java 四种实现延迟加载的方法
1. 延迟初始化
2. 虚拟代理(virtual proxy)
原文地址: http://www.oodesign.com/proxy-pattern.html
Intent
- The intent of this pattern is to provide a 《Placeholder》 for an object to control references to it.
Implementation
The figure below shows a UML class diagram for the Proxy Pattern:
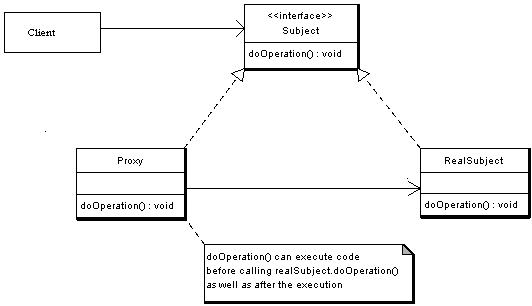
The participants classes in the proxy pattern are:
- Subject - Interface implemented by the RealSubject and representing its services. The interface must be implemented by the proxy as well so that the proxy can be used in any location where the RealSubject can be used.
- Proxy
- Maintains a reference that allows the Proxy to access the RealSubject.
- Implements the same interface implemented by the RealSubject so that the Proxy can be substituted for the RealSubject.
- Controls access to the RealSubject and may be responsible for its creation and deletion.
- Other responsibilities depend on the kind of proxy.
- RealSubject - the real object that the proxy represents.
Applicability & Examples
The Proxy design pattern is applicable when there is a need to control access to an Object, as well as when there is a need for a sophisticated reference to an Object. Common Situations where the proxy pattern is applicable are:
- Virtual Proxies: delaying the creation and initialization of expensive objects until needed, where the objects are created on demand (For example creating the RealSubject object only when the doSomething method is invoked).
- Remote Proxies: providing a local representation for an object that is in a different address space. A common example is Java RMI stub objects. The stub object acts as a proxy where invoking methods on the stub would cause the stub to communicate and invoke methods on a remote object (called skeleton) found on a different machine.
- Protection Proxies: where a proxy controls access to RealSubject methods, by giving access to some objects while denying access to others.
- Smart References: providing a sophisticated access to certain objects such as tracking the number of references to an object and denying access if a certain number is reached, as well as loading an object from database into memory on demand.
Example - Virtual Proxy Example.
Consider an image viewer program that lists and displays high resolution photos. The program has to show a list of all photos however it does not need to display the actual photo until the user selects an image item from a list.
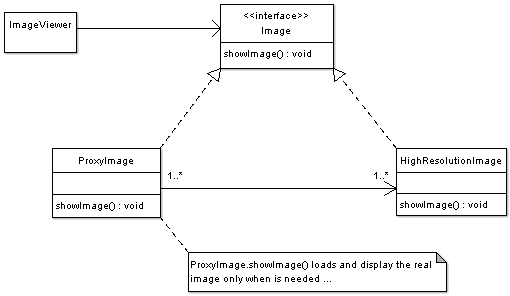
The code below shows the Image interface representing the Subject. The interface has a single method showImage() that the Concrete Images must implement to render an image to screen.
package proxy;/*** Subject Interface*/
public interface Image {public void showImage();}
|
The code below shows the Proxy implementation, the image proxy is a virtual proxy that creates and loads the actual image object on demand, thus saving the cost of loading an image into memory until it needs to be rendered:
package proxy;/*** Proxy*/
public class ImageProxy implements Image {/*** Private Proxy data */private String imageFilePath;/*** Reference to RealSubject*/private Image proxifiedImage;public ImageProxy(String imageFilePath) {this.imageFilePath= imageFilePath; }@Overridepublic void showImage() {// create the Image Object only when the image is required to be shownproxifiedImage = new HighResolutionImage(imageFilePath);// now call showImage on realSubjectproxifiedImage.showImage();}}
|
The code below displays the RealSubject Implementation, which is the concrete and heavyweight implementation of the image interface. The High resolution image, loads a high resolution image from disk, and renders it to screen when showImage() is called.
package proxy;/*** RealSubject*/
public class HighResolutionImage implements Image {public HighResolutionImage(String imageFilePath) {loadImage(imageFilePath);}private void loadImage(String imageFilePath) {// load Image from disk into memory// this is heavy and costly operation}@Overridepublic void showImage() {// Actual Image rendering logic}}
|
The code below illustrates a sample image viewer program; the program simply loads three images, and renders only one image, once using the proxy pattern, and another time directly. Note that when using the proxy pattern, although three images have been loaded, the High resolution image is not loaded into memory until it needs to be rendered, while in the part not using the proxy, the three images are loaded into memory although one of them is actually rendered.
