Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 2)
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Where do odds begin, and where do they end? Where does hope emerge, and will they ever break?
Given an integer sequence a1, a2, ..., an of length n. Decide whether it is possible to divide it into an odd number of non-empty subsegments, the each of which has an odd length and begins and ends with odd numbers.
A subsegment is a contiguous slice of the whole sequence. For example, {3, 4, 5} and {1} are subsegments of sequence {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, while {1, 2, 4} and {7} are not.
The first line of input contains a non-negative integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the length of the sequence.
The second line contains n space-separated non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100) — the elements of the sequence.
Output "Yes" if it's possible to fulfill the requirements, and "No" otherwise.
You can output each letter in any case (upper or lower).
31 3 5
Yes
51 0 1 5 1
Yes
34 3 1
No
43 9 9 3
No
In the first example, divide the sequence into 1 subsegment: {1, 3, 5} and the requirements will be met.
In the second example, divide the sequence into 3 subsegments: {1, 0, 1}, {5}, {1}.
In the third example, one of the subsegments must start with 4 which is an even number, thus the requirements cannot be met.
In the fourth example, the sequence can be divided into 2 subsegments: {3, 9, 9}, {3}, but this is not a valid solution because 2 is an even number.
问你把长度为n的序列化为奇数开头奇数结尾而且个数是奇数的数列
首先分析偶数,凑两个奇数数列,然后这个子序列个数就又是偶数了
所以只有奇数个符合要求,开头结尾必须是,合并为一个就好了
我错了是因为优先级 判断末位是不是奇数要用 (n&1)==0
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{int n;cin>>n;int a[102];for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];int f=0;if(n&1&&a[1]&1&&a[n]&1)f=1;printf("%s",f?"Yes":"No");return 0;
}1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Connect the countless points with lines, till we reach the faraway yonder.
There are n points on a coordinate plane, the i-th of which being (i, yi).
Determine whether it's possible to draw two parallel and non-overlapping lines, such that every point in the set lies on exactly one of them, and each of them passes through at least one point in the set.
The first line of input contains a positive integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 1 000) — the number of points.
The second line contains n space-separated integers y1, y2, ..., yn ( - 109 ≤ yi ≤ 109) — the vertical coordinates of each point.
Output "Yes" (without quotes) if it's possible to fulfill the requirements, and "No" otherwise.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
57 5 8 6 9
Yes
5-1 -2 0 0 -5
No
55 4 3 2 1
No
51000000000 0 0 0 0
Yes
In the first example, there are five points: (1, 7), (2, 5), (3, 8), (4, 6) and (5, 9). It's possible to draw a line that passes through points 1, 3, 5, and another one that passes through points 2, 4 and is parallel to the first one.
In the second example, while it's possible to draw two lines that cover all points, they cannot be made parallel.
In the third example, it's impossible to satisfy both requirements at the same time.
这个题嘛就是给你一堆点,让你判断在不在两条平行(不重合)的直线上
我选用前三个点在不在一条直线上,在的话就是其他点还有一条直线
不在的话就分三种情况讨论
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL a[1005];int n;
bool check()
{int f=-1;LL f1=a[3]-a[2];if(a[2]*2==a[1]+a[3]){for(int i=4; i<=n; i++){if((a[i]-a[1])!=(i-1)*f1){if(f==-1)f=i;else{if((a[i]-a[f])!=(i-f)*f1){return 0;}}}}if(f==-1){return 0;}}else{f=0,f1=a[2]-a[1];for(int i=4; i<=n; i++){if((a[i]-a[1])!=(i-1)*f1&&((a[i]-a[3])!=(i-3)*f1)){f++;break;}}f1=a[3]-a[2];for(int i=4; i<=n; i++){if((a[i]-a[2])!=(i-2)*f1&&((a[i]-a[1])!=(i-1)*f1)){f++;break;}}f1=a[3]-a[1];for(int i=4; i<=n; i++){if(2*(a[i]-a[2])!=(i-2)*f1&&(2*(a[i]-a[1])!=(i-1)*f1)){f++;break;}}if(f==3)return 0;}return 1;
}
int main()
{scanf("%d",&n);for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)scanf("%lld",a+i);if(!check())printf("No\n");else printf("Yes\n");return 0;
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=1005;
ll y[N];
int n;
bool gx(int a,int b,int c,int d)
{return (b-a)*(y[d]-y[c])==(d-c)*(y[b]-y[a]);
}
int check(int d,int f)
{vector<int>V;for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)if(!gx(d,f,f,i))V.push_back(i);if(V.size()==0)return 0;if(V.size()==1)return 1;for(int i=1; i<(int)V.size(); i++)if(!gx(d,f,V[i],V[i-1]))return 0;return 1;
}
int main()
{cin>>n;for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)cin>>y[i];if(check(1,2)||check(2,3)||check(1,3))cout<<"YES";else cout<<"NO";return 0;
}1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
From beginning till end, this message has been waiting to be conveyed.
For a given unordered multiset of n lowercase English letters ("multi" means that a letter may appear more than once), we treat all letters as strings of length 1, and repeat the following operation n - 1 times:
- Remove any two elements s and t from the set, and add their concatenation s + t to the set.
The cost of such operation is defined to be 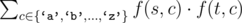 , where f(s, c) denotes the number of times character c appears in string s.
, where f(s, c) denotes the number of times character c appears in string s.
Given a non-negative integer k, construct any valid non-empty set of no more than 100 000 letters, such that the minimum accumulative cost of the whole process is exactly k. It can be shown that a solution always exists.
The first and only line of input contains a non-negative integer k (0 ≤ k ≤ 100 000) — the required minimum cost.
