChildren;for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {// 遍历ViewGroup中的子控件final int childIndex = customOrder? getChildDrawingOrder(childrenCount, i) : i;// 得到子控件绘画的顺序final View child = (preorderedList == null)? children[childIndex] : preorderedList.get(childIndex);// If there is a view that has accessibility focus we want it// to get the event first and if not handled we will perform a// normal dispatch. We may do a double iteration but this is// safer given the timeframe.if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != null) {if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != child) {continue;}childWithAccessibilityFocus = null;i = childrenCount - 1;}if (!canViewReceivePointerEvents(child)|| !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) {ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);continue;}newTouchTarget = getTouchTarget(child);if (newTouchTarget != null) {// Child is already receiving touch within its bounds.// Give it the new pointer in addition to the ones it is handling.newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;break;}resetCancelNextUpFlag(child);// 判断是否有子控件,如果没有就不会执行里面的操作,如果有子控件则执行内部的操作if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {// Child wants to receive touch within its bounds.mLastTouchDownTime = ev.getDownTime();if (preorderedList != null) {// childIndex points into presorted list, find original indexfor (int j = 0; j < childrenCount; j++) {if (children[childIndex] == mChildren[j]) {mLastTouchDownIndex = j;break;}}} else {mLastTouchDownIndex = childIndex;}mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX();// 拿到X、Y位置mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY();// newTouchTarget用到了单向链表newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);// 找到最终触摸的对象alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;// 已经分发给一个新触摸的对象break;}// The accessibility focus didn't handle the event, so clear// the flag and do a normal dispatch to all children.ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);}if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear();}if (newTouchTarget == null && mFirstTouchTarget != null) {// 如果newTouchTarge为空 且 mFirstTouchTarget不为空// Did not find a child to receive the event.// Assign the pointer to the least recently added target.newTouchTarget = mFirstTouchTarget;while (newTouchTarget.next != null) {newTouchTarget = newTouchTarget.next;}newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;}}}// Dispatch to touch targets.分发给touch targetsif (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {// 没有触摸的对象就把它当做一个普通的View// No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view.handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);// 第三个参数本应为child,这里是null意味着需要调用父类View的dispatchTouchEvent方法,然后调用onTouch方法} else {// 找到最终消费事件的对象// Dispatch to touch targets, excluding the new touch target if we already// dispatched to it. Cancel touch targets if necessary.TouchTarget predecessor = null;TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;while (target != null) {final TouchTarget next = target.next;if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) {handled = true;// 找到了} else {final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child)|| intercepted;if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild,target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) {handled = true;}if (cancelChild) {if (predecessor == null) {// 为空mFirstTouchTarget = next;// 里面没有子控件} else {predecessor.next = next;// 里面有子控件,后面需要消耗此事件}target.recycle();target = next;continue;}}predecessor = target;target = next;}}// Update list of touch targets for pointer up or cancel, if needed.if (canceled|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {resetTouchState();} else if (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP) {final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex();final int idBitsToRemove = 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex);removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToRemove);}}if (!handled && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(ev, 1);}return handled;}ViewGroup拦截情况源码分析
首先我们来看一下第34行~48行的代码,ViewGroup在如下两种情况下会判断是否要拦截当前事件:
事件类型为ACTION_DOWN或者 mFirstTouchTarget != null
即,当事件由ViewGroup的子元素成功处理时,mFirstTouchTarget 会被赋值并指向子元素,换句话说,当ViewGroup不拦截事件并将事件交由子元素处理时mFirstTouchTarget != null。反过来,一旦事件由当前的ViewGroup拦截时,mFirstTouchTarget != null条件就不成立。那么当ACTION_MOVE和UP事件到来时,由于actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN || mFirstTouchTarget != null这个条件为false,导致ViewGroup的onInterceptTouchEvent不会再被调用,并且同一序列中的其他事件都会默认交给它处理。
另外,这里有一种特殊情况,我们看36行代码,有个FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT标记为,这个标记是通过requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent()方法来设置的,一般用在子View中。如果我们通过reqeustDisallowInterceptTouchEvent()方法设置了FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT标记位后,ViewGroup将无法拦截除了ACTION_DOWN以外的其他方法(即调用该方法并不影响ACTION_DOWN事件处理)。因为ViewGroup会在ACTION_DWON事件到来时做重置状态操作,这里从代码第22~29行可以看出。
requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent源码解析
