机器学习实战:GBDT Xgboost LightGBM对比
Mnist数据集识别
使用Sklearn的GBDT
GradientBoostingClassifier
GradientBoostingRegressor
import gzip
import pickle as pkl
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitdef load_data(path):f = gzip.open(path, 'rb')try:#Python3train_set, valid_set, test_set = pkl.load(f, encoding='latin1')except:#Python2train_set, valid_set, test_set = pkl.load(f)f.close()return(train_set,valid_set,test_set)path = 'mnist.pkl.gz'
train_set,valid_set,test_set = load_data(path)Xtrain,_,ytrain,_ = train_test_split(train_set[0], train_set[1], test_size=0.9)
Xtest,_,ytest,_ = train_test_split(test_set[0], test_set[1], test_size=0.9)
print(Xtrain.shape, ytrain.shape, Xtest.shape, ytest.shape)
(5000, 784) (5000,) (1000, 784) (1000,)
参数说明:
learning_rate: The learning parameter controls the magnitude of this change in the estimates. (default=0.1)
n_extimators: The number of sequential trees to be modeled. (default=100)
max_depth: The maximum depth of a tree. (default=3)
min_samples_split: Tthe minimum number of samples (or observations) which are required in a node to be considered for splitting. (default=2)
min_samples_leaf: The minimum samples (or observations) required in a terminal node or leaf. (default=1)
min_weight_fraction_leaf: Similar to min_samples_leaf but defined as a fraction of the total number of observations instead of an integer. (default=0.)
subsample: The fraction of observations to be selected for each tree. Selection is done by random sampling. (default=1.0)
max_features: The number of features to consider while searching for a best split. These will be randomly selected. (default=None)
max_leaf_nodes: The maximum number of terminal nodes or leaves in a tree. (default=None)
min_impurity_decrease: A node will be split if this split induces a decrease of the impurity greater than or equal to this value. (default=0.)
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
import numpy as np
import time clf = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=10, learning_rate=0.1, max_depth=3)# start training
start_time = time.time()
clf.fit(Xtrain, ytrain)
end_time = time.time()
print('The training time = {}'.format(end_time - start_time))# prediction and evaluation
pred = clf.predict(Xtest)
accuracy = np.sum(pred == ytest) / pred.shape[0]
print('Test accuracy = {}'.format(accuracy))
The training time = 11.989675521850586
Test accuracy = 0.825
集成算法可以得出特征重要性,说白了就是看各个树使用特征的情况,使用的多当然就重要了,这是分类器告诉我们的。
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.hist(clf.feature_importances_)
print(max(clf.feature_importances_), min(clf.feature_importances_))
0.0249318971528 0.0
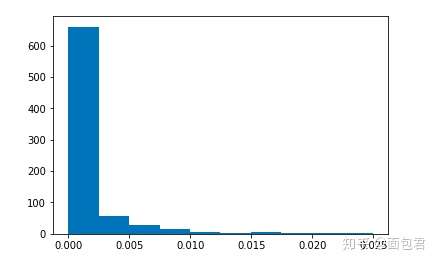
一般情况下,我们还可以筛选一下。
from collections import OrderedDict
d = {}
for i in range(len(clf.feature_importances_)):if clf.feature_importances_[i] > 0.01:d[i] = clf.feature_importances_[i]sorted_feature_importances = OrderedDict(sorted(d.items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True))
D = sorted_feature_importances
rects = plt.bar(range(len(D)), D.values(), align='center')
plt.xticks(range(len(D)), D.keys(),rotation=90)
plt.show()
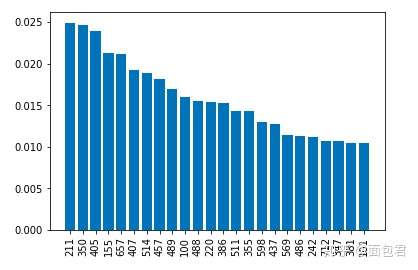
由于是像素点,所以看的没那么直观,正常特征看起来其实蛮直接的。
XGBoost
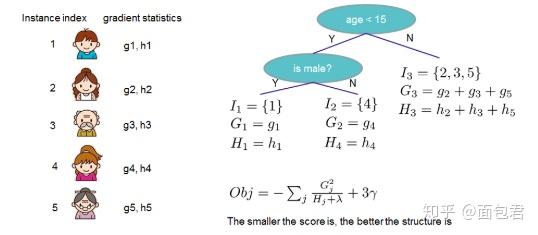
加入了更多的剪枝策略和正则项,控制过拟合风险。传统的GBDT用的是CART,Xgboost能支持的分类器更多,也可以是线性的。GBDT只用了一阶导,但是xgboost对损失函数做了二阶的泰勒展开,并且还可以自定义损失函数。
import xgboost as xgb
import numpy as np
import time# read data into Xgboost DMatrix format
