cnn 分层 可视化 网站_如何可视化分层数据以显示整体关系
cnn 分层 可视化 网站
重点 (Top highlight)
I worked on infographics for one chapter of UNDERSTANDING USA, a TED conference textbook back in the year 2000. So why talk about infographics from such an old book now?
早在2000年,我就为UNDERSTANDING USA (一本TED会议教材)的一章编写了信息图表。那么,为什么现在要从这么一本老书中谈谈信息图表呢?
The loss of my favorite teacher, Krzysztof Lenk, gave me an opportunity to reflect on what I worked on under his direction back then. What I realized was that there are so many insights from this project that can still be applied to today’s work of UX designers and information designers. I would like to share my re-discovery of the project.
失去了我最喜欢的老师Krzysztof Lenk,这使我有机会反思一下我当时在他的指导下所做的工作。 我意识到,这个项目有很多见解,仍然可以应用于当今的UX设计人员和信息设计人员。 我想分享我对该项目的重新发现。

UNDERSTANDING USA was a textbook for TEDX conference, which took place in Monterey, California, on February 23–26, 2000. This was the same conference where Global Village (which I wrote about in my last article) was presented. I initially worked on UNDERSTANDING USA before Global Village.
理解美国是TEDX会议的教科书, 该会议于2000年2月23日至26日在加利福尼亚州蒙特雷举行。这是与我在上一篇文章中提到的Global Village一样的会议。 在加入Global Village之前,我最初在UNDERSTANDING USA工作。
In 1999, Krzysztof Lenk and Paul Kahn from Dynamic Diagrams were invited by Richard Saul Wurman (the founder of TED) to be part of a team of 12 information architects to contribute to the book. I had an opportunity to work with Krzysztof and Paul on this project.
1999年,Dynamic Diagrams的Krzysztof Lenk和Paul Kahn受TED的创始人Richard Saul Wurman邀请,成为由12位信息架构师组成的团队的一员,为本书做出了贡献。 我有机会与Krzysztof和Paul合作进行这个项目。

Below is a quote from Richard Saul Wurman on how he introduced the concept of UNDERSTANDING USA in his letter to the contributors on November 13, 1998. He initially called it “Atlas of Understanding.”
以下是理查德·索尔·沃曼(Richard Saul Wurman)在1998年11月13日给投稿人的信中如何介绍“理解美国”概念的引文。他最初将其称为“理解地图集”。
The Book: Atlas of Understanding:
书:理解图集:
To answer the complex TEDX questions, my staff and I are researching government statistics, recent studies by foundations and think-tanks, timely articles by leading journalists and relevant material from industry groups and trade associations.The resulting book will be the Atlas of Understanding — a comprehensive fact-based guide to the fruits of our research. The Atlas will be the TEDX Bible, its blueprint, its compass and its yardstick — striving to be Solomonic in its fairness and impartiality.
为了回答TEDX的复杂问题,我和我的工作人员正在研究政府统计数据,基金会和智囊团的近期研究报告,领先新闻工作者的及时文章以及行业组织和行业协会的相关材料。最终的书将是《理解图集》-基于事实的综合指南,可为我们的研究成果提供帮助。 该地图集将成为TEDX圣经,其蓝图,其指南针和它的标尺-力求在公正性和公正性上成为所罗门语。
But please don’t make the mistake of thinking of this book’s neutrality will translate into something dry, academic and boring. On the contrary, I intend to make the Atlas a showpiece, a demonstration of how complex data can be accessible, engaging and entertaining — without sacrificing its integrity or its nuances. How? There exists within the upper echelon of America’s graphic designers an elite group I call the Information Architects. These talented designers (some of whom are profiled in my 1997 book Information Architects) will condense the TEDX research into its most revealing and informative components. Their extraordinary graphs, maps, video, computer simulations and a host of other media will bring the TEDX information to life. The Atlas will be like a master class in effective information design. Trust me; it won’t be boring.
但是请不要误以为这本书的中立性会转化为枯燥,学术和无聊的东西。 相反,我打算将Atlas用作展示品,展示如何可以访问,吸引和娱乐复杂数据,而又不会牺牲其完整性或细微差别。 怎么样? 在美国平面设计师的高层中,有一个精英团体,我称为信息建筑师。 这些才华横溢的设计师(其中一些人在我1997年的书《 Information Architects》中进行了介绍)将TEDX的研究浓缩为最具启发性和信息性的组成部分。 他们非凡的图形,地图,视频,计算机模拟和许多其他媒体将使TEDX信息栩栩如生。 该地图集将像有效信息设计的大师班一样。 相信我; 不会很无聊。

When Krzysztof and I visited Richard Saul Wurman’s house in Newport, Rhode Island, we were handed over a box full of statistics, hundreds of pages. The topic our team got assigned was “Global Economy / Foreign Trade / Immigration / Balance of Payments / Business / Workforce / Jobs”, among eleven broad social issue areas defined by Richard to be covered by the TEDX Conference.
