8.3实例程序:平面阴影
在场景中被灯光照射的地方会产生阴影,这将使场景变的更真实。在这一部分我们将演示怎样实现平面阴影,即在平面上的阴影(如图8.5)。
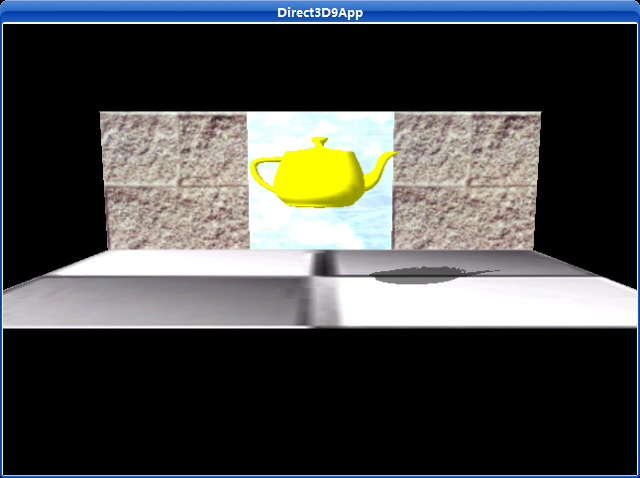
使用这种阴影只是一种权宜之计,虽然它增强了场景的真实效果,但是这并不是现实中的阴影。
为了实现平面阴影,我们首先必须找到物体投射到平面上的阴影并进行几何建模以便我们能够渲染它,用一些3D数学就能很容易的实现它,然后我们用50%透明度的黑色材质来渲染描述阴影的多边形。渲染阴影时可能出现“双倍混合”,我们将用一小部分进行解释,并使用模板缓存来防止双倍混合发生。
8.3.1平行光阴影
图8.6显示了物体在平行光照射下得到的阴影。光线是从平行光源放射出的,它的方向是L,通过顶点p得到r(t) = p + tL。光线r(t)和平面n * p + d = 0 相交得到 s 。
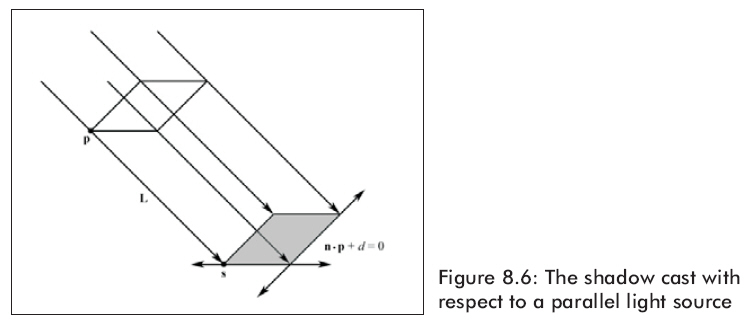
An intersection point s is easily found with a ray/plane intersection test:

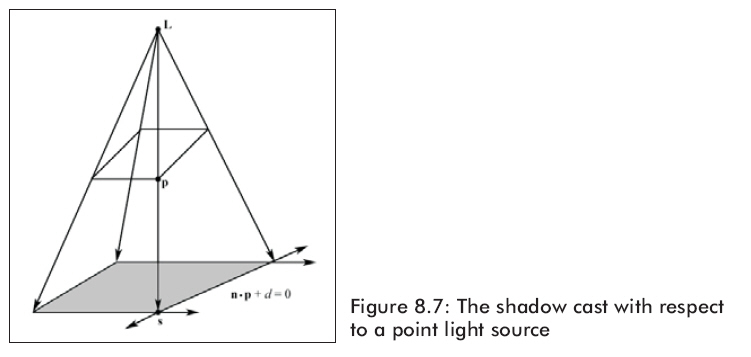
8.3.2点光源阴影
图8.7显示了物体在点光源照射下得到的阴影。点光源的位置是L。光线通过顶点p,则得到 r(t) = p + t ( p – L )。光线r(t)和平面n * p + d = 0 相交得到 s 。用8.3.1同样的方法我们可以得到s。
注意:在点光源和平行光中的L是不同的。对于点光源,我们用L来表示点光源的位置。而对于平行光,我们则是用L来表示平行光的照射方向。
8.3.3阴影矩阵
注意图8.6中所示的平行光,影子本质上是把物体按照灯光照射方向平行地投射到平面n*p+d=0之上。同样的,图8.7中所示的点光源,影子本质上是把物体按照透视画法从光源投射到平面n*p+d=0之上。
我们能够使用一个矩阵来表示从一个顶点p变换到平面n*p=d=0上的s的变化。而且,我们能够用同一个矩阵来表现正交投影和透视投影。
我们用一个4D向量(nx, ny, nz, d)来表示将要用于投射阴影平面的平面等式中的各个系数。让4D向量L=(Lx, Ly, Lz, Lw)来表示平行光的照射方向或点光源的位置。我们用w来区别:
1.假如w=0,那么L表示平行光的照射方向。
2.假如w=1 ,那么L表示点光源的位置。
假定平面的法向量已经单位化,我们让k=(nx, ny, nz, d)*(Lx, Ly, Lz, Lw)= nxLx+nyLy+nzLz+dLw
那么我们就可得到表示点p到点s的变换矩阵,即阴影矩阵:
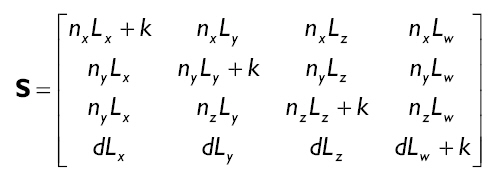
因为在其他地方已经被推导出来了,对于我们来说推导它并没有重大的意义,在这里我们就不再演示推导怎样得到这个矩阵的过程了。但是对与感兴趣的读者可以自己到网上查找相应的信息。
