Kubernetes StatefulSet源码分析
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
Author: xidianwangtao@gmail.com,Based on Kubernetes 1.9
摘要:Kubernetes StatefulSet在1.9版本中stable了,相信以后会有越老越多的企业会使用它来部署有状态应用,比如Mysql、Zookeeper、ElasticSearch、Redis等等。本文是对StatefulSet的源码分析,包括其Inner Structure、Sync的核心逻辑、Update的主要流程说明、完整的Code Logic Diagram及一些思考。
Inner Structure
下面是简单的StatefulSet Controller工作的内部结构图。 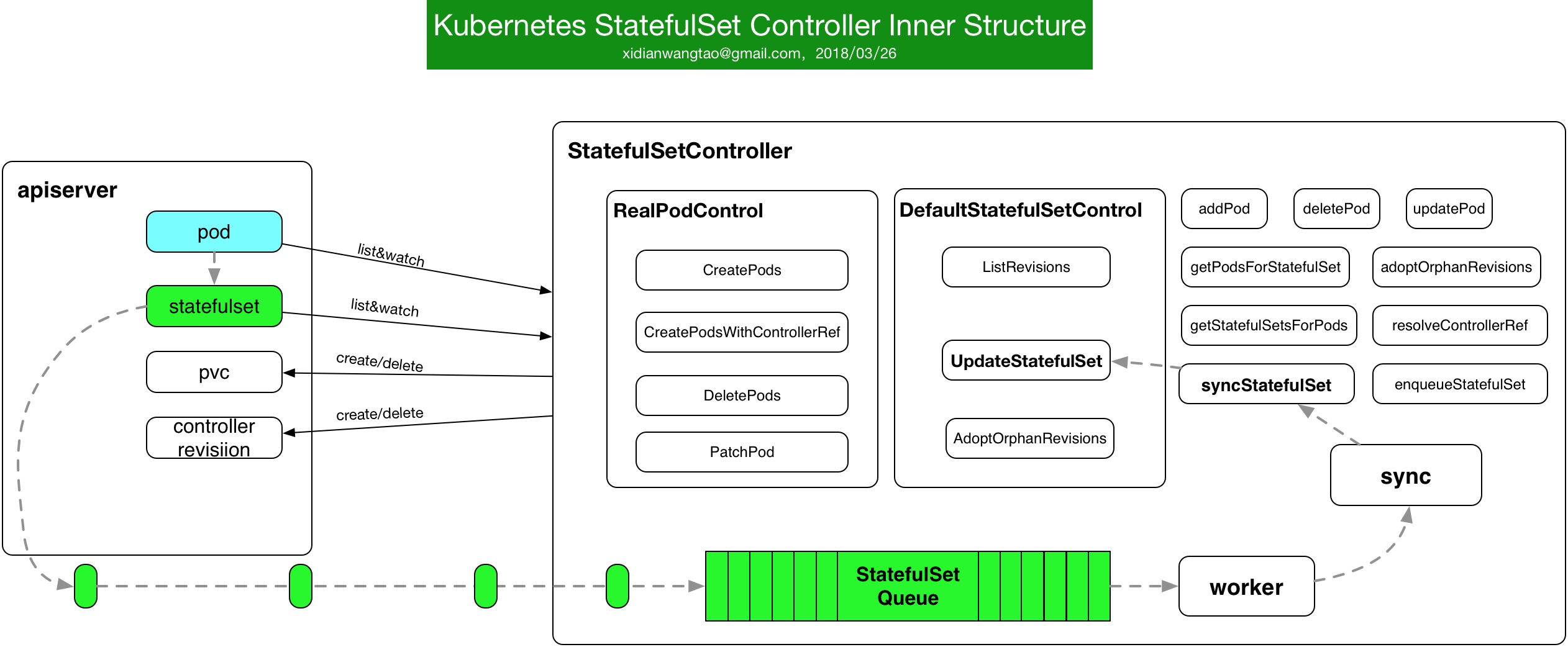
NewStatefulSetController
同其他Controller一样,StatefulSet Controller也是由ControllerManager初始化时负责启动。
// NewStatefulSetController creates a new statefulset controller.