当我和Krzysztof参观位于罗德岛州纽波特的Richard Saul Wurman的房屋时,我们收到了一个装满数百页统计数据的盒子。 我们团队分配的主题是“全球经济/外贸/移民/国际收支/业务/劳动力/就业”,这是理查德定义的11个广泛的社会问题领域,属于TEDX会议的范围。
深入了解大量统计数据 (Deep dive into piles of statistic data)
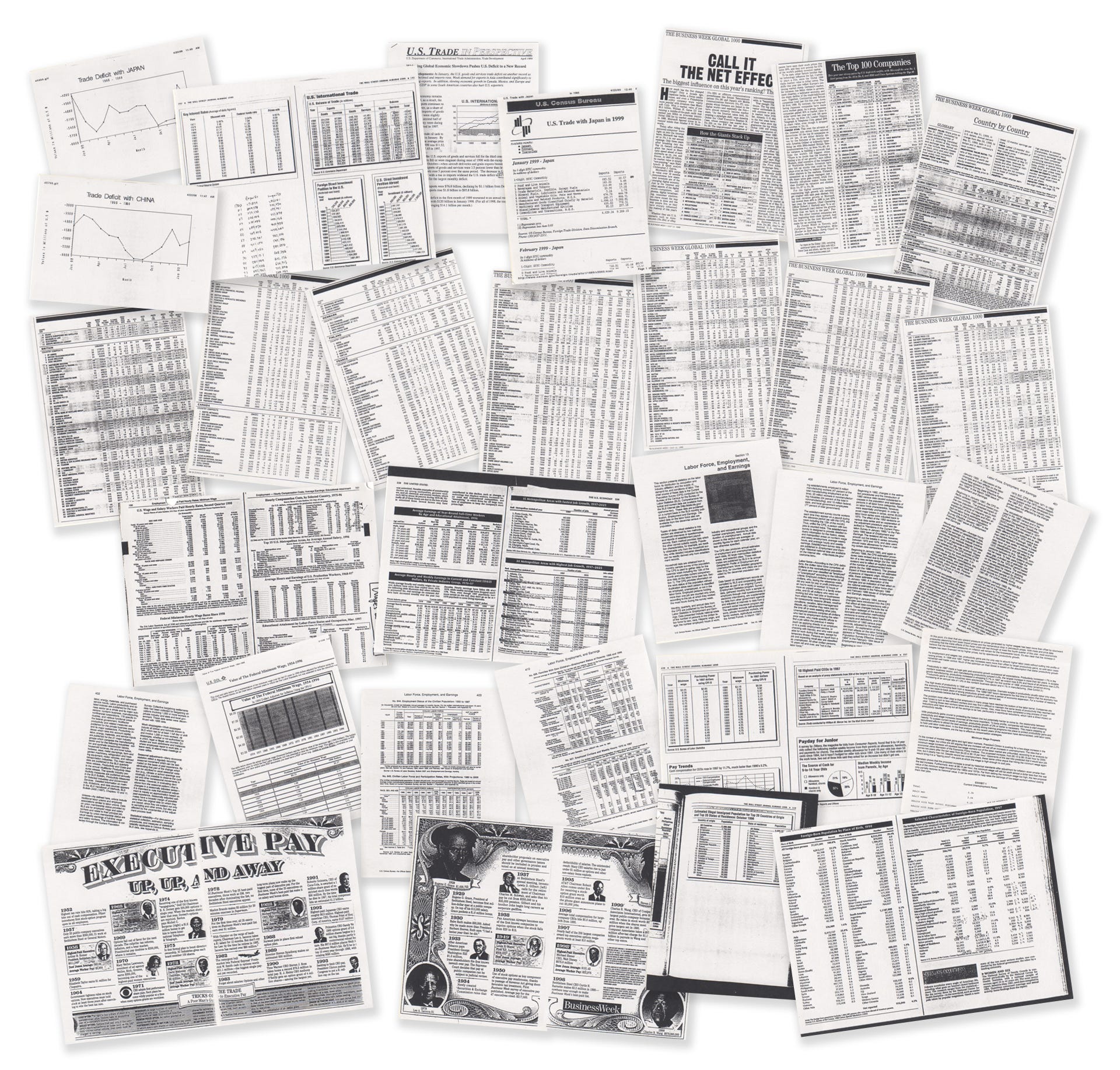
Typically, most design works start with content that is already curated, edited, and selected by a client, an editor, or a writer. However, in this project, we were able to start from which statistics to pick and choose from piles of raw data, loosely organized based on broad questions provided by Richard Saul Wurman as a guide.
通常,大多数设计作品都是从客户,编辑者或作家已经策划,编辑和选择的内容开始的。 但是,在该项目中,我们能够从一堆原始数据中挑选和选择统计数据,这些数据是根据Richard Saul Wurman提供的广泛问题作为指导而松散组织的。

Obviously, in order to pick and choose, you first need to fully understand all the statistics packed in the box. This by itself was a lot of work. But it was a lot of fun too, getting immersed deeply into the sea of data.