D3DX库中已经给我们提供了一个建立阴影矩阵的函数。其中当w=0时表示平行光,当w=1时表示点光源:
Builds a matrix that flattens geometry into a plane.
D3DXMATRIX * D3DXMatrixShadow(D3DXMATRIX * pOut,CONST D3DXVECTOR4 * pLight,CONST D3DXPLANE * pPlane);
Parameters
- pOut
- [in, out] Pointer to the D3DXMATRIX structure that is the result of the operation.
- pLight
- [in] Pointer to a D3DXVECTOR4 structure describing the light's position.
- pPlane
- [in] Pointer to the source D3DXPLANE structure.
Return Values
Pointer to a D3DXMATRIX structure that flattens geometry into a plane.
Remarks
The D3DXMatrixShadow function flattens geometry into a plane, as if casting a shadow from a light.
The return value for this function is the same value returned in the pOut parameter. In this way, the D3DXMatrixShadow function can be used as a parameter for another function.
This function uses the following formula to compute the returned matrix.
P = normalize(Plane);L = Light;d = dot(P, L) P.a * L.x + d P.a * L.y P.a * L.z P.a * L.w P.b * L.x P.b * L.y + d P.b * L.z P.b * L.w P.c * L.x P.c * L.y P.c * L.z + d P.c * L.w P.d * L.x P.d * L.y P.d * L.z P.d * L.w + d
If the light's w-component is 0, the ray from the origin to the light represents a directional light. If it is 1, the light is a point light.