func NewStatefulSetController(podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer,setInformer appsinformers.StatefulSetInformer,pvcInformer coreinformers.PersistentVolumeClaimInformer,revInformer appsinformers.ControllerRevisionInformer,kubeClient clientset.Interface,
) *StatefulSetController {...ssc := &StatefulSetController{kubeClient: kubeClient,control: NewDefaultStatefulSetControl(NewRealStatefulPodControl(kubeClient,setInformer.Lister(),podInformer.Lister(),pvcInformer.Lister(),recorder),NewRealStatefulSetStatusUpdater(kubeClient, setInformer.Lister()),history.NewHistory(kubeClient, revInformer.Lister()),),pvcListerSynced: pvcInformer.Informer().HasSynced,queue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter(), "statefulset"),podControl: controller.RealPodControl{KubeClient: kubeClient, Recorder: recorder},revListerSynced: revInformer.Informer().HasSynced,}podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{// lookup the statefulset and enqueueAddFunc: ssc.addPod,// lookup current and old statefulset if labels changedUpdateFunc: ssc.updatePod,// lookup statefulset accounting for deletion tombstonesDeleteFunc: ssc.deletePod,})ssc.podLister = podInformer.Lister()ssc.podListerSynced = podInformer.Informer().HasSyncedsetInformer.Informer().AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{AddFunc: ssc.enqueueStatefulSet,UpdateFunc: func(old, cur interface{}) {oldPS := old.(*apps.StatefulSet)curPS := cur.(*apps.StatefulSet)if oldPS.Status.Replicas != curPS.Status.Replicas {glog.V(4).Infof("Observed updated replica count for StatefulSet: %v, %d->%d", curPS.Name, oldPS.Status.Replicas, curPS.Status.Replicas)}ssc.enqueueStatefulSet(cur)},DeleteFunc: ssc.enqueueStatefulSet,},statefulSetResyncPeriod,)ssc.setLister = setInformer.Lister()ssc.setListerSynced = setInformer.Informer().HasSynced// TODO: Watch volumesreturn ssc
}
很熟悉的代码风格,也是创建对应的eventBroadcaster,然后给对应的objectInformer注册对应的eventHandler:
- StatefulSetController主要ListWatch Pod和StatefulSet对象;
- Pod Informer注册了add/update/delete EventHandler,这三个EventHandler都会将Pod对应的StatefulSet加入到StatefulSet Queue中。
- StatefulSet Informer同样注册了add/update/event EventHandler,也都会将StatefulSet加入到StatefulSet Queue中。
- 目前StatefulSetController还未感知PVC Informer的EventHandler,这里继续按照PVC Controller全部处理。在StatefulSet Controller创建和删除Pod时,会调用apiserver创建和删除对应的PVC。
- RevisionController类似,在StatefulSet Controller Reconcile时会创建或者删除对应的Revision。
StatefulSetController sync
接下来,会进入StatefulSetController的worker(只有一个worker,也就是只一个go routine),worker会从StatefulSet Queue中pop out一个StatefulSet对象,然后执行sync进行Reconcile操作。
// sync syncs the given statefulset.
func (ssc *StatefulSetController) sync(key string) error {startTime := time.Now()defer func() {glog.V(4).Infof("Finished syncing statefulset %q (%v)", key, time.Now().Sub(startTime))}()namespace, name, err := cache.SplitMetaNamespaceKey(key)if err != nil {return err}set, err := ssc.setLister.StatefulSets(namespace).Get(name)if errors.IsNotFound(err) {glog.Infof("StatefulSet has been deleted %v", key)return nil}if err != nil {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to retrieve StatefulSet %v from store: %v", key, err))return err}selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(set.Spec.Selector)if err != nil {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("error converting StatefulSet %v selector: %v", key, err))// This is a non-transient error, so don't retry.return nil}if err := ssc.adoptOrphanRevisions(set); err != nil {return err}pods, err := ssc.getPodsForStatefulSet(set, selector)if err != nil {return err}return ssc.syncStatefulSet(set, pods)
}
sync中根据setLabel匹配出所有revisions、然后检查这些revisions中是否有OwnerReference为空的,如果有,那说明存在Orphaned的Revisions。
注意:只要检查到有一个History Revision就会触发给所有的Resivions打上Patch:
{"metadata":{"ownerReferences":[{"apiVersion":"%s","kind":"%s","name":"%s","uid":"%s","controller":true,"blockOwnerDeletion":true}],"uid":"%s"}}调用getPodsForStatefulSet获取这个StatefulSet应该管理的Pods。
- 获取该StatefulSet对应Namesapce下所有的Pods;
- 执行ClaimPods操作:检查set和pod的Label是否匹配上,如果Label不匹配,那么需要release这个Pod,然后检查pod的name和StatefulSet name的格式是否能匹配上。对于都匹配上的,并且ControllerRef UID也相同的,则不需要处理。
- 如果Selector和ControllerRef都匹配不上,则执行ReleasePod操作,给Pod打Patch:
{“metadata":{"ownerReferences":[{"$patch":"delete","uid":"%s"}],"uid":"%s"}} - 对于Label和name格式能匹配上的,但是controllerRef为空的Pods,就执行AdoptPod,给Pod打上Patch:
{“metadata":{"ownerReferences":[{"apiVersion":"%s","kind":"%s","name":"%s","uid":"%s","controller":true,"blockOwnerDeletion":true}],"uid":"%s"}}
UpdateStatefulSet
syncStatefulSet的实现只是调用UpdateStatefulSet。
func (ssc *defaultStatefulSetControl) UpdateStatefulSet(set *apps.StatefulSet, pods []*v1.Pod) error {// list all revisions and sort themrevisions, err := ssc.ListRevisions(set)if err != nil {return err}history.SortControllerRevisions(revisions)// get the current, and update revisionscurrentRevision, updateRevision, collisionCount, err := ssc.getStatefulSetRevisions(set, revisions)if err != nil {return err}// perform the main update function and get the statusstatus, err := ssc.updateStatefulSet(set, currentRevision, updateRevision, collisionCount, pods)if err != nil {return err}// update the set's statuserr = ssc.updateStatefulSetStatus(set, status)if err != nil {return err}glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s pod status replicas=%d ready=%d current=%d updated=%d",set.Namespace,set.Name,status.Replicas,status.ReadyReplicas,status.CurrentReplicas,status.UpdatedReplicas)glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s revisions current=%s update=%s",set.Namespace,set.Name,status.CurrentRevision,status.UpdateRevision)// maintain the set's revision history limitreturn ssc.truncateHistory(set, pods, revisions, currentRevision, updateRevision)
}
UpdateStatefulSet主要流程为:
- ListRevisions获取该StatefulSet的所有Revisions,并按照Revision从小到大进行排序。
- getStatefulSetRevisions获取currentRevison和UpdateRevision。
- 只有当RollingUpdate策略时Partition不为0时,才会有部分Pods是updateRevision。
- 其他情况,所有Pods都得维持currentRevision。
- updateStatefulSet是StatefulSet Controller的核心逻辑,负责创建、更新、删除Pods,使得声明式target得以维护:
- 使得target state始终有Spec.Replicas个Running And Ready的Pods。
- 如果更新策略是RollingUpdate,并且Partition为0,则保证所有Pods都对应Status.CurrentRevision。
- 如果更新策略是RollingUpdate,并且Partition不为0,则ordinal小于Partition的Pods保持Status.CurrentRevision,而ordinal大于等于Partition的Pods更新到Status.UpdateRevision。
- 如果更新策略是OnDelete,则只有删除Pods时才会触发对应Pods的更新,也就是说与Revisions不关联。
- truncateHistory维护History Revision个数不超过
.Spec.RevisionHistoryLimit。
updateStatefulSet
updateStatefulSet是整个StatefulSetController的核心。
func (ssc *defaultStatefulSetControl) updateStatefulSet(set *apps.StatefulSet,currentRevision *apps.ControllerRevision,updateRevision *apps.ControllerRevision,collisionCount int32,pods []*v1.Pod) (*apps.StatefulSetStatus, error) {// get the current and update revisions of the set.currentSet, err := ApplyRevision(set, currentRevision)if err != nil {return nil, err}updateSet, err := ApplyRevision(set, updateRevision)if err != nil {return nil, err}// set the generation, and revisions in the returned statusstatus := apps.StatefulSetStatus{}status.ObservedGeneration = new(int64)*status.ObservedGeneration = set.Generationstatus.CurrentRevision = currentRevision.Namestatus.UpdateRevision = updateRevision.Namestatus.CollisionCount = new(int32)*status.CollisionCount = collisionCountreplicaCount := int(*set.Spec.Replicas)// slice that will contain all Pods such that 0 <= getOrdinal(pod) < set.Spec.Replicasreplicas := make([]*v1.Pod, replicaCount)// slice that will contain all Pods such that set.Spec.Replicas <= getOrdinal(pod)condemned := make([]*v1.Pod, 0, len(pods))unhealthy := 0firstUnhealthyOrdinal := math.MaxInt32var firstUnhealthyPod *v1.Pod// First we partition pods into two lists valid replicas and condemned Podsfor i := range pods {status.Replicas++// count the number of running and ready replicasif isRunningAndReady(pods[i]) {status.ReadyReplicas++}// count the number of current and update replicasif isCreated(pods[i]) && !isTerminating(pods[i]) {if getPodRevision(pods[i]) == currentRevision.Name {status.CurrentReplicas++} else if getPodRevision(pods[i]) == updateRevision.Name {status.UpdatedReplicas++}}if ord := getOrdinal(pods[i]); 0 <= ord && ord < replicaCount {// if the ordinal of the pod is within the range of the current number of replicas,// insert it at the indirection of its ordinalreplicas[ord] = pods[i]} else if ord >= replicaCount {// if the ordinal is greater than the number of replicas add it to the condemned listcondemned = append(condemned, pods[i])}// If the ordinal could not be parsed (ord < 0), ignore the Pod.