显然,为了进行选择,您首先需要完全了解包装盒中提供的所有统计信息。 这本身就是很多工作。 但这也很有趣,因为它沉浸在数据的海洋中。
In the box, the statistics were organized by folders based on topics. Krzysztof would give me one or two folders at a time, and I would take those home, scrutinize all the data, take notes, hand-drawn graphs and charts out of tables, and playback my learnings to him at the next meeting at his studio.
在框中,统计信息是基于主题的文件夹组织的。 Krzysztof一次给我一个或两个文件夹,然后我将它们带回家,仔细检查所有数据,在表中做笔记,手绘的图形和图表,并在下一次在他的工作室的会议上向他回放我的知识。

When I went through this data-immersion process, I gradually started to paint a picture, started to connect dots. Then I was hit by various “ah-ha” moments when various connected dots came together all of the sudden and started to shape a new meaning.
当我经历了数据浸入过程时,我逐渐开始绘制图片,开始连接点。 然后我被各种“啊哈”的时刻打动了,各种连接的点突然之间突然汇合在一起,并开始塑造新的含义。
有效,整体地可视化分层信息以显示其相互关系 (Visualizing layered information effectively and holistically to show its inter-relationships)
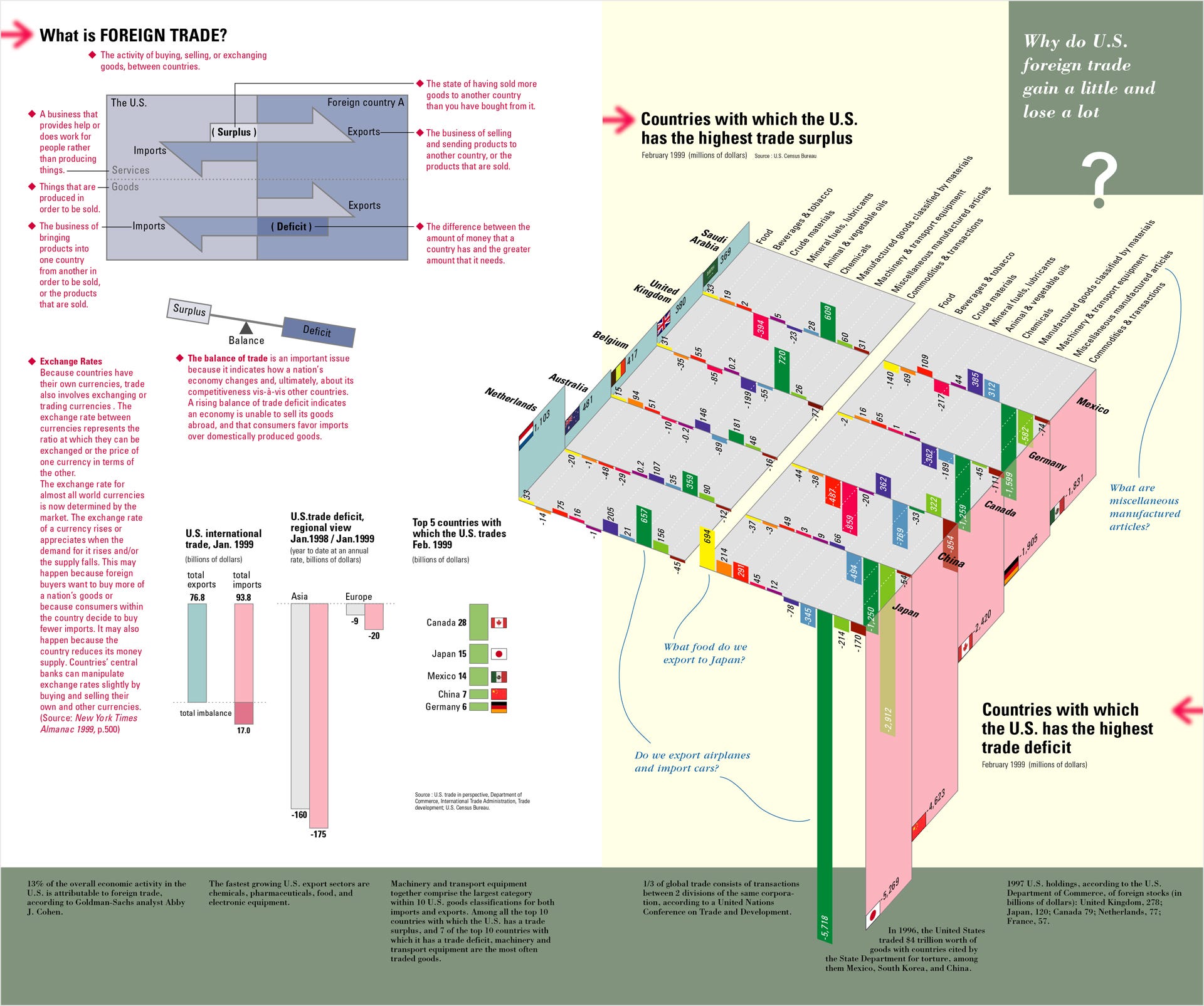
One of the interesting things from an information design perspective that came out from this project was how to visualize layered information effectively and create a holistic view of encapsulated data and their relationships. The above spread showed data about foreign trade, based on a simple question: Why did U.S. foreign trade gain a little and lose a lot?