8.3.4用模板缓存防止双倍混合
几何学上,当我们将一个物体投影到一个平面上时,很可能会有两个或者更多的投影三角形被重叠到一起。若我们就这样渲染,那么有重叠三角形的地方就会被多次混合以至这些地方将会变得更黑。图8.8就是这种情况。
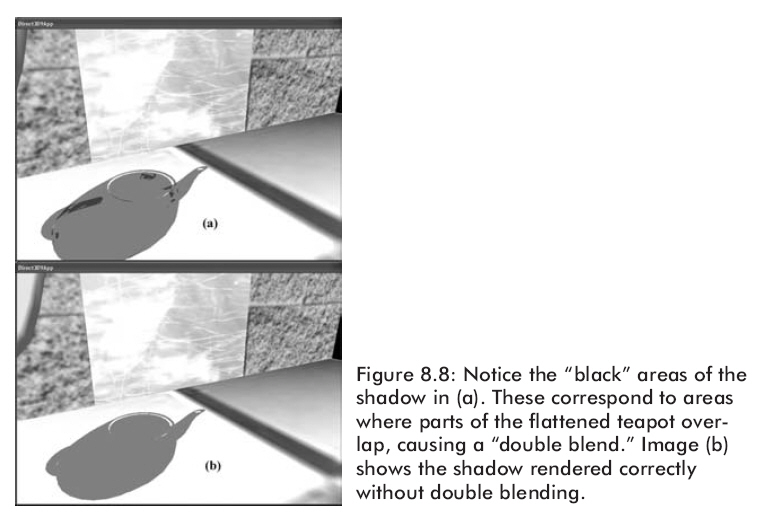
使用模板缓存来解决这个问题,设置模板测试为允许像素第一次被渲染。即,当把影子像素渲染到后台缓存时,我们同时在模板缓存中做好标记。然后,如果试图把像素向一个已经渲染过的地方写,那么模板测试将会失败。这样,我们就防止了重复写像素也就是防止了二次融合的发生。
8.3.5代码和解释
下面的代码就是讲解影子例子。本例的相关代码都在RenderShadow函数中。注意我们假设模板缓存都已经被清除为0了。
首先设置模板渲染状态。将模板比较运算设为D3DCMP_EQUAL且将D3DRS_STENCILREF渲染状态设置为0x0,因此假如在模板缓存中相应的值为0x0,那么就指定渲染阴影到后台缓存中。
因为模板缓存是被清除为0x0的,所以我们第一次将影子像素写入的时候总是正确的;不过因为我们设置D3DRS_STENCILPASS为D3DSTENCILOP_INCR,假如你试图将已经写过的像素写入的话,这个测试将会失败。在第一次写入的时候模板像素已经被写成了0x1,因此假如你再一次写入,模板测试将会失败。因此,我们避免了重复写像素,也避免了二次融合。
|
void RenderShadow() { Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILENABLE, true); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILFUNC, D3DCMP_EQUAL); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILREF, 0x0); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILMASK, 0xffffffff); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILWRITEMASK, 0xffffffff); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILZFAIL, D3DSTENCILOP_KEEP); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILFAIL, D3DSTENCILOP_KEEP); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILPASS, D3DSTENCILOP_INCR); |
下一步,我们计算阴影变换并将它放置到场景中适当的位置。
|
// compute the transformation to flatten the teapot into a shadow. D3DXVECTOR4 lightDirection(0.707f, -0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f); D3DXPLANE groundPlane(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); D3DXMATRIX S; D3DXMatrixShadow(&S, &lightDirection, &groundPlane); D3DXMATRIX T; D3DXMatrixTranslation(&T, TeapotPosition.x, TeapotPosition.y, TeapotPosition.z); D3DXMATRIX W = T * S; Device->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, &W); |
最后,我们设置一个50%透明度的黑色材质,关闭深度测试,渲染阴影,然后开启深度缓存同时关闭alpha混合和模板测试。我们关闭深度缓存来防止z-fighting,它是当两个不同的表面在深度缓存中有同样的深度值时出现的现象;深度缓存不知道那一个是在前面,此时就会产生讨厌的闪动。因为阴影和地板是在同一个平面上,z-fighting很可能就会出现。通过先渲染地板然后禁用深度测试并绘制阴影,这样我们就能够保证阴影将绘制在地面只之上。
|
Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ALPHABLENDENABLE, true); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_SRCBLEND, D3DBLEND_SRCALPHA); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_DESTBLEND, D3DBLEND_INVSRCALPHA); D3DMATERIAL9 mtrl = d3d::InitMtrl(d3d::BLACK, d3d::BLACK, d3d::BLACK, d3d::BLACK, 0.0f); mtrl.Diffuse.a = 0.5f; // 50% transparency. // Disable depth buffer so that z-fighting doesn't occur when we // render the shadow on top of the floor. Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ZENABLE, false); Device->SetMaterial(&mtrl); Device->SetTexture(0, 0); Teapot->DrawSubset(0); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ZENABLE, true); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ALPHABLENDENABLE, false); Device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILENABLE, false); }//end RenderShadow() |
主程序:
Demonstrates shadows with stencils.