/** * {@inheritDoc} */public void requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(boolean disallowIntercept) {if (disallowIntercept == ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0)) {// We're already in this state, assume our ancestors are tooreturn;}if (disallowIntercept) {mGroupFlags |= FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;} else {mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;}// Pass it up to our parentif (mParent != null) {mParent.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(disallowIntercept);}}取消、清理、重置之前的触摸状态
/** * Cancels and clears all touch targets. */private void cancelAndClearTouchTargets(MotionEvent event) {if (mFirstTouchTarget != null) {// 如果保存的第一个触摸View对象不为空boolean syntheticEvent = false;if (event == null) {final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();event = MotionEvent.obtain(now, now,MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0);event.setSource(InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCHSCREEN);syntheticEvent = true;}for (TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget; target != null; target = target.next) {resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child);dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(event, true, target.child, target.pointerIdBits);}clearTouchTargets();if (syntheticEvent) {event.recycle();}}}/** * Resets all touch state in preparation for a new cycle. */private void resetTouchState() {clearTouchTargets();resetCancelNextUpFlag(this);mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT;mNestedScrollAxes = SCROLL_AXIS_NONE;}因此我们可以得出如下结论:
1.当ViewGroup决定拦截事件后,那么点击事件将会默认交给它处理并且不再调用它的onInterceptTouchEvent方法,FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT这个标记的作用是ViewGroup不再拦截事件,前提是ViewGroup不拦截ACTION_DOWN事件处理。
2.如果事件能够传递到当前的ViewGroup,且我们要提前处理所有点击事件,应该选择dispatchTouchEvent方法,因为只有这个方法能确保每次都会被调用;而onInterceptTouchEvent()却无法保证每次事件都会被调用。
3.FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT标记位可以用于解决滑动冲突问题。
ViewGroup不拦截情况源码分析
ViewGroup不拦截事件的时候,事件会向下分发交由它的子View进行处理。先来看下代码64行(!canceled && !intercepted)这里的canceled和intercepted都为false时,条件成立,也就是说不拦截。接下来74行的条件判断:
actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN || (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN) || actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE在该if条件内,看到第86行,如果newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0,即子控件的个数不为0 且 newTouchTarget为空,在95行中遍历整个ViewGroup中的子控件,这里的集合做了个倒序排列,如果两个View交叉覆盖在一起,下面的子控件先放进集合,因为后被添加的子控件会浮在上面,通常我们会希望点击的时候最上层的那个组件先去响应事件。接着105行代码开始判断子控件是否能够接收到点击事件,主要依赖于两个条件:第一子控件是否在播动画;第二点击事件是否落在子控件的区域内。如果某个子控件满足这两个条件,那么事件就会传递给它来处理。
buildOrderedChildList方法解析
/** * 实现倒序排序 * Populates (and returns) mPreSortedChildren with a pre-ordered list of the View's children, * sorted first by Z, then by child drawing order (if applicable). This list must be cleared * after use to avoid leaking child Views. * Uses a stable, insertion sort which is commonly O(n) for ViewGroups with very few elevated * children. */ArrayList<View> buildOrderedChildList() {final int count = mChildrenCount;if (count <= 1 || !hasChildWithZ()) return null;if (mPreSortedChildren == null) {mPreSortedChildren = new ArrayList<View>(count);} else {mPreSortedChildren.ensureCapacity(count);}final boolean useCustomOrder = isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();for (int i = 0; i < mChildrenCount; i++) {// add next child (in child order) to end of listint childIndex = useCustomOrder ? getChildDrawingOrder(mChildrenCount, i) : i;View nextChild = mChildren[childIndex];float currentZ = nextChild.getZ();// insert ahead of any Views with greater Zint insertIndex = i;while (insertIndex > 0 && mPreSortedChildren.get(insertIndex - 1).getZ() > currentZ) {insertIndex--;}mPreSortedChildren.add(insertIndex, nextChild);}return mPreSortedChildren;}接着看代码,129行通过dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()这一重要方法(后面有详细分析),判断是否有子控件,如果有子控件则执行内部的操作,并找到最终触摸的对象,通过addTouchTarget方法赋值给newTouchTarget。在dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()方法中,如果子控件的dispatchTouchEvent()方法返回true,那么mFirstTouchTarget就会被赋值,同时跳出for循环,详见148行代码。同样如果dispatchTouchEvent()方法返回false,ViewGroup就会把事件分发给下一个子控件(如果还有下一个子控件)。
mFirstTouchEvent的真正赋值其实是在addTouchTarget方法中完成的,mFirstTouchEvent其实是一个单链表结构,如果mFirstTouchEvent为null,那么ViewGroup就会默认拦截下来同一序列中所有的点击事件。
addTouchTarget方法解析
/** * Adds a touch target for specified child to the beginning of the list. * Assumes the target child is not already present. */private TouchTarget addTouchTarget(View child, int pointerIdBits) {TouchTarget target = TouchTarget.obtain(child, pointerIdBits);// 往链表中插入一个元素target.next = mFirstTouchTarget;// 将mFirstTouchTarget赋值给target.nextmFirstTouchTarget = target;// 将target赋值给mFirstTouchTargetreturn target;}
接着我们看到171行代码中,如果mFirstTouchEvent为null,也就是说要么ViewGroup中没有子控件,要么是子控件处理了点击事件,但是在dispatchTouchEvent中返回了false(子控件在onTouchEvent中返回了false),那么ViewGroup就会自己处理点击事件,需要说明的是175行代码中,第三个参数本应为child,这里是null意味着需要调用父类View的dispatchTouchEvent方法,然后调用onTouch方法。
TouchTarget 内部类源码解析