从该项目的信息设计角度来看,有趣的事情之一是如何有效地可视化分层信息并创建封装数据及其关系的整体视图。 上面的价差基于一个简单的问题显示了有关外贸的数据:为什么美国的外贸会有一点收益却有很多损失?
The spread was designed in a way so that a viewer naturally went through a three-step progression in order to fully understand the information. The page greeted its viewer first by (A) introducing a basic definition of foreign trade, showing what trade surplus and deficit meant through a simple diagram. Then it continued to (B) a basic concept of a balance of trade, top countries that U.S. traded, and how the U.S. had huge trade deficits.
传播的设计方式是让观众自然地经历了三个步骤,以便完全理解信息。 该页面首先通过(A)介绍了外贸的基本定义,向观众表示欢迎,并通过一个简单的图表显示了贸易盈余和赤字的含义。 然后,它继续(B)贸易平衡的基本概念,美国进行贸易的主要国家以及美国如何出现巨额贸易逆差。
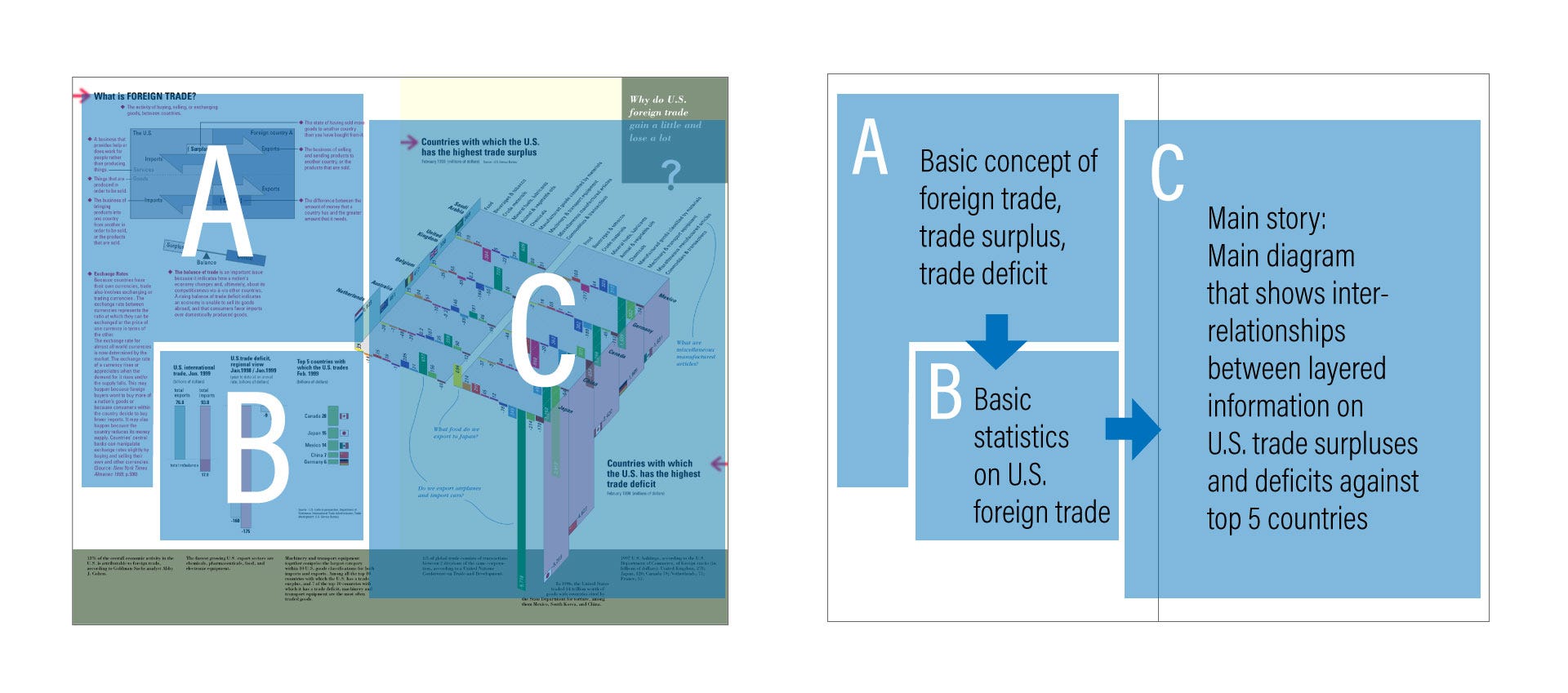
After these introduction made by A and B, the third step, (C) a highlight of the story was represented on the right page in the form of a pair of three-dimensional diagrams, which illustrated a contrasting two diagrams side by side, one showing the top five countries that U.S. had trade surpluses against, the other depicting the top five countries that the U.S. had trade deficits against, as of February 1999.