}// for any empty indices in the sequence [0,set.Spec.Replicas) create a new Pod at the correct revisionfor ord := 0; ord < replicaCount; ord++ {if replicas[ord] == nil {replicas[ord] = newVersionedStatefulSetPod(currentSet,updateSet,currentRevision.Name,updateRevision.Name, ord)}}// sort the condemned Pods by their ordinalssort.Sort(ascendingOrdinal(condemned))// find the first unhealthy Podfor i := range replicas {if !isHealthy(replicas[i]) {unhealthy++if ord := getOrdinal(replicas[i]); ord < firstUnhealthyOrdinal {firstUnhealthyOrdinal = ordfirstUnhealthyPod = replicas[i]}}}for i := range condemned {if !isHealthy(condemned[i]) {unhealthy++if ord := getOrdinal(condemned[i]); ord < firstUnhealthyOrdinal {firstUnhealthyOrdinal = ordfirstUnhealthyPod = condemned[i]}}}if unhealthy > 0 {glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s has %d unhealthy Pods starting with %s",set.Namespace,set.Name,unhealthy,firstUnhealthyPod.Name)}// If the StatefulSet is being deleted, don't do anything other than updating// status.if set.DeletionTimestamp != nil {return &status, nil}monotonic := !allowsBurst(set)// Examine each replica with respect to its ordinalfor i := range replicas {// delete and recreate failed podsif isFailed(replicas[i]) {glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s is recreating failed Pod %s",set.Namespace,set.Name,replicas[i].Name)if err := ssc.podControl.DeleteStatefulPod(set, replicas[i]); err != nil {return &status, err}if getPodRevision(replicas[i]) == currentRevision.Name {status.CurrentReplicas--} else if getPodRevision(replicas[i]) == updateRevision.Name {status.UpdatedReplicas--}status.Replicas--replicas[i] = newVersionedStatefulSetPod(currentSet,updateSet,currentRevision.Name,updateRevision.Name,i)}// If we find a Pod that has not been created we create the Podif !isCreated(replicas[i]) {if err := ssc.podControl.CreateStatefulPod(set, replicas[i]); err != nil {return &status, err}status.Replicas++if getPodRevision(replicas[i]) == currentRevision.Name {status.CurrentReplicas++} else if getPodRevision(replicas[i]) == updateRevision.Name {status.UpdatedReplicas++}// if the set does not allow bursting, return immediatelyif monotonic {return &status, nil}// pod created, no more work possible for this roundcontinue}// If we find a Pod that is currently terminating, we must wait until graceful deletion// completes before we continue to make progress.if isTerminating(replicas[i]) && monotonic {glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to Terminate",set.Namespace,set.Name,replicas[i].Name)return &status, nil}// If we have a Pod that has been created but is not running and ready we can not make progress.// We must ensure that all for each Pod, when we create it, all of its predecessors, with respect to its// ordinal, are Running and Ready.if !isRunningAndReady(replicas[i]) && monotonic {glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to be Running and Ready",set.Namespace,set.Name,replicas[i].Name)return &status, nil}// Enforce the StatefulSet invariantsif identityMatches(set, replicas[i]) && storageMatches(set, replicas[i]) {continue}// Make a deep copy so we don't mutate the shared cachereplica := replicas[i].DeepCopy()if err := ssc.podControl.UpdateStatefulPod(updateSet, replica); err != nil {return &status, err}}// At this point, all of the current Replicas are Running and Ready, we can consider termination.// We will wait for all predecessors to be Running and Ready prior to attempting a deletion.// We will terminate Pods in a monotonically decreasing order over [len(pods),set.Spec.Replicas).// Note that we do not resurrect Pods in this interval. Also not that scaling will take precedence over// updates.for target := len(condemned) - 1; target >= 0; target-- {// wait for terminating pods to expireif isTerminating(condemned[target]) {glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to Terminate prior to scale down",set.Namespace,set.Name,condemned[target].Name)// block if we are in monotonic modeif monotonic {return &status, nil}continue}// if we are in monotonic mode and the condemned target is not the first unhealthy Pod blockif !isRunningAndReady(condemned[target]) && monotonic && condemned[target] != firstUnhealthyPod {glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to be Running and Ready prior to scale down",set.Namespace,set.Name,firstUnhealthyPod.Name)return &status, nil}glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s terminating Pod %s for scale dowm",set.Namespace,set.Name,condemned[target].Name)if err := ssc.podControl.DeleteStatefulPod(set, condemned[target]); err != nil {return &status, err}if getPodRevision(condemned[target]) == currentRevision.Name {status.CurrentReplicas--} else if getPodRevision(condemned[target]) == updateRevision.Name {status.UpdatedReplicas--}if monotonic {return &status, nil}}// for the OnDelete strategy we short circuit. Pods will be updated when they are manually deleted.if set.Spec.UpdateStrategy.Type == apps.OnDeleteStatefulSetStrategyType {return &status, nil}// we compute the minimum ordinal of the target sequence for a destructive update based on the strategy.updateMin := 0if set.Spec.UpdateStrategy.RollingUpdate != nil {updateMin = int(*set.Spec.UpdateStrategy.RollingUpdate.Partition)}// we terminate the Pod with the largest ordinal that does not match the update revision.for target := len(replicas) - 1; target >= updateMin; target-- {// delete the Pod if it is not already terminating and does not match the update revision.if getPodRevision(replicas[target]) != updateRevision.Name && !isTerminating(replicas[target]) {glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s terminating Pod %s for update",set.Namespace,set.Name,replicas[target].Name)err := ssc.podControl.DeleteStatefulPod(set, replicas[target])status.CurrentReplicas--return &status, err}// wait for unhealthy Pods on updateif !isHealthy(replicas[target]) {glog.V(4).Infof("StatefulSet %s/%s is waiting for Pod %s to update",set.Namespace,set.Name,replicas[target].Name)return &status, nil}}return &status, nil
}
主要流程:
获取currentRevision和updateRevision对应的StatefulSet Object,并设置generation,currentRevision, updateRevision等信息到StatefulSet status。
将前面getPodsForStatefulSet获取到的pods分成两个slice:
- valid replicas slice: : 0 <= getOrdinal(pod) < set.Spec.Replicas
- condemned pods slice: set.Spec.Replicas <= getOrdinal(pod)
如果valid replicas中存在某些ordinal没有对应的Pod,则创建对应Revision的Pods Object,后面会检测到该Pod没有真实创建就会去创建对应的Pod实例:
- 如果更新策略是RollingUpdate且Partition为0或者ordinal < Partition,则使用currentRevision创建该Pod Object。
- 如果更新策略时RollingUpdate且Partition不为0且ordinal >= Partition,则使用updateRevision创建该Pod Object。
从valid repilcas和condemned pods两个slices中找出第一个unhealthy的Pod。(ordinal最小的unhealth pod)
healthy pods means:pods is running and ready, and not terminating.
对于正在删除(DeletionTimestamp非空)的StatefulSet,不做任何操作,直接返回当前status。
遍历valid replicas中pods,保证valid replicas中index在[0,spec.replicas)的pod都是Running And Ready的:
- 如果检测到某个pod Failed (pod.Status.Phase = Failed), 则删除这个Pod,并重新new这个pod object(注意revisions匹配)
- 如果这个pod还没有recreate,则Create it。
- 如果ParallelPodManagement = "OrderedReady”,则直接返回当前status。否则ParallelPodManagement = "Parallel”,则循环检测下一个。
- 如果pod正在删除并且ParallelPodManagement = "OrderedReady”,则返回status结束。
- 如果pod不是RunningAndReady状态,并且ParallelPodManagement = "OrderedReady”,则返回status结束。
- 检测该pod与statefulset的identity和storage是否匹配,如果有一个不匹配,则调用apiserver Update Stateful Pod进行updateIdentity和updateStorage(并创建对应的PVC),返回status,结束。
Pod is Running and Ready means:
pod.Status.Phase = Runnin,
pod.Status.Condition = Ready遍历condemned replicas中pods,index由大到小的顺序,确保这些pods最终都被删除:
- 如果这个Pod正在删除(DeletionTimestamp),并且Pod Management是OrderedReady,则进行Block住,返回status,流程结束。
- 如果是OrderedReady策略,Pod不是处于Running and Ready状态,且该pod不是first unhealthy pod,则返回status,流程结束。
- 其他情况,则删除该statefulset pod。
- 根据该pod的controller-revision-hash Label获取Revision,如果等于currentRevision,则更新status.CurrentReplicas;如果等于updateRevision,则更新status.UpdatedReplicas;
- 如果是OrderedReady策略,则返回status,流程结束。
OnDelete更新策略:删除Pod才会触发更新这个ordinal的更新 如果UpdateStrategy Type是OnDelete, 意味着只有当对应的Pods被手动删除后,才会触发Recreate,因此直接返回status,流程结束。
RollingUpdate更新策略:(Partition不设置就相当于0,意味着全部pods进行滚动更新) 如果UpdateStrategy Type是RollingUpdate, 根据RollingUpdate中
Partition配置得到updateMin作为update replicas index区间最小值,遍历valid replicas,index从最大值到updateMin递减的顺序:- 如果pod revision不是updateRevision,并且不是正在删除的,则删除这个pod,并更新status.CurrentReplicas,然后返回status,流程结束。
- 如果pod不是healthy的,那么将等待它变成healthy,因此这里就直接返回status,流程结束。
Identity Match
updateStatefulSet Reconcile中,会检查identity match的情况,具体包含哪些?