/* Describes a touched view and the ids of the pointers that it has captured. * 链表实现的内部类,解决多指触控问题用来指定当前触摸的对象,多个手指触控(0~31个手指) * This code assumes that pointer ids are always in the range 0..31 such that * it can use a bitfield to track which pointer ids are present. * As it happens, the lower layers of the input dispatch pipeline also use the * same trick so the assumption should be safe here... */private static final class TouchTarget {private static final int MAX_RECYCLED = 32;private static final Object sRecycleLock = new Object[0];private static TouchTarget sRecycleBin;private static int sRecycledCount;public static final int ALL_POINTER_IDS = -1; // all ones// The touched child view.public View child;// The combined bit mask of pointer ids for all pointers captured by the target.public int pointerIdBits;// The next target in the target list.public TouchTarget next;private TouchTarget() {}public static TouchTarget obtain(View child, int pointerIdBits) {final TouchTarget target;synchronized (sRecycleLock) {if (sRecycleBin == null) {target = new TouchTarget();} else {target = sRecycleBin;sRecycleBin = target.next;sRecycledCount--;target.next = null;}}target.child = child;target.pointerIdBits = pointerIdBits;// 手指的IDreturn target;}public void recycle() {synchronized (sRecycleLock) {if (sRecycledCount < MAX_RECYCLED) {next = sRecycleBin;sRecycleBin = this;sRecycledCount += 1;} else {next = null;}child = null;}}}至关重要的dispatchTransformedTouchEvent方法解析
/** * Transforms a motion event into the coordinate space of a particular child view, * filters out irrelevant pointer ids, and overrides its action if necessary. * If child is null, assumes the MotionEvent will be sent to this ViewGroup instead. */private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {final boolean handled;// Canceling motions is a special case. We don't need to perform any transformations// or filtering. The important part is the action, not the contents.final int oldAction = event.getAction();if (cancel || oldAction == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) {event.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL);if (child == null) {// 如果child为空,则调用自己的分发方法handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);} else {// 否则调用child的分发方法handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event);}event.setAction(oldAction);return handled;}// Calculate the number of pointers to deliver.final int oldPointerIdBits = event.getPointerIdBits();final int newPointerIdBits = oldPointerIdBits & desiredPointerIdBits;// If for some reason we ended up in an inconsistent state where it looks like we// might produce a motion event with no pointers in it, then drop the event.if (newPointerIdBits == 0) {return false;}// If the number of pointers is the same and we don't need to perform any fancy// irreversible transformations, then we can reuse the motion event for this// dispatch as long as we are careful to revert any changes we make.// Otherwise we need to make a copy.final MotionEvent transformedEvent;if (newPointerIdBits == oldPointerIdBits) {if (child == null || child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {if (child == null) {handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);} else {final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;event.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event);event.offsetLocation(-offsetX, -offsetY);}return handled;}transformedEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(event);} else {transformedEvent = event.split(newPointerIdBits);}// Perform any necessary transformations and dispatch.if (child == null) {// 如果ViewGroup中没有子控件,调用父类View的dispatchTouchEventhandled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);} else {// 如果有子控件final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix());}
// 调用子控件的dispatchTouchEvent,有两种情况,如果是子控件是View,又分成两种情况(Button返回true,TextView返回false);如果是ViewGroup则进入递归了,又回到了这段代码,最终要么没有任何消耗事件的View,要么找到消费事件的Viewhandled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);}// Done.transformedEvent.recycle();return handled;}
该方法在dispatchTouchEvent()中被调用,用于将事件分发给子View处理。我们重点看一下60~71行代码。在dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()方法一共有三个参数,其中第三个参数View child有时为null,有时不为null。61行代码中,child==null意味着事件没有被消费,ViewGroup中没有子控件需要调用父类View的dispatchTouchEvent方法,即super.dispatchTouchEvent(event)。
接着我们关注下handled这个变量,可以发现dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()方法return handled,而handled的值其实是取决于dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()方法递归调用dispatchTouchEvent()方法的结果,也就是说在子控件中dispatchTouchEvent()方法的onTouchEvent()是否消费了Touch事件的返回值决定了dispatchTransformedTouchEvent()的返回值,从而决定mFirstTouchTarget是否为null,更进一步决定了ViewGroup是否处理Touch事件。
(二)onInterceptTouchEvent源码解析
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {return false;// 默认不拦截}你没有看错,这方法就是简简单单的一个布尔值返回,当返回true时,对事件进行拦截,返回false则不拦截。
(三)ViewGroup点击事件分发小结
Android点击事件分发是到达顶级View后(一般是ViewGroup),会调用ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法,其中它的onInterceptTouchEvent方法如果返回true,则会对事件传递进行拦截,事件由ViewGroup处理;如果onInterceptTouchEvent方法返回false,则代表不对事件进行拦截,默认返回false,即所有的ViewGroup都是默认不拦截的。则此时子View中的dispatchTouchEvent方法将被调用,到此,事件已经由顶级View传递给了下一层的View,接下来的过程是一个递归循环的过程,和顶级View事件分发过程是一致的,直到完成整个事件分发。
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/u/3126720/blog/803550
Android6.0源码解读之ViewGroup点击事件分发机制相关推荐
- android6.0源码分析之AMS服务源码分析
activitymanagerservice服务源码分析 1.ActivityManagerService概述 ActivityManagerService(以下简称AMS)作为Android中最核心 ...