在由A和B进行介绍之后,第三步(C)在故事的亮点上以一对三维图的形式在右侧页面上进行了展示,其中并排展示了两个对比图。显示了美国对其具有贸易顺差的前五个国家,另一个国家描述了截至1999年2月美国对其具有贸易逆差的前五个国家。
These three-dimensional diagrams attempted to highlight stark contrasts at multiple levels altogether, such as:
这些三维图试图在多个层次上突出显示鲜明的对比,例如:
An overall trade surplus vs. deficit (and the deficit was overwhelmingly large)
总体贸易顺差与赤字(赤字绝大多数)
Among the top five countries with a U.S. deficit, Japan and China stood out significantly
在美国赤字排名前五的国家中,日本和中国表现突出
Among the top five countries with a U.S. surplus, the Netherlands stood out slightly, but no match for how Japan and China stood out in deficit
在美国顺差排名前五位的国家中,荷兰的表现略有出众,但与日本和中国的逆差如何脱颖而出
Machinery and transport equipment was the biggest category in both surplus and deficit, with a deficit from Japan being the largest by far
机械和运输设备是盈余和赤字中最大的类别,日本的赤字迄今为止是最大的
Now, some people might question the use of three-dimensionality incorporated here. But our team, primarily Krzysztof and myself, concluded that this three-dimensional approach enabled not only an aesthetically intriguing visual impact but also a meaningful interrelationship between complex layered data. As a result, while it did require some time to decode the meaning of the diagram, we were able to create a holistic view of the foreign trade problems that U.S. faced at the time, presenting all the above in one pair of diagrams.
现在,有些人可能会质疑此处包含的三维的使用。 但是我们的团队(主要是Krzysztof和我本人)得出结论,这种三维方法不仅实现了美学上吸引人的视觉效果,而且还实现了复杂分层数据之间有意义的相互关系。 结果,虽然确实需要一些时间来解释该图的含义,但我们仍能够对美国当时所面临的外贸问题进行整体分析,并在一对图中展示了以上所有内容。
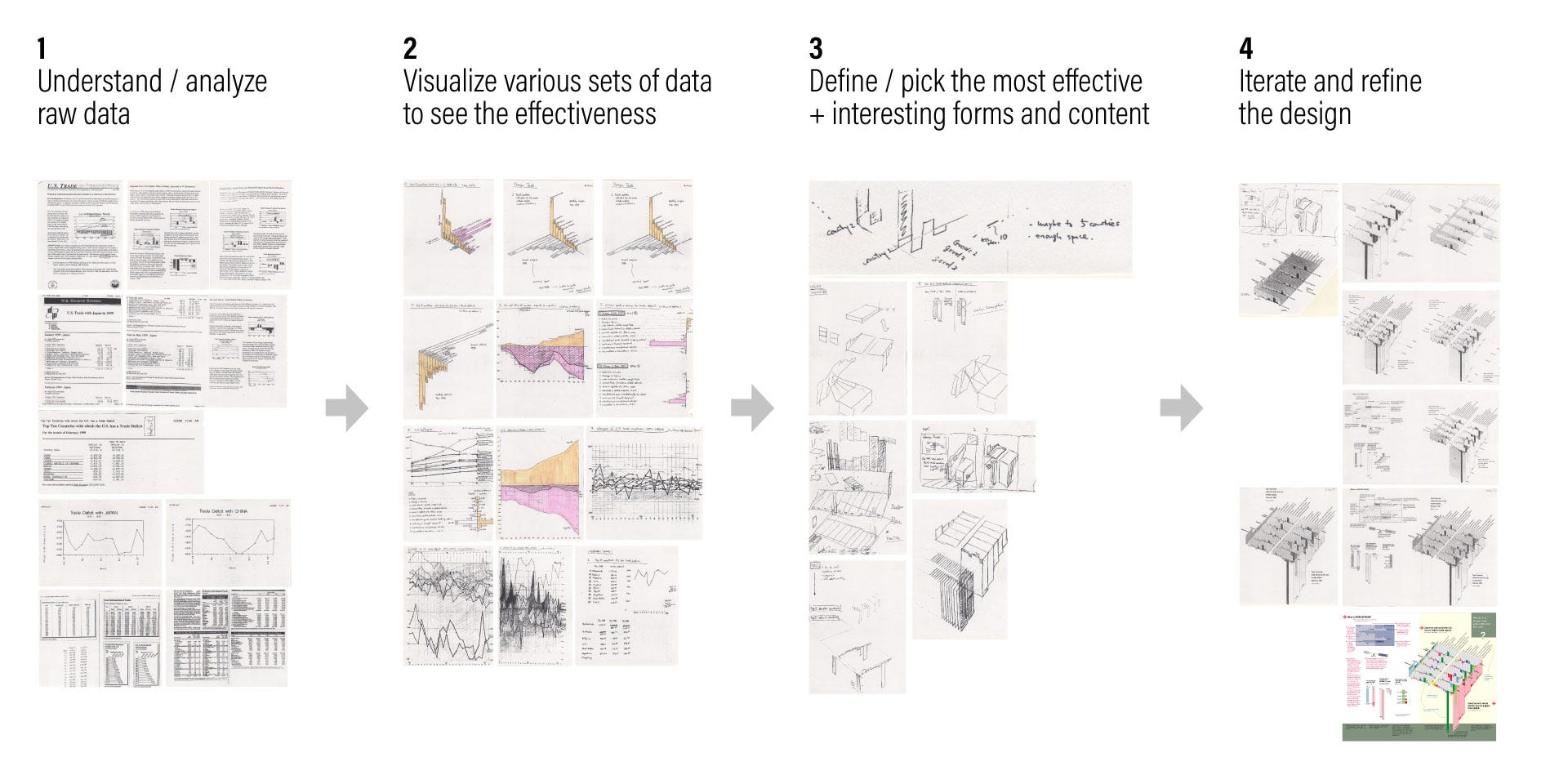
Below outlined the basic process our team went through from the data analysis to the final design.