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(Xtrain, label=ytrain)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(Xtest, label=ytest)# specify parameters via map
params = {'booster':'gbtree', # tree-based models'objective': 'multi:softmax', 'num_class':10, 'eta': 0.1, # Same to learning rate'gamma':0, # Similar to min_impurity_decrease in GBDT'alpha': 0, # L1 regularization term on weight (analogous to Lasso regression)'lambda': 2, # L2 regularization term on weights (analogous to Ridge regression)'max_depth': 3, # Same as the max_depth of GBDT'subsample': 1, # Same as the subsample of GBDT'colsample_bytree': 1, # Similar to max_features in GBM'min_child_weight': 1, # minimum sum of instance weight (Hessian) needed in a child'nthread':1, # default to maximum number of threads available if not set
}
num_round = 10# start training
start_time = time.time()
bst = xgb.train(params, dtrain, num_round)
end_time = time.time()
print('The training time = {}'.format(end_time - start_time))# get prediction and evaluate
ypred = bst.predict(dtest)
accuracy = np.sum(ypred == ytest) / ypred.shape[0]
print('Test accuracy = {}'.format(accuracy))
The training time = 13.496984481811523
Test accuracy = 0.821
Xgboost参数
LightGBM
放到最后肯定有一堆优点的:
- 更快的训练效率
- 低内存使用
- 更好的准确率
- 支持并行学习
- 可处理大规模数据
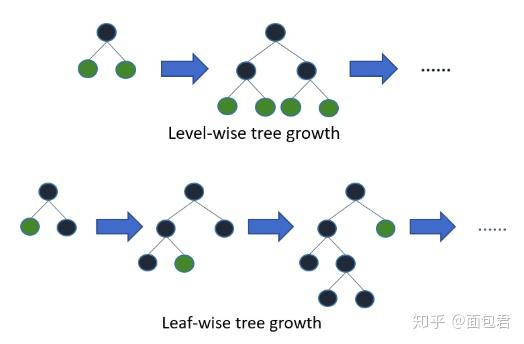
它摒弃了现在大部分GBDT使用的按层生长(level-wise)的决策树生长策略,使用带有深度限制的按叶子生长(leaf-wise)的策略。level-wise过一次数据可以同时分裂同一层的叶子,容易进行多线程优化,也好控制模型复杂度,不容易过拟合。但实际上level-wise是一种低效的算法,因为它不加区分的对待同一层的叶子,带来了很多没必要的开销,因为实际上很多叶子的分裂增益较低,没必要进行搜索和分裂。
Leaf-wise则是一种更为高效的策略,每次从当前所有叶子中,找到分裂增益最大的一个叶子,然后分裂,如此循环。因此同Level-wise相比,在分裂次数相同的情况下,Leaf-wise可以降低更多的误差,得到更好的精度。Leaf-wise的缺点是可能会长出比较深的决策树,产生过拟合。因此LightGBM在Leaf-wise之上增加了一个最大深度的限制,在保证高效率的同时防止过拟合。
安装指引
import lightgbm as lgb
train_data = lgb.Dataset(Xtrain, label=ytrain)
test_data = lgb.Dataset(Xtest, label=ytest)# specify parameters via map
params = {'num_leaves':31, # Same to max_leaf_nodes in GBDT, but GBDT's default value is None'max_depth': -1, # Same to max_depth of xgboost'tree_learner': 'serial', 'application':'multiclass', # Same to objective of xgboost'num_class':10, # Same to num_class of xgboost'learning_rate': 0.1, # Same to eta of xgboost'min_split_gain': 0, # Same to gamma of xgboost'lambda_l1': 0, # Same to alpha of xgboost'lambda_l2': 0, # Same to lambda of xgboost'min_data_in_leaf': 20, # Same to min_samples_leaf of GBDT'bagging_fraction': 1.0, # Same to subsample of xgboost'bagging_freq': 0,'bagging_seed': 0,'feature_fraction': 1.0, # Same to colsample_bytree of xgboost'feature_fraction_seed': 2,'min_sum_hessian_in_leaf': 1e-3, # Same to min_child_weight of xgboost'num_threads': 1
}
num_round = 10# start training
start_time = time.time()
bst = lgb.train(params, train_data, num_round)
end_time = time.time()
print('The training time = {}'.format(end_time - start_time))# get prediction and evaluate
ypred_onehot = bst.predict(Xtest)
ypred = []
for i in range(len(ypred_onehot)):ypred.append(ypred_onehot[i].argmax())accuracy = np.sum(ypred == ytest) / len(ypred)
print('Test accuracy = {}'.format(accuracy))
The training time = 4.891559839248657
Test accuracy = 0.902
参数解释
结果对比
| | time(s) | accuracy(%) | |----------|---------|-------------| | GBDT | 11.98 | 0.825 | | XGBoost | 13.49 | 0.821 | | LightGBM | 4.89 | 0.902 |
http://lightgbm.apachecn.org/cn/latest/Parameters-Tuning.html
机器学习实战:GBDT Xgboost LightGBM对比相关推荐
- [机器学习] 树模型(xgboost,lightgbm)特征重要性原理总结
在使用GBDT.RF.Xgboost等树类模型建模时,往往可以通过 feature_importance 来返回特征重要性,各模型输出特征重要性的原理与方法 一 计算特征重要性方法 首先,目前计算特征 ...