package proxy;/*** Image Viewer program*/
public class ImageViewer {public static void main(String[] args) {// assuming that the user selects a folder that has 3 images //create the 3 images Image highResolutionImage1 = new ImageProxy("sample/veryHighResPhoto1.jpeg");Image highResolutionImage2 = new ImageProxy("sample/veryHighResPhoto2.jpeg");Image highResolutionImage3 = new ImageProxy("sample/veryHighResPhoto3.jpeg");// assume that the user clicks on Image one item in a list// this would cause the program to call showImage() for that image only// note that in this case only image one was loaded into memoryhighResolutionImage1.showImage();// consider using the high resolution image object directlyImage highResolutionImageNoProxy1 = new HighResolutionImage("sample/veryHighResPhoto1.jpeg");Image highResolutionImageNoProxy2 = new HighResolutionImage("sample/veryHighResPhoto2.jpeg");Image highResolutionImageBoProxy3 = new HighResolutionImage("sample/veryHighResPhoto3.jpeg");// assume that the user selects image two item from images listhighResolutionImageNoProxy2.showImage();// note that in this case all images have been loaded into memory // and not all have been actually displayed// this is a waste of memory resources}}
|
Specific problems and implementation
Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI)
In java RMI an object on one machine (executing in one JVM) called a client can invoke methods on an object in another machine (another JVM) the second object is called a remote object. The proxy (also called a stub) resides on the client machine and the client invokes the proxy in as if it is invoking the object itself (remember that the proxy implements the same interface that RealSubject implements). The proxy itself will handle communication to the remote object, invoke the method on that remote object, and would return the result if any to the client. The proxy in this case is a Remote proxy.
3. 保值器(value holder)
4. 备份(ghost)
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/davidwang456/p/4071607.html
java 四种实现延迟加载的方法相关推荐
- JAVA四种遍历Map的方法
导入java.util.hashmap: 导入java.util.iterator: 导入java.util.map: 导入java.util.set: 公共类映射{ 公共静态void main(st ...
- java中高效遍历list_Java中四种遍历List的方法总结(推荐)
实例如下: package com.ietree.basic.collection.loop; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterato ...
- java遍历list_Java中四种遍历List的方法总结(推荐)
实例如下: package com.ietree.basic.collection.loop; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterato ...
- JAVA四种基本排序总结
JAVA四种基本排序,包括冒泡法,插入法,选择法,SHELL排序法.其中选择法是冒泡法的改进,SHELL排序法是 插入法的改进.所以从根本上来说可以归纳为两种不同的排序方法:即:插入法&冒泡法 ...
- [转]new Thread的弊端及Java四种线程池的使用
介绍new Thread的弊端及Java四种线程池的使用,对Android同样适用.本文是基础篇,后面会分享下线程池一些高级功能. 1.new Thread的弊端 执行一个异步任务你还只是如下new ...
- java 四种元注解@Target、@Retention、@Documented 和@Inherited
java 四种元注解@Target.@Retention.@Documented 和@Inherited @Target 表示该注解用于什么地方,可能的值在枚举类 ElemenetType 中,包括: ...
- Java四种线程池使用
Java 四种线程池的使用 https://juejin.im/post/59df0c1af265da432f301c8d 1,线程池的作用 线程池作用就是限制系统中执行线程的数量. 根据系统的环 ...
- WindowsServer2012史记7-茴香豆的五种写法和四种”显示计算机”的方法
消失的"计算机"? [这周九叔工作比较忙,还有其他琐事缠身,因此SystemCenter2012SP1系列的发布稍慢,抱歉了各位.] 众所周知,WindowsServer2012和 ...
- JAVA四种引用方式
JAVA四种引用方式: java.lang.ref: 强引用(直接变量赋值) 软引用(SoftReference): 只有在要发生OOM错误之前才会回收掉老的软引用对象,应用场景主要防止内存溢出.(缓 ...
最新文章
- CVPR2020 | 商汤-港中文等提出PV-RCNN:3D目标检测新网络
- 学python用什么系统好-Python用什么系统环境好?老男孩Python
- COM原理与应用之COM的实现
- 【论文学习】ICLR2021,鲁棒早期学习法:抑制记忆噪声标签ROBUST EARLY-LEARNING: HINDERING THE MEMORIZATION OF NOISY LABELS
- java解决斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence)
- linux线程同步 eventfd,用 eventfd 在线程之间通信
- node.js超过php,在nodejs中如何解决超出最大的调用栈错误
- Bookshelf 2 POJ - 3628(01背包||DFS)
- sharepoint 2010如何下载文件
- 风力摆控制系统,stm32f1程序,通过pid控制算法实现了风力摆摆定长直线,变长直线,一定角度摆动,定点停滞
- IDM统一认证功能说明
- Docker入门之-网络(三):容器如何与外部世界通信
- 思科交换机的基础操作命令有这些!
- XPDL与WS-BPEL的比较之二:二者内容的大致概述
- Vue3 异步组件 suspense
- 【亲测成功】Ubuntu18.04升级GLIBC2.27——解决报错:ibc.so.6: version `GLIBC_2.28‘ not found
- SAP PI/PO 视频,自己录制
- 跨境电商B2B是什么?跨境电商B2B模式如何定义?
- DPR300 超声波高压脉冲发生/接收器
- 力扣PTA~每天至少三题