下面概述了我们团队从数据分析到最终设计所经历的基本过程。
使人们可以理解信息—整体概述,广泛的模式和相互关系 (Making information understandable to humans — Holistic overview, broad patterns, and interrelationships)
Today, we live in a high-paced information world, where a huge amount of data is constantly captured via sensors, collected via various software, analyzed via machine learning algorithms, and then visualized through computer automation. We live in a world where data visualization is ubiquitous.
如今,我们生活在一个快节奏的信息世界中,其中不断通过传感器捕获大量数据,通过各种软件收集这些数据,通过机器学习算法进行分析,然后通过计算机自动化进行可视化。 我们生活在数据可视化无处不在的世界中。
More than ever, we need designers to design frameworks for these data visualizations to accommodate ever-increasing demands. Because most of these data visualizations require data to be fed into “template designs” automatically, it’s getting out of designers’ controls.
我们比以往任何时候都需要设计师为这些数据可视化设计框架,以适应不断增长的需求。 由于大多数这些数据可视化要求将数据自动输入“模板设计”中,因此它脱离了设计人员的控制。
Computers have a superior ability to perform astronomically complex and massive calculations within a second. But at the end of the day, it’s humans who make the good use of those data collected, calculated, and presented automatically by computers. In order for us humans to grasp the meaning of data, we need to visualize data in a way that humans can comprehend.
计算机具有出色的能力,可以在一秒钟内完成天文复杂的大规模计算。 但归根结底,是人类充分利用了计算机自动收集,计算和呈现的那些数据。 为了使人类能够理解数据的含义,我们需要以一种人类可以理解的方式可视化数据。
Humans are bad at precision and massive calculations. What humans are good at, however, are seeing a forest as a whole, rather than precisely counting how many trees make up the forest. We seek a holistic overview, broad patterns, and trends, interrelationships between various data points. These holistic overview, broad patterns and trends, and interrelationships between various data points are what we base our actions on. These are the types of things that designers are responsible for. And I believe these are the areas that we as humans are still better at over computers.
人类不擅长精确和庞大的计算。 然而,人类擅长的事情是看到整个森林,而不是精确地计算出森林中有多少树。 我们寻求全面的概述,广泛的模式,趋势以及各种数据点之间的相互关系。 这些整体概览,广泛的模式和趋势以及各个数据点之间的相互关系是我们采取行动的基础。 这些是设计师负责的事情类型。 而且我相信,这些都是我们人类在计算机领域仍擅长的领域。
为用户设计自然会将用户和内容放在中心 (Designing for a user naturally puts the user and the content at the center)
Because 12 designers (information architects) were invited and designed each assigned chapter of the book, the book as a whole ended up a bit chaotic, even though the information contained was really amazing, and it certainly became an entertaining showpiece as Richard Saul Wurman envisioned. It was really interesting to see how various information architects ended up trying to flex their visual muscles with cool effects, vibrant colors and beautiful pages. On the contrary, Dynamic Diagrams remained grounded with a more controlled, classic visual design style, focusing on the content rather than presentation effects to wow the viewers. Ironically, Dynamic Diagram stood out from the rest.
由于邀请了12位设计师(信息架构师)并设计了本书的每一章,因此,尽管其中包含的信息确实令人惊讶,但本书的整体还是有些混乱,而且正如理查德·索尔·沃曼(Richard Saul Wurman)所设想的那样,它无疑成为了一个有趣的展览。 。 看到各种信息架构师最终如何尝试以炫酷的效果,鲜艳的色彩和漂亮的页面来展示自己的视觉肌肉,真是很有趣。 相反,动态图仍然以更具控制性的经典视觉设计风格为基础,着重于内容而不是呈现效果,以吸引观众。 具有讽刺意味的是,动态图在其他方面脱颖而出。

The above-left spread was designed by Ramana Rao, presenting “Food: How did food production keep pace with population growth? How much of what kinds of proteins do we consume?” The page was beautifully designed, so it was successful in attracting viewers into the page in the first place. However, a dominant photograph took too much attention away from the graphs themselves, which made the graphs look insignificant.