Output a non-empty string of no more than 100 000 lowercase English letters — any multiset satisfying the requirements, concatenated to be a string.
Note that the printed string doesn't need to be the final concatenated string. It only needs to represent an unordered multiset of letters.
12
abababab
3
codeforces
For the multiset {'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b'}, one of the ways to complete the process is as follows:
- {"ab", "a", "b", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 0;
- {"aba", "b", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "ab", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 0;
- {"abab", "aba", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "abab"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abababab"}, with a cost of 8.
The total cost is 12, and it can be proved to be the minimum cost of the process.
就是贪心构造,合并花费是0,但是连续的某个字母生成的话费是n*(n-1)/2,每次生成最多就好的
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[500];
int main()
{int k;scanf("%d",&k);for(int i=1;i<450;i++)a[i]=i*(i-1)/2;if(k==0)printf("a");else{int f=0;char c='a';while(k){int pos=lower_bound(a+1,a+450,k)-a;if(a[pos]>k)pos--;for(int i=0;i<pos;i++)printf("%c",c);k-=a[pos];c++;}}return 0;
}转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/BobHuang/p/7465836.html
Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 2)相关推荐
- Codeforces Round #506 (Div. 3)
Codeforces Round #506 (Div. 3) 实习期间事不多,对div3 面向题解和数据编程了一波 A. Many Equal Substrings 题目链接 A题就是找后缀和前缀重合 ...
- Codeforces Round #563 (Div. 2)/CF1174
Codeforces Round #563 (Div. 2)/CF1174 CF1174A Ehab Fails to Be Thanos 其实就是要\(\sum\limits_{i=1}^n a_i ...
- 构造 Codeforces Round #302 (Div. 2) B Sea and Islands
题目传送门 1 /* 2 题意:在n^n的海洋里是否有k块陆地 3 构造算法:按奇偶性来判断,k小于等于所有点数的一半,交叉输出L/S 4 输出完k个L后,之后全部输出S:) 5 5 10 的例子可以 ...
- Codeforces Round #696 (Div. 2) (A ~ E)超高质量题解(每日训练 Day.16 )
整理的算法模板合集: ACM模板 点我看算法全家桶系列!!! 实际上是一个全新的精炼模板整合计划 Codeforces Round #696 (Div. 2) (A ~ E)超高质量题解 比赛链接:h ...
- Codeforces Round #712 Div.2(A ~ F) 超高质量题解(每日训练 Day.15 )
整理的算法模板合集: ACM模板 点我看算法全家桶系列!!! 实际上是一个全新的精炼模板整合计划 Codeforces Round #712 Div.2(A ~ F) 题解 比赛链接:https:// ...
- Codeforces Round #701 (Div. 2) A ~ F ,6题全,超高质量良心题解【每日亿题】2021/2/13
整理的算法模板合集: ACM模板 点我看算法全家桶系列!!! 实际上是一个全新的精炼模板整合计划 目录 A - Add and Divide B - Replace and Keep Sorted C ...
- Codeforces Round #700 (Div. 2) D2 Painting the Array II(最通俗易懂的贪心策略讲解)看不懂来打我 ~
整理的算法模板合集: ACM模板 点我看算法全家桶系列!!! 实际上是一个全新的精炼模板整合计划 整场比赛的A ~ E 6题全,全部题目超高质量题解链接: Codeforces Round #700 ...
- Codeforces Round #699 (Div. 2) F - AB Tree(贪心、树上DP)超级清晰,良心题解,看不懂来打我 ~
整理的算法模板合集: ACM模板 点我看算法全家桶系列!!! 实际上是一个全新的精炼模板整合计划 Codeforces Round #699 (Div. 2) F - AB Tree Problem ...
- Codeforces Round #699 (Div. 2) (A ~ F)6题全,超高质量良心题解【每日亿题】2021/2/6
整理的算法模板合集: ACM模板 点我看算法全家桶系列!!! 实际上是一个全新的精炼模板整合计划 Codeforces Round #699 (Div. 2) (A.B.C)[每日亿题]2021/2/ ...
最新文章
- Tensorrt一些优化技术介绍
- Jmeter 压力测试中关于 Http 的那些事儿
- tomcat架构之-----基本概念
- 【pyqt5学习】——tableWidget学习
- ios--小结系列六
- 转:android学习帖子大汇集
- 前端本地使用线上数据
- HDU2012 素数判定【入门】
- 参考文献标号字体_论文参考文献字体大小
- Java知识点_类锁和对象锁的区别?
- Python文本处理——中文标点符号处理
- Apache DBUtils
- mac上安装Enterprise Architect
- Synopsys Formality 2018操作流程
- backtrader回测框架实例
- Direct2D编程入门
- Spring Boot拦截器(Interceptor)详解
- Ubuntu之[福昕pdf安装与卸载]
- stream之List转Map---Collectors.toMap()介绍
- 那些三十五岁失业的程序员,后来都干什么去了?
热门文章
- mysql 引擎是表级别_Mysql表引擎优化
- android wear2.9新功能,Android Wear 2.0确认2月9日正式登场
- python开发范围_Python上的字母范围
- linux进程 面试题,Linux面试题,浅析常见Linux命令面试题及答案
- 液晶弹性自由能计算_自由能方法应用(一)开放计算平台BRIDGE的介绍及使用案例...
- vue mui html不解析,记下Vue中使用Mui.js踩到的坑
- 毫米波雷达数据处理_毫米波雷达开启4D时代,助力几何伙伴抢滩自动驾驶量产...
- Visual Source Safe的安装和使用简明教程
- PHP Deprecated: Function ereg_replace() is deprecated in 的解决方法
- C语言3中方法判断32还是64位机