Use the arrow keys and the 'A' and 'S' key to navigate the scene and translate the teapot.
**************************************************************************************/
#include "d3dUtility.h"
#pragma warning(disable : 4100)
class cTextureVertex
{
public:
float _x, _y, _z;
float _nx, _ny, _nz;
float _u, _v;
cTextureVertex() { }
cTextureVertex(float x, float y, float z,
float nx, float ny, float nz,
float u, float v)
{
_x = x; _y = y; _z = z;
_nx = nx; _ny = ny; _nz = nz;
_u = u; _v = v;
}
};
const DWORD TEXTURE_VERTEX_FVF = D3DFVF_XYZ | D3DFVF_NORMAL | D3DFVF_TEX1;
////
const int WIDTH = 640;
const int HEIGHT = 480;
IDirect3DDevice9* g_d3d_device;
IDirect3DVertexBuffer9* g_vertex_buffer;
IDirect3DTexture9* g_floor_texture;
IDirect3DTexture9* g_wall_texture;
IDirect3DTexture9* g_mirror_texture;
D3DMATERIAL9 g_floor_material = WHITE_MATERIAL;
D3DMATERIAL9 g_wall_material = WHITE_MATERIAL;
D3DMATERIAL9 g_mirror_material = WHITE_MATERIAL;
ID3DXMesh* g_teapot_mesh;
D3DXVECTOR3 g_teapot_pos(0.0f, 3.0f, -7.5f);
D3DMATERIAL9 g_teapot_material = YELLOW_MATERIAL;
void render_scene();
void render_shadow();
////
bool setup()
{
// make walls have low specular reflectance - 20%
g_wall_material.Specular = WHITE * 0.2f;
D3DXCreateTeapot(g_d3d_device, &g_teapot_mesh, NULL);
// Create and specify geometry. For this sample we draw a floor and a wall with a mirror on it.
// We put the floor, wall, and mirror geometry in one vertex buffer.
//
// |----|----|----|
// |Wall|Mirr|Wall|
// | | or | |
// /--------------/
// / Floor /
// /--------------/
g_d3d_device->CreateVertexBuffer(24 * sizeof(cTextureVertex), 0, TEXTURE_VERTEX_FVF, D3DPOOL_MANAGED,
&g_vertex_buffer, NULL);
cTextureVertex* v;
g_vertex_buffer->Lock(0, 0, (void**)&v, 0);
// floor
v[0] = cTextureVertex(-7.5f, 0.0f, -10.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
v[1] = cTextureVertex(-7.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
v[2] = cTextureVertex( 7.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
v[3] = cTextureVertex(-7.5f, 0.0f, -10.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
v[4] = cTextureVertex( 7.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
v[5] = cTextureVertex( 7.5f, 0.0f, -10.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
// wall
v[6] = cTextureVertex(-7.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
v[7] = cTextureVertex(-7.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
v[8] = cTextureVertex(-2.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
v[9] = cTextureVertex(-7.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
v[10] = cTextureVertex(-2.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
v[11] = cTextureVertex(-2.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
// Note: We leave gap in middle of walls for mirror
v[12] = cTextureVertex(2.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
v[13] = cTextureVertex(2.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
v[14] = cTextureVertex(7.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
v[15] = cTextureVertex(2.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
v[16] = cTextureVertex(7.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
v[17] = cTextureVertex(7.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
// mirror
v[18] = cTextureVertex(-2.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
v[19] = cTextureVertex(-2.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
v[20] = cTextureVertex( 2.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