StatefulSetPodNameLabel = "statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name"// identityMatches returns true if pod has a valid identity and network identity for a member of set.
func identityMatches(set *apps.StatefulSet, pod *v1.Pod) bool {parent, ordinal := getParentNameAndOrdinal(pod)return ordinal >= 0 &&set.Name == parent &&pod.Name == getPodName(set, ordinal) &&pod.Namespace == set.Namespace &&pod.Labels[apps.StatefulSetPodNameLabel] == pod.Name
}
- pod name和statefulset name内容匹配。
- namespace匹配。
- Pod的Label:
statefulset.kubernetes.io/pod-name与Pod name真实匹配。
Storage Match
updateStatefulSet Reconcile中,会检查Storage match的情况,具体怎么匹配的呢?
// storageMatches returns true if pod's Volumes cover the set of PersistentVolumeClaims
func storageMatches(set *apps.StatefulSet, pod *v1.Pod) bool {ordinal := getOrdinal(pod)if ordinal < 0 {return false}volumes := make(map[string]v1.Volume, len(pod.Spec.Volumes))for _, volume := range pod.Spec.Volumes {volumes[volume.Name] = volume}for _, claim := range set.Spec.VolumeClaimTemplates {volume, found := volumes[claim.Name]if !found ||volume.VolumeSource.PersistentVolumeClaim == nil ||volume.VolumeSource.PersistentVolumeClaim.ClaimName !=getPersistentVolumeClaimName(set, &claim, ordinal) {return false}}return true
}
Code Logic Diagram
基于上述分析,下面是一个相对完整的StatefulSetController的代码逻辑图。 (不支持大于2MB的图片,所以不太清晰,不过基本在前面内容都提到了。)
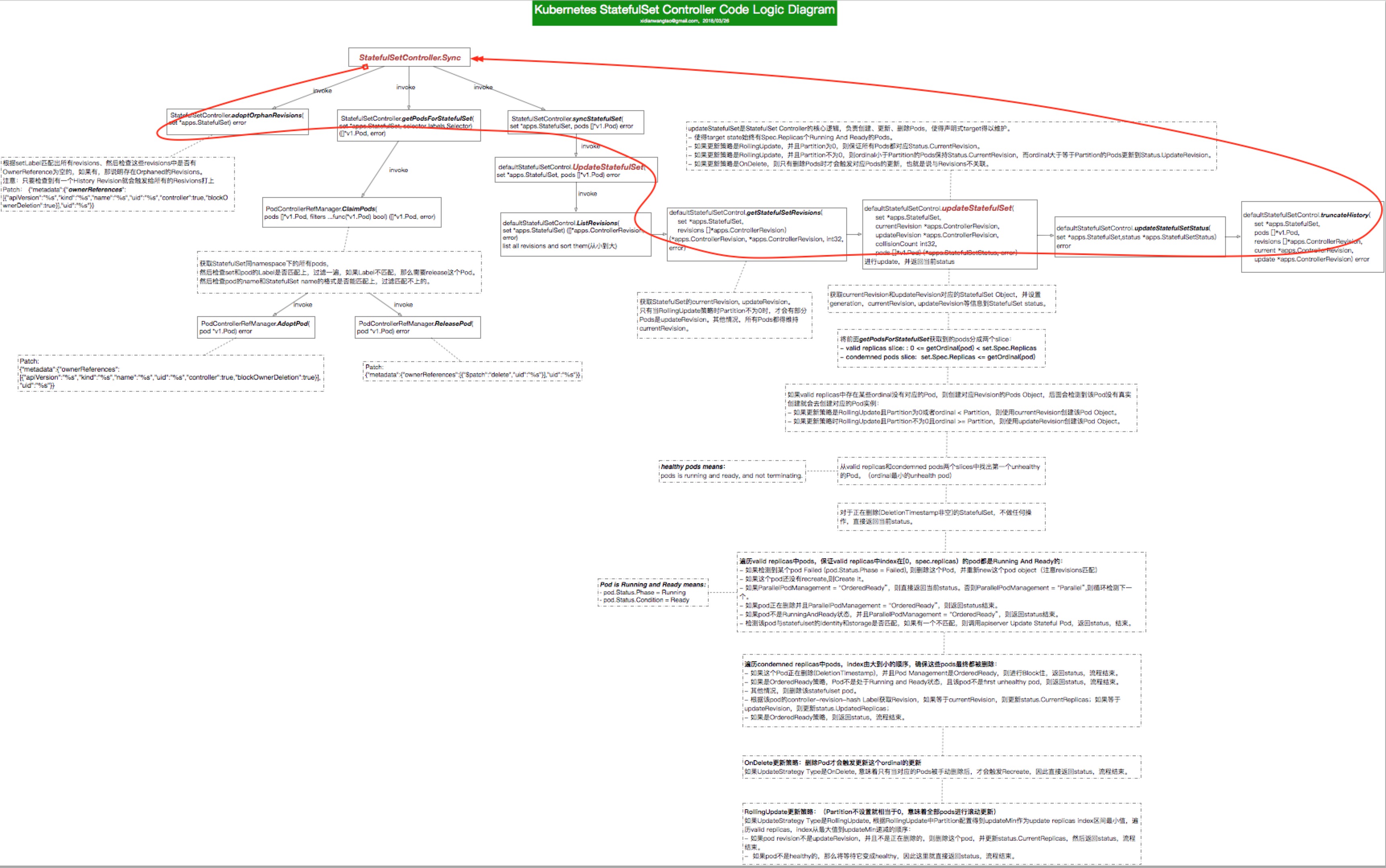
思考
滚动更新过程中出现异常
在上一篇博文浅析Kubernetes StatefulSet中遗留了一个问题:StatefulSet滚动更新时,如果某个Pod更新失败,会怎么办呢?
通过上面源码分析中滚动更新部分的分析,我们知道:
- 如果UpdateStrategy Type是RollingUpdate, 根据RollingUpdate中
Partition(Partition不设置就相当于0,意味着全部pods进行滚动更新)配置得到updateMin作为update replicas index区间最小值,遍历valid replicas,index从最大值到updateMin递减的顺序:- 如果pod revision不是updateRevision,并且不是正在删除的,则删除这个pod,并更新status.CurrentReplicas,然后返回status,流程结束。
