python3练习题:1-10
#practice1:在字典、列表、集合中按条件筛选数据
- 列表解析
#如何在列表、字典、集合中按条件筛选数据
from random import randint
from timeit import timeit
#因为for提取的变量在randint函数中未使用,所以用_,而非一个变量名
a = [randint(-10,10) for _ in range(10)]
print(a)
#方法1
b = filter(lambda x: x > 0,a)
print(list(b))
#方法2
c = [x for x in a if x > 0]
print(c)
#测试速度
print(timeit("[x for x in a if x > 0]","from __main__ import a",number=10))
print(timeit("filter(lambda x: x > 0,a)","from __main__ import a",number=10))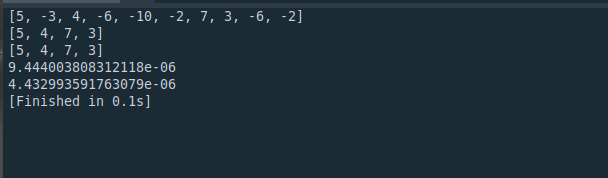
一般情况下,列表解析快一点。。。
- 字典解析
from random import randint
d = {x:randint(-10,10) for x in range(10)}
print(d)
#字典解析
result = {v:k for k,v in d.items() if v > 0}
print(result)
#不适合用filter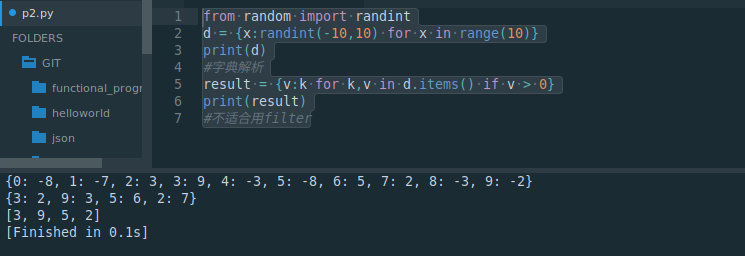
- 字典解析
from random import randinta = {randint(-20,20) for _ in range(10)}print(a)
result = {x for x in a if x > 0}
print(result)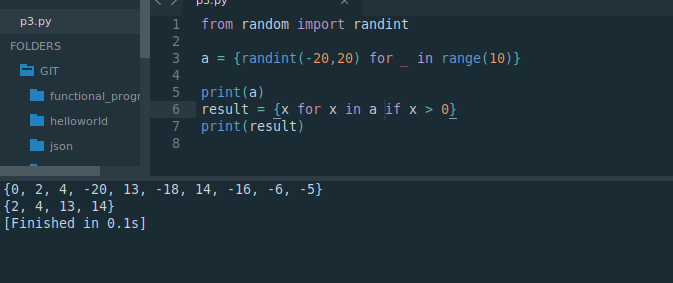
#practice2:为元组中每个元素命名
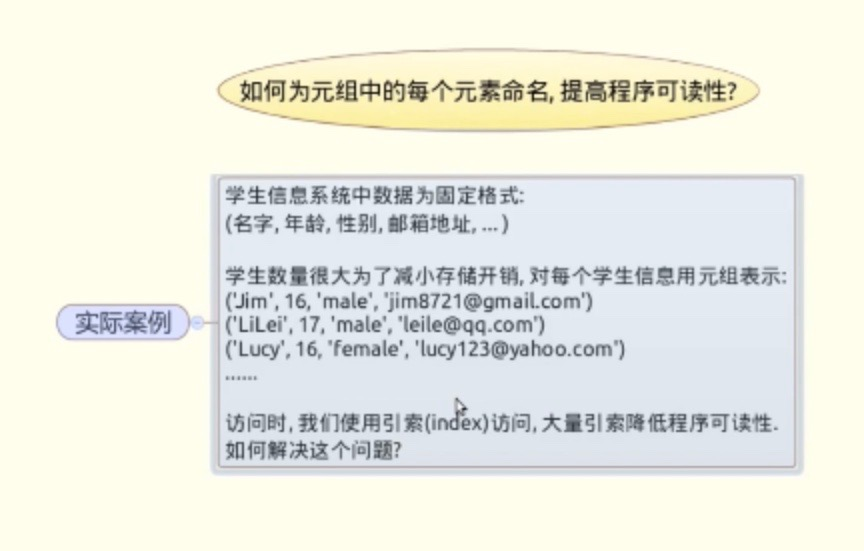
- 法一:用伪常亮+序列拆包
- 法二:用namedtuple函数
student = ('jim',18,'shanxi','china')#方法一:伪常亮
#增添了全局变量,不推荐