- android6.0源码分析之Zygote进程分析
在android6.0源码分析之Runtime的初始化一文中,对Zygote进程的初期的Runtime初始化过程进行了分析,在Runtime启动结束后,会对Zygote进程进行初始化,其它Java进程 ...
- android6.0源码分析之Runtime的初始化
Android运行时作为android架构的一部分,起着非常重要的作用,它和核心库(Core Libraries)组成了Android运行时库层.本文将依据android源码对AndroidRunti ...
- android6.0源码分析之Camera2 HAL分析
1.Camera HAL的初始化 Camera HAL的初始加载是在Native的CameraService初始化流程中的,而CameraService初始化是在Main_mediaServer.cp ...
- android6.0源码分析之Camera API2.0下的Preview(预览)流程分析
1.Camera2 preview的应用层流程分析 preview流程都是从startPreview开始的,所以来看startPreview方法的代码: <code class="hl ...
- android6.0源码分析之Camera API2.0下的初始化流程分析
1.Camera2初始化的应用层流程分析 Camera2的初始化流程与Camera1.0有所区别,本文将就Camera2的内置应用来分析Camera2.0的初始化过程.Camera2.0首先启动的是C ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(十)之 UIActivityIndicatorView/UIRefreshControl/UIImageView + AFNetworking...
我们应该看到过很多类似这样的例子:某个控件拥有加载网络图片的能力.但这究竟是怎么做到的呢?看完这篇文章就明白了. 前言 这篇我们会介绍 AFNetworking 中的3个UIKit中的分类.UIAct ...
- Android6.0 源码修改之 仿IOS添加全屏可拖拽浮窗返回按钮...
Android6.0 源码修改之 仿IOS添加全屏可拖拽浮窗返回按钮 前言 之前写过屏蔽系统导航栏功能的文章,具体可看Android6.0 源码修改之屏蔽导航栏虚拟按键(Home和RecentAPP) ...
- 在Ubuntu Server14.04上编译Android6.0源码
此前编译过Android4.4的源码,但是现在Android都到了7.0的版本,不禁让我感叹Google的步伐真心难跟上,趁这周周末时间比较充裕,于是在过去的24小时里,毅然花了9个小时编译了一把An ...
最新文章
- LDO和DC-DC有什么不同?如何选型?
- c语言俄罗斯方块注释,C语言学习1年-俄罗斯方块(无注释)
- 扩增子图表解读8网络图:节点OTU或类Venn比较
- Vue 后台模板 [Vue admin] SanJi Boot Admin Iview
- 华为手机如何升级鸿蒙系统_华为杨海松:明年所有华为自研设备升级鸿蒙系统...
- 计算机二进制加减符号,(带符号的二进制数的表示方法及加减法运算).ppt
- 数字图像处理中常用的插值方法
- ArcEngine 获取HDF文件中的子文件
- Xcode搭建真机调试环境 图文实例
- java持久性与安全性_Java持久性锁定初学者指南
- 微信小程序图片选择,预览和删除
- SqlHelper帮助类_上(SQLServer数据库含Connection详解)
- windows系统清理磁盘临时文件,及缓冲文件,及离线文件和空闲文件
- (转载)程序员文史综合题目一(附答案)
- 在WPF中开启摄像头扫描二维码(Media+Zxing)
- 人工智能——微粒群优化算法
- 服务器虚拟连接按键精灵,服务器运行按键精灵
- Linux 创建用户角色并添加ssh登录权限
- TLS Lab(Transport Layer Security Lab,SEED实验)基于PKI实验内容进行中间人攻击实验
- 大鱼吃小鱼java程序设计