左上方的传播是由Ramana Rao设计的,主题为“食品:食品生产如何与人口增长保持同步? 我们消耗多少种蛋白质?” 该页面的设计精美,因此一开始就成功吸引了观众。 但是,一张占主导地位的照片将注意力从图表本身转移了很多,这使得图表显得微不足道。
The above-right was designed by Hani Rashid and Lise Anne Couture, visualizing “Transportation: How do Americans get around?” The sculptural object looked intriguing because it was so unusual. Again, it was successful in stimulating the viewer’s curiosity, but at the same time, the way the statistical graph was mapped onto the surface of such an irregular form factor made it hard to read.
右上角由Hani Rashid和Lise Anne Couture设计,可视化为“运输:美国人如何出行?” 雕塑的对象看起来很有趣,因为它是如此不寻常。 再次,它成功地激发了观众的好奇心,但与此同时,统计图被映射到这种不规则形状因素的表面上的方式使其难以阅读。
This goes back to a principle of user-centered design that became common practice for today’s designers, primarily UX designers.
这可以追溯到以用户为中心的设计原则,该原则已成为当今设计人员(主要是UX设计人员)的惯用做法。
Whether it’s a user experience for a digital product, a data visualization, or infographics, or any products, the design should never be treated as a “designer’s playground” to selfishly satisfy themselves. Designers should always work FOR users/viewers/audiences. Design is just a vehicle to deliver the message to its users/viewers. When that was successfully done without ego, the design itself recedes to the background, almost becoming transparent, so that a viewer is fully immersed with the content itself.
无论是数字产品,数据可视化,信息图表还是任何产品的用户体验,都不应将设计视为自私自利的“设计师游乐场”。 设计人员应始终为用户/观看者/观众服务。 设计只是将消息传递给用户/查看者的一种手段。 成功地做到这一点之后,设计本身便退回到了背景中,几乎变得透明了,从而使观看者完全沉浸在内容本身中。
These insights are what I re-discovered from a 20-year-old print-based infographics project, the importance of putting a user and the content at the center as a designer, which is the very essence of user-centered design. In order to properly execute this, you need to go through a process of content analysis to acquire a deep understanding of the content. And finally, this deep understanding of the content gives you an ability to present a holistic overview of the information in a meaningful way so that humans can easily comprehend and act upon.
这些见解是我从一个已有20年历史的基于打印的信息图表项目中重新发现的,他们将以用户和内容为中心的重要性作为设计师,这是以用户为中心的设计的本质。 为了正确执行此操作,您需要经历内容分析过程以对内容进行深入的了解。 最后,对内容的深刻理解使您能够以有意义的方式呈现信息的整体概览,以便人类可以轻松理解并采取行动。
I am grateful that I had a chance to reflect on this project now at the beginning of the new decade and share my journey with you.
我很高兴在新的十年开始之际有机会对此项目进行反思,并与您分享我的旅程。

Here’s a PDF version of business chapter of UNDERSTANDING USA.
这是UNDERSTANDING USA商业章节的PDF版本 。
A bit more background…
更多背景信息…

Richard Saul Wurman is an architect, information designer, a founder of TED. He is also an author of Information Anxiety, one of early books that pointed out the problem that we all face in today’s world: information overload, and resulting information anxiety. He coined the term “Information Architect”.
Richard Saul Wurman是TED的创始人,建筑师,信息设计师。 他还是《 信息焦虑 》一书的作者,《 信息焦虑》是指出当今我们所有人都面临的问题:信息超载和随之而来的信息焦虑的早期著作之一。 他创造了“信息架构师”一词。
UNDERSTANDING USA was a textbook for the TEDX Conference in Monterey California, on February 2000. Richard Saul Wurman invited 12 information architects to design infographics of various social issues, including Krzysztof Lenk and Paul Kahn from Dynamic Diagrams. Krzysztof was one of my thesis advisors at RISD.