NAME,AGE,PROVINCE,COUNTRY = range(4)
print(student[NAME])
print(student[AGE])#方法二:使用namedtuple
from collections import namedtuple#参数1:namedtuple函数返回一个Tuple子类,第一个参数是子类名称;参数2:index名称列表
Student = namedtuple('Student',['name','age','province','country'])
#Student元组类实例化,s是一个带名称的元组
s = Student('jim',18,'shanxi','china')
print(s.name) 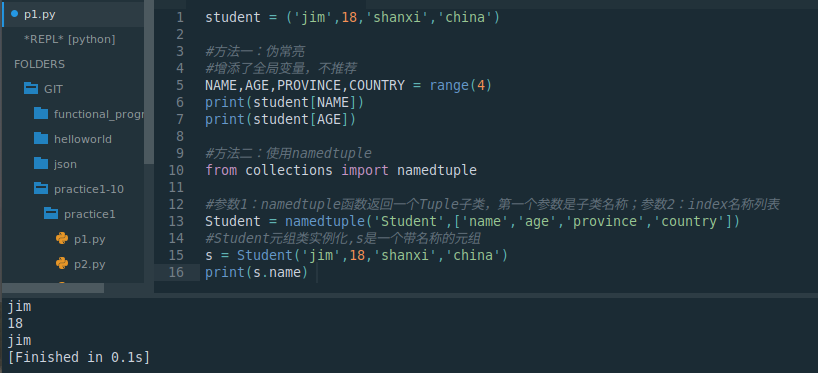
#practice3:统计序列中元素出现频率

案例1
- 方法一:dict.fromkeys函数+字典排序
from random import randintl = [randint(0,10) for _ in range(20)]
print(l)#方法一:使用dict.fromkeys构建字典,用value来计数
#fromkeys方法构建的字典会自动去重
mydict = dict.fromkeys(l,0)
print(mydict)
#计算频率
for x in l:mydict[x] += 1
print(mydict)
#把字典转化为类列表,然后用sorted+key关键字按序排列
print((mydict.items()))
newdict = sorted(mydict.items(),key=lambda x:x[1])
print(newdict)
#取出频率最高的三个
newdict = newdict[-3:]
print(newdict)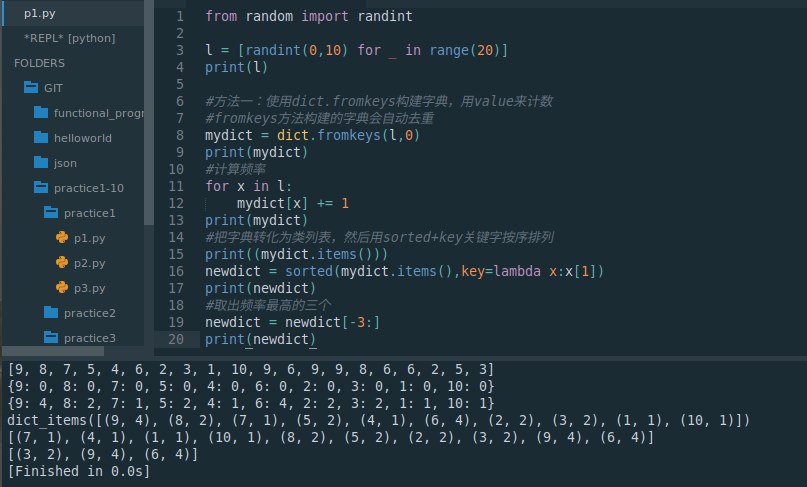
- 方法二:使用collections.Counter类
from random import randint
from collections import Counterl = [randint(0,10) for _ in range(20)]
print(l)countdict = Counter(l)
#countdict是一个类字典对象,因为Counter继承了内置Dict类,所以countdict拥有所有字典的方法!