- 如果pod不是healthy的,那么将等待它变成healthy,因此这里就直接返回status,流程结束。
知道这一点后,就能回答这个问题了,答案很简单:
- 如果更新策略是RollingUpdate,则逐个滚动更新过程中,如果在更新某个ordinal replica时这个Pod一直无法达到Running and Ready状态,那么整个滚动更新流程将Block在这里。还没有更新的replicas将不会触发更新,已经更新成功的replicas就保持更新后的版本,并不存在什么自动回滚的机制。在下一次sync时,检测到这个Pod isFailed(pod.Status.Phase = Failed),会delete and recreate这个failed pod。
podManagementPolicy设置为Parallel时,体现在哪?
问题:podManagementPolicy: "Parallel"体现在什么时候呢?Scale的时候?RollingUpdate的时候?
- 在前面代码分析中updateStatefulSet中那段-"遍历valid replicas中pods,保证valid replicas中index在[0,spec.replicas)的pod都是Running And Ready的":如果发现某个ordinal replica应该创建但是还没被创建,则会触发create。如果podManagementPolicy设置为Parallel,则会继续
delete then create其他应该创建的replicas,而不会等待前面创建的replicas成为Running and Ready。 - 在前面代码分析中updateStatefulSet中那段-”遍历condemned replicas中pods,index由大到小的顺序,确保这些pods最终都被删除":podManagementPolicy设置为Parallel,如果发现某个ordinal replica正在删除,则继续删除其他应该删除的replicas,而不会等待之前删除的replica重建并成为Running and Ready状态。
因此Parallel体现在以下场景:
- 初始化部署StatefulSet时,并行create pods。
- 级联删除StatefulSet时,并行delete pods。
- Scale up时,并行create pods。
- Scale down时,并行delete pods。
而在滚动更新时,是不会受podManagementPolicy的配置影响的,都是按照逐个地、ordinal从大到小的的顺序,保证前者Running and Ready的原则,进行RollingUpdate。
如果更新策略是OnDelete呢?那情况就不同于RollingUpdate了,因为update的流程就体现在前面提到的两个阶段了,因此Parallel是会启作用的。
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/jxcdwangtao/blog/1784739
Kubernetes StatefulSet源码分析相关推荐
- k8s源码分析 pdf_Spark Kubernetes 的源码分析系列 - features
1 Overview features 包里的代码,主要是用于构建 Spark 在 K8S 中的各类资源所需要的特征,个人觉得可以理解成这些 features 就是帮你写各类 Kind 的 YAML ...
- kubernetes apiserver源码分析二之路由
apiserver的man函数在 k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kube-apiserver 目录. 但是大部分源码却在 k8s.io/apiserver 这个库里面. cmd 目录下的 ...