v[21] = cTextureVertex(-2.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
v[22] = cTextureVertex( 2.5f, 5.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
v[23] = cTextureVertex( 2.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
g_vertex_buffer->Unlock();
// create the texture and set filters
D3DXCreateTextureFromFile(g_d3d_device, "checker.jpg", &g_floor_texture);
D3DXCreateTextureFromFile(g_d3d_device, "brick0.jpg", &g_wall_texture);
D3DXCreateTextureFromFile(g_d3d_device, "ice.bmp", &g_mirror_texture);
g_d3d_device->SetSamplerState(0, D3DSAMP_MAGFILTER, D3DTEXF_LINEAR);
g_d3d_device->SetSamplerState(0, D3DSAMP_MINFILTER, D3DTEXF_LINEAR);
g_d3d_device->SetSamplerState(0, D3DSAMP_MIPFILTER, D3DTEXF_POINT);
// lights
D3DXVECTOR3 light_dir(0.707f, -0.707f, 0.707f);
D3DXCOLOR color(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
D3DLIGHT9 light = init_directional_light(&light_dir, &color);
g_d3d_device->SetLight(0, &light);
g_d3d_device->LightEnable(0, TRUE);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_NORMALIZENORMALS, TRUE);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_SPECULARENABLE, TRUE);
// set the projection matrix
D3DXMATRIX proj;
D3DXMatrixPerspectiveFovLH(&proj, D3DX_PI/4.0f, (float)WIDTH/HEIGHT, 1.0f, 1000.0f);
g_d3d_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_PROJECTION, &proj);
return true;
}
///
void cleanup()
{
safe_release<IDirect3DVertexBuffer9*>(g_vertex_buffer);
safe_release<IDirect3DTexture9*>(g_floor_texture);
safe_release<IDirect3DTexture9*>(g_wall_texture);
safe_release<IDirect3DTexture9*>(g_mirror_texture);
safe_release<ID3DXMesh*>(g_teapot_mesh);
}
///
bool display(float time_delta)
{
// update the scene
if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_LEFT) & 0x80000f)
g_teapot_pos.x -= 3.0f * time_delta;
if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_RIGHT) & 0x80000f)
g_teapot_pos.x += 3.0f * time_delta;
static float radius = 20.0f;
if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_UP) & 0x80000f)
radius -= 2.0f * time_delta;
if(GetAsyncKeyState(VK_DOWN) & 0x80000f)
radius += 2.0f * time_delta;
static float angle = (3.0f * D3DX_PI) / 2.0f;
if(GetAsyncKeyState('A') & 0x80000f)
angle -= 0.5f * time_delta;
if(GetAsyncKeyState('S') & 0x80000f)
angle += 0.5f * time_delta;
D3DXVECTOR3 position(cosf(angle) * radius, 3.0f, sinf(angle) * radius);
D3DXVECTOR3 target(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
D3DXVECTOR3 up(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
D3DXMATRIX view_matrix;
D3DXMatrixLookAtLH(&view_matrix, &position, &target, &up);
g_d3d_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_VIEW, &view_matrix);
// render now
g_d3d_device->Clear(0, NULL, D3DCLEAR_TARGET | D3DCLEAR_ZBUFFER | D3DCLEAR_STENCIL, 0xff000000, 1.0f, 0);
g_d3d_device->BeginScene();
render_scene();
render_shadow();
g_d3d_device->EndScene();
g_d3d_device->Present(NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
return true;
}
///
void render_scene()
{
D3DXMATRIX identity_matrix;
D3DXMatrixIdentity(&identity_matrix);
g_d3d_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, &identity_matrix);
g_d3d_device->SetStreamSource(0, g_vertex_buffer, 0, sizeof(cTextureVertex));
g_d3d_device->SetFVF(TEXTURE_VERTEX_FVF);
// draw the floor
g_d3d_device->SetMaterial(&g_floor_material);
g_d3d_device->SetTexture(0, g_floor_texture);
g_d3d_device->DrawPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST, 0, 2);
// draw the walls
g_d3d_device->SetMaterial(&g_wall_material);