- 机器学习实战:使用lightGBM预测饭店流量
饭店来客数据 CSV数据源:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1mLZBNv1SszQEnRoBGOYX7w 密码:mmrf import pandas as pdair_visi ...
- GBDT Xgboost LightGBM区别与联系
https://www.cnblogs.com/mata123/p/7440774.html
- 机器学习时代的三大神器:GBDT,XGBOOST和LightGBM
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/bbbeoy/article/details/79590981 本文主要简要的比较了常用的boosting算法的一些区别,从AdaBoost到Ligh ...
- 机器学习-决策树(XGBoost、LightGBM)
[机器学习]决策树--XGBoost.LightGBM 主要介绍基于 Boosting 框架的主流集成算法,包括 XGBoost 和 LightGBM. 1. XGBoost XGBoost 是大规模 ...
- 机器学习实战 | LightGBM建模应用详解
作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI 教程地址:https://www.showmeai.tech/tutorials/41 本文地址:https://www.showmeai.tech/article-d ...
- 【机器学习】深度剖析 LightGBM vs XGBOOST 哪个更胜一筹
今天就 LightGBM 和 XGBOOST 放在一起对比学习下,以便加深印象. 写在前面 作为一个机器学习研习者,大概会了解 Boosting Machines 及其功能.Boosting Mach ...
- 机器学习实战四:好事达保险索赔预测 Allstate Claims Severity (xgboost)
好事达保险索赔预测 Allstate Claims Severity (xgboost) 在这次Machine Learning中,我用了一个在学校做的一个项目来进行实战,当时老师给的数据还是比较小的 ...
- 随机森林RF、XGBoost、GBDT和LightGBM的原理和区别
随机森林RF.XGBoost.GBDT和LightGBM的原理和区别 https://www.cnblogs.com/hugechuanqi/p/10554156.html
最新文章
- CAS 与.net 集成的 “循环重定向”问题分析
- C#数据库(MySQL)帮助类
- 汇编中的条件转移指令
- linux 增加回环设备,linux命令练习:mount fdisk swap dd创建本地回环设备
- oracle grid需要安装,Oracle 11g Grid for Linux安装指南
- SharePoint 2010 RBS 安装和配置遇到的一个问题
- VMware虚拟机软件
- calc BZOJ 2655
- C#编码规范2[转]
- 【PHP代码审计】 那些年我们一起挖掘SQL注入 - 4.全局防护Bypass之二次注入
- wordpress登录美化css,wordpress后台login界面美化
- 走进中关村软件园-光环敏捷PMI-ACP落地分享会
- 《2019年中国互联网网络安全报告》发布,恶意程序攻击半数来自美国
- 音乐类软件LoveMusic开发(三)----登录界面
- Kaleao推出基于ARM的服务器Kmax
- 经典的股票量化交易策略(含源码)
- 【JS代码提高--003】:JavaScript 生成间于最小值和最大值之间的随机数
- Latex引用参考文献-BibTex的使用
- 在互联网大厂的程序员多久能挣够100万?
- clk子系统 - 驱动框架
热门文章
- excel 文档管理服务器,Excel Server Tutorial
- OpenStack的部署T版(七)——cinder模块
- 现实生活中常用的动态路由—OSPF路由重分发
- python炫酷特效代码_推荐几个炫酷的 Python 开源项目
- C语言浮点数据在内存中的存储方式
- c语言 字符串 正序再倒序_新特性解读 | MySQL 8.0 索引特性3 -倒序索引
- linux 循环每个月,SHELL脚本每月最后一天判断
- 道java_请问这道java里的这几个语句是什么意思
- mysql的安装胚子_下列哪个制剂是以主要药味缩写加剂型的原则命名的
- execjs回调python_python使用execJS运行js函数例子