理解美国是2000年2月在加利福尼亚州蒙特雷举行的TEDX会议的教科书。理查德·索尔· 沃曼( Richard Saul Wurman)邀请了12位信息设计师来设计各种社会问题的图表,包括Dynamic Diagrams的Krzysztof Lenk和Paul Kahn 。 Krzysztof是我在RISD的论文顾问之一。

翻译自: https://medium.com/nightingale/how-to-visualize-layered-data-to-show-holistic-relationships-59843e003018
cnn 分层 可视化 网站
http://www.taodudu.cc/news/show-4554552.html
相关文章:
- VUE2笔记
- IB36分斩获藤校?看艺术设计类专业
- 【EE308FZ Lab3-2-1】Sprint Plan: RISD-IoT-Group
- ImportError: numpy.core.multiarray failed to impor
- 打开anaconda prompt 出错 import ctypes
- Leetcode刷题100天(阿里云周赛)—查找数组中的所有重复项(哈希)—day42
- 17.python-解决 pycharm运行提示:from PyQt5 impor ImportError:DLL load failed while importing QtCore
- VSCode:python import下载的第三方库,报错问题解决
- java 获取包下的所有类,附完整源码和测试代码
- import 库、from 库 import 函数、from 库 impor *、import 库 as 别名的区别
- 1 invalid import format(s) Postman Collection Format v1 is no longer supported and can not be import
- 错误提示:“ReferenceError: require is not defined in ES module scope, you can use impor”解决方法
- Python:环境变量设置PYTHONPATH解决impor导入模块报错
- Maven——maven中的 pom和import的作用到底是什么
- onnx 模型推理示例-Python 实现 |【onnx 模型推理】
- numpy.core.multiarray failed to impor
- XX is not defined import impor了还是not defined ant design组件import还是not defined
- Java:文件写入读取操作和工具类
- 支付宝小程序手机相册上传多个图片踩坑
- Android 外部存储App私有目录下照片和视频显示到相册
- jupyter 中重新 import 模块
- GPU0和GPU1的区别
- int i = 0 与 int i(0)的区别
- EnableLUA改为0是什么意思
- border:none以及border:0的区别
- D0、T0、S0到账模式的区别
- NULL和0的区别
- [附源码]Python计算机毕业设计办公用品管理系统Django(程序+LW)
- Django计算机毕业设计办公用品管理系统(程序+LW)Python
- [附源码]Java计算机毕业设计SSM办公用品管理系统
cnn 分层 可视化 网站_如何可视化分层数据以显示整体关系相关推荐
- 数据可视化 工具_卓越中心和数据可视化工具2020中的组织中的数据聚合
数据可视化 工具 人工智能 (ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE) Data consumption is rising steadily in 2020 with estimates s ...
- c++可视化开发_页面可视化配置搭建工具技术要点
点击上方"IT平头哥联盟",选择"置顶或者星标" 与你一起成长- 前言 最近公司也在计划做可视化配置平台,从本文原作者(腾讯AlloyTeam@陈韩杰)的分析中 ...
- 可视化管理_供应链可视化管理的应用与展望
一.供应链可视化定义及基本内容 1.供应链可视化的定义供应链可视化就是利用信息技术,采集.传递.存储.分析.处理供应链中的订单.物流以及库存等相关指标信息,按照需求以图形化的方式展现出来.2.供应链 ...
- 数据库可视化库_漂亮的javascript数据可视化库
数据库可视化库 If you're building a web app using JavaScript, it is inevitable that at some point you'll ne ...
- git 可视化工具_版本控制可视化神器Gource:简单易上手,效果恰似烟花秀
鱼羊 发自 凹非寺 量子位 报道 | 公众号 QbitAI 如此华丽的绽放,莫非是一场动画烟火秀? 非也,这其实是GitLab社区版的进化史,7年间82000次commit,尽皆在2.5分钟的视频内展 ...
- 数据可视化原理_格式塔原理是数据可视化的实用方面
数据可视化原理 Data Visualisation is not just about making good-looking and understandable charts by transf ...
- python 地图可视化工具_【可视化】python地图可视化_Folium
本文简单介绍python语言的地图可视化库Folium 效果图 能力概述 Python语言 地图可视化 可以换(高德)底图 有添加点线面和简单配色的功能 可以导出为html页 简介 Folium是Le ...
- 如何取消高亮显示重复项_如何将重复数据突出显示?
将表格中一列数据中重复的,使用特殊颜色突出显示或者使用一些符号标记出来. 例如: 一个供应商,可以邀请别的供应商加入成为联合体,报表要显示所有供应商,然后供应商最后一列显示所有联合体,当联合体供应商跟 ...
- c语言可视化_这些算法可视化网站助你轻松学算法
前言 无疑,数据结构与算法学习最大的难点之一就是如何在脑中形象化其抽象的逻辑步骤.而图像在很多时候能够大大帮助我们理解其对应的抽象化的东西,而如果这个图像还是我们自己一点点画出来的,那么无疑这个印象是 ...
最新文章
- MFC获取文字高宽设置字符间隔
- C#文件路径操作总结
- cad常用字体_2300多种CAD字体免费送给你!绘图必备,一键解决你的CAD文字乱码问题...
- 强大的Mockito测试框架(转)
- hapRroxy 安装配置详解
- 03-命令图片.doc
- webflow如何使用_我如何使用Webflow构建辅助项目以帮助设计人员进行连接
- 蓝桥杯基础模块4_1:独立按键
- vb combox获取选定index_Python-新闻评论获取
- 倒车出库何时开始打方向盘,车头似乎很容易撞到左右两侧的车?
- hutool BigExcelWriter 下的autoSizeColumnAll异常问题
- 汤小丹计算机操作系统慕课版课后题答案第三章:处理机调度与死锁
- linux ll -hrt,Linux col(每日一令之十六)
- Xcode调试中如何将指定地址转换为其指向的对象
- C语言实现建立顺序表,修改顺序表,插入顺序表,删除顺序表
- Qt开源版下载官网地址 macOS
- UNI-APP,网络下载.bin二进制文件并保存到手机,在其他页面读取该.bin文件,按照协议封装后,发送给硬件设备
- 迄今为止10大最佳SDN解决方案
- labelImg的汉化与打包
- java乱码问题解决总结