- 【kubernetes/k8s源码分析】 kubelet cgroup 资源预留源码分析
kubernetes 1.13 WHY 默认情况下 pod 能够使用节点全部可用资源.用户 pod 中的应用疯狂占用内存,pod 将与 node 上的系统守护进程和 kubernetes 组件争夺资源 ...
- kubernetes hpa源码分析
初始化 文件位置:cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/controllermanager.go func NewControllerInitializers(loopMod ...
- 【kubernetes/k8s源码分析】eviction机制原理以及源码解析
kubernetes v1.12.1 What? kubelet 驱赶的是节点上的某些 Pod,驱赶哪些 Pod与 Qos 机制有关(1.8),1.9 以后的版本请看下文分解 只有当节点内存和磁盘资源 ...
- Kubernetes Scheduler源码分析--启动过程与多队列缓存(续)
继续上文对Scheduler的分析,分析在Scheduler主循环处理过程中,podQueue,Queue和assumePod 三个队列的处理. Scheduler中SchedulerOne为主要的处 ...
- 【kubernetes/k8s源码分析】kubelet cri源码分析
CRI基本原理 早期的 kubernetes 使用 docker 作为默认的 runtime,后来又加入 rkt,每加入一种新运行时,k8s 都要修改接口.container runtime 加入,不 ...
- kubernetes 源码分析之节点异常时 pod 驱逐过程
概述 在 Kubernetes 集群中,当节点由于某些原因(网络.宕机等)不能正常工作时会被认定为不可用状态(Unknown 或者 False 状态),当时间超过了 pod-eviction-time ...
- kubeadm源码分析(内含kubernetes离线包,三步安装)
k8s离线安装包 三步安装,简单到难以置信 kubeadm源码分析 说句实在话,kubeadm的代码写的真心一般,质量不是很高. 几个关键点来先说一下kubeadm干的几个核心的事: kubeadm ...
最新文章
- html5 将id的值用于top_web前端分享HTML5常见面试题集锦四
- 三心二意,助你好运?
- 《工具癖》Mac与Windows获取文件绝对路径的快捷键
- JSON 在线工具 BeJson
- 夜神模拟器连接手柄无反应_夜神模拟器怎么连接手柄?夜神模拟器连接手柄具体操作...
- StarUML画用例图
- internal, switching, leakage power区别
- centos 安装SDCC编译器
- 如何在五分钟让你的应用拥有高精度定位功能
- 什么是restful,什么是rest风格
- 一节课轻松通关 Spark
- 20套各种风格影视动画公司响应式企业模电影上映影讯网站模板电影软件网页CSS模板html5网页静态模板Bootstrap扁平化网站源码css3手机seo自适响应
- == 和 === 有什么区别?
- 微信小程序怎么集成腾讯IM
- 1、编写一个程序,将一个小写字母(如a)转换成相应的大写字母并显示输出。
- 驾图车联网:区块链重塑汽车大数据的价值链和生态链
- 【模拟】寄居蟹与海葵
- IOS查看包名、版本号、设备信息、签名、进程ID
- 03_根据配置文件创建SqlSessionFactory(Configuration的创建过程)
- matlab肺部病灶提取,肺结节CT影像特征提取(四)——肺结节CT影像特征提取MATLAB代码实现...
热门文章
- 武汉大学计算机学院 毕业答辩,“云答辩”详细流程出炉! 武大本科生毕业答辩这样办...
- 平流式初沉池贮砂斗计算_给排水之市政污水处理构筑物:平流式、曝气式、旋流式三大沉砂池...
- 混合app用百分比还是rem_一次搞懂前端所有CSS长度单位,px、em、rem、rpx、%....
- vue判断浏览器是否id_QQ被曝读取浏览器历史记录!回应称系用于判断是否恶意登录...
- matlab--奇奇怪怪函数
- 【 Vivado 】工程模式下运用Tcl脚本示范
- 【 MATLAB 】使用 MATLAB 得到高密度谱(补零得到DFT)和高分辨率谱(获得更多的数据得到DFT)的方式对比(附MATLAB脚本)
- C# WPF动点任意移动气泡画法(解决方案使用到数学勾股定理、正弦定理、向量知识)。...
- Spring MVC 解读——mvc:annotation-driven/
- 2017 CIO展望:新IT运营模式的5大元素