g_d3d_device->SetTexture(0, g_wall_texture);
g_d3d_device->DrawPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST, 6, 4);
// draw the mirror
g_d3d_device->SetMaterial(&g_mirror_material);
g_d3d_device->SetTexture(0, g_mirror_texture);
g_d3d_device->DrawPrimitive(D3DPT_TRIANGLELIST, 18, 2);
// draw teapot
g_d3d_device->SetMaterial(&g_teapot_material);
g_d3d_device->SetTexture(0, NULL);
D3DXMATRIX world_matrix;
D3DXMatrixTranslation(&world_matrix, g_teapot_pos.x, g_teapot_pos.y, g_teapot_pos.z);
g_d3d_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, &world_matrix);
g_teapot_mesh->DrawSubset(0);
}
///
void render_shadow()
{
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILENABLE, TRUE);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILFUNC, D3DCMP_EQUAL);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILREF, 0x0);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILMASK, 0xffffffff);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILWRITEMASK, 0xffffffff);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILZFAIL, D3DSTENCILOP_KEEP);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILFAIL, D3DSTENCILOP_KEEP);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILPASS, D3DSTENCILOP_INCR); // increment to 1
// position shadow
D3DXVECTOR4 light_dir(0.707f, -0.707f, 0.707f, 0.0f);
D3DXPLANE ground_plane(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // xz plane
D3DXMATRIX shadow_matrix;
D3DXMatrixShadow(&shadow_matrix, &light_dir, &ground_plane);
D3DXMATRIX tran_matrix;
D3DXMatrixTranslation(&tran_matrix, g_teapot_pos.x, g_teapot_pos.y, g_teapot_pos.z);
D3DXMATRIX world_matrix = tran_matrix * shadow_matrix;
g_d3d_device->SetTransform(D3DTS_WORLD, &world_matrix);
// alpha blend the shadow
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ALPHABLENDENABLE, TRUE);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_SRCBLEND, D3DBLEND_SRCALPHA);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_DESTBLEND, D3DBLEND_INVSRCALPHA);
D3DMATERIAL9 material = init_material(BLACK, BLACK, BLACK, BLACK, 0.0f);
material.Diffuse.a = 0.5f; // 50% transparancy
// disable depth buffer so that z-fighting doesn't occur when we render the shadow
// on top of the floor.
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ZENABLE, FALSE);
g_d3d_device->SetMaterial(&material);
g_d3d_device->SetTexture(0, NULL);
g_teapot_mesh->DrawSubset(0);
// restore render states
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ZENABLE, TRUE);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_ALPHABLENDENABLE, FALSE);
g_d3d_device->SetRenderState(D3DRS_STENCILENABLE, FALSE);
}
///
LRESULT CALLBACK wnd_proc(HWND hwnd, UINT msg, WPARAM word_param, LPARAM long_param)
{
switch(msg)
{
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
case WM_KEYDOWN:
if(word_param == VK_ESCAPE)
DestroyWindow(hwnd);
break;
}
return DefWindowProc(hwnd, msg, word_param, long_param);
}
///
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE inst, HINSTANCE, PSTR cmd_line, int cmd_show)
{
if(! init_d3d(inst, WIDTH, HEIGHT, true, D3DDEVTYPE_HAL, &g_d3d_device))
{
MessageBox(NULL, "init_d3d() - failed.", 0, MB_OK);
return 0;
}
if(! setup())
{
MessageBox(NULL, "Steup() - failed.", 0, MB_OK);
return 0;
}
enter_msg_loop(display);
cleanup();
g_d3d_device->Release();
return 0;
}
下载源程序
8.3实例程序:平面阴影相关推荐
- mysql plsql循环语句吗,Oracle PLSQL 在游标中用while循环实例程序
Oracle PLSQL 在游标中用while循环实例程序 Oracle PLSQL 在游标中用while循环实例程序 Oracle PLSQL 在游标中用while循环实例程序 declare cu ...
- C#2.0实例程序STEP BY STEP--实例二:数据类型
C#2.0实例程序STEP BY STEP--实例二:数据类型 与其他.NET语言一样,C#支持Common Type Sysem(CTS),其中的数据类型集合不仅包含我们熟悉的基本类型,例如int, ...
- matlab 向量模量,有限元分析简单实例之平面矩形薄板(matlab)
有限元分析简单实例之平面矩形薄板(matlab) 问题描述 对于如图所示的一个平面矩形薄板结构,施加如右图所示的几个方向力,对其进行有限元分析,计算各个节点的位移及支座反力.(其中F是合力,E是弹性模 ...
- 欧姆龙plc解密实例_3000多套PLC实例程序大合集自动控制系统程序电气系统程序...
3000多套PLC实例程序源文件获取请见文章末尾图片 3000多套PLC实例程序内容简介: ★[文件总大小] : 1.92G ★[文件格式] :各品牌的程序文件 ★[类容介绍]:西门子PLC例程777 ...
- 【Unity】Planar Shadows平面阴影的实现
Plannar Shadows,即平面阴影,是一个适用于平坦地形的假阴影技术.要求阴影的Receiver为平面,Occluder不与其他物体穿插. 实现效果 1.定向光源Planar Shadows ...
- 欧姆龙plc解密实例_西门子、施耐德、欧姆龙等13大PLC品牌8000个实例程序资料包...
程序案例为PLC学习者和开发工程师提供一个很好的参考和思路引导,实例程序可以用直接用对应版本PLC编程软件打开!有些程序稍作修改就可以用到自己的设备中,省去了大量编程的时间和费用成本. 为此,我们给大 ...
- opc服务器消息通知代码,OPCClient浏览OPCServer的简单实例程序源代码.doc
OPCClient浏览OPCServer的简单实例程序源代码 OPC Client浏览OPC Server的简单实例简单程序//main.cpp //************************* ...
- C/C++:Windows编程—IAT Hook实例(程序启动拦截)
C/C++:Windows编程-IAT Hook实例(程序启动拦截) 前言+思路 本文默认读者有IAT Hook的相关的基础知识了哈,记录笔者在IAT Hook实战中遇到到问题以及解决思路. 笔者想实 ...
- 基于json-lib.jar包Json实例程序
基于json-lib.jar包Json实例程序 1.JSONObject to DynaBean String json = "{name=\"json\",bool:t ...
最新文章
- 检测硬盘使用时长_如何检测硬盘问题
- AI | 优化背后的数学基础
- .Net 2.0 新功能:迭代器(Iterators)
- [Vue 牛刀小试]:第八章 - 组件的基础知识
- 钢体pdc钻头计算机辅助设计和绘图,PDC钻头三维设计软件的研究与设计
- 如何关闭SAP Fiori的病毒扫描设置
- 检查异常和非检查异常 有空你去学一下检查异常和非检查异常
- 【转】架构师Jack专访:全面认识软件测试架构师
- JDK 8_jstack命令使用
- python requests urlencode_关于requests的urlencode问题
- NUMA架构下的CPU拓扑
- 关于 K8S 探针(startupProbe、livenessProbe、readinessProbe)的最佳实践
- 2020年MySQL数据库面试题(50道题含答案和思维导图总结)
- obs多推流地址_推流篇| 如何在广交会直播中使用OBS推流,播放视频、PPT等
- Java使用aspose合并两个PDF文件
- ubuntu 22.04安装独立显卡驱动方法以及一些问题,以及安装pytorchcuda和cudnn的问题
- 在Swift中使用dispatch_once单例模型
- 从键盘输入一个整数,判断它是正数,负数,0
- 特征图注意力_计算机视觉中的Non-local-Block以及其他注意力机制
- 极大似然估计法的理解和用途