#countdict还有新方法most_common
print(countdict)
#返回3个频率最高的单元,默认由高到低
print(countdict.most_common(3))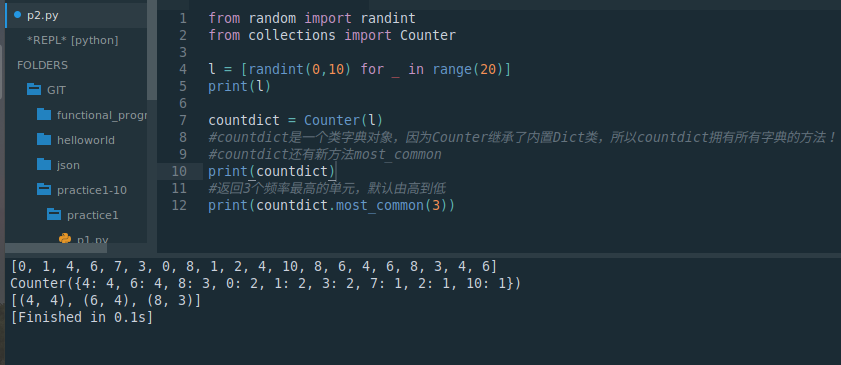
- 案例2
查找一段文本中出现最高的十个短语
import subprocess
from collections import Counter
out_bytes = subprocess.check_output(['netstat','-a'])
out_text = out_bytes.decode('utf-8')
print(type(out_text))
print(out_text)out_text = out_text.split()
wordcounter = Counter(out_text)
print(wordcounter.most_common(10))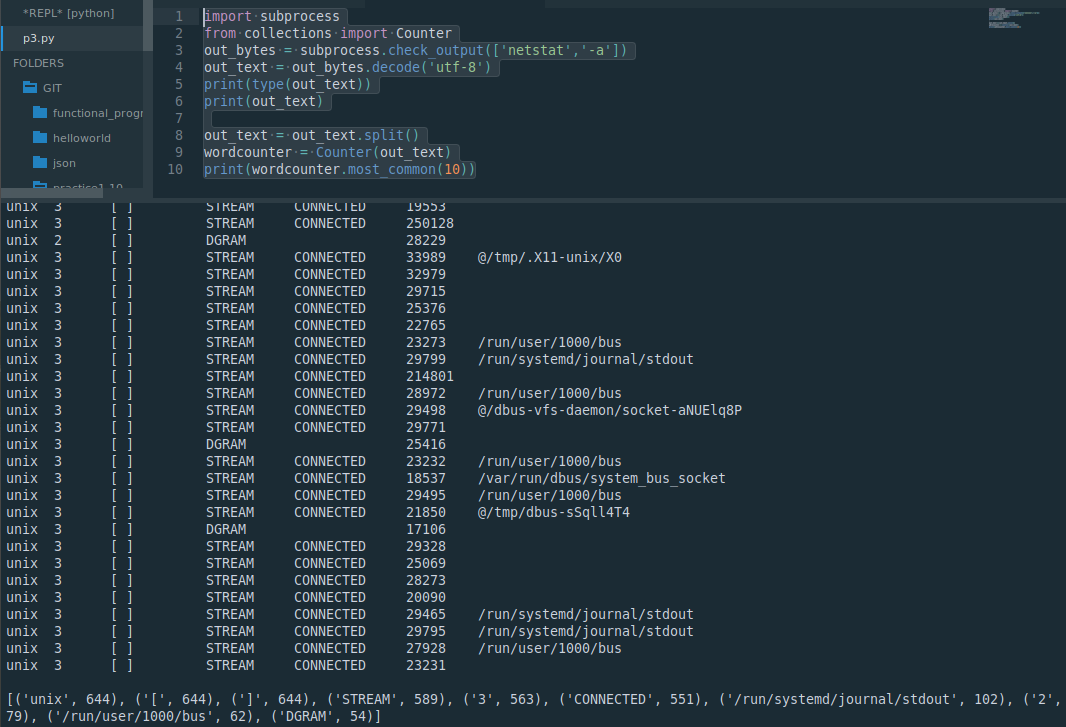
#practice4:把字典按value排序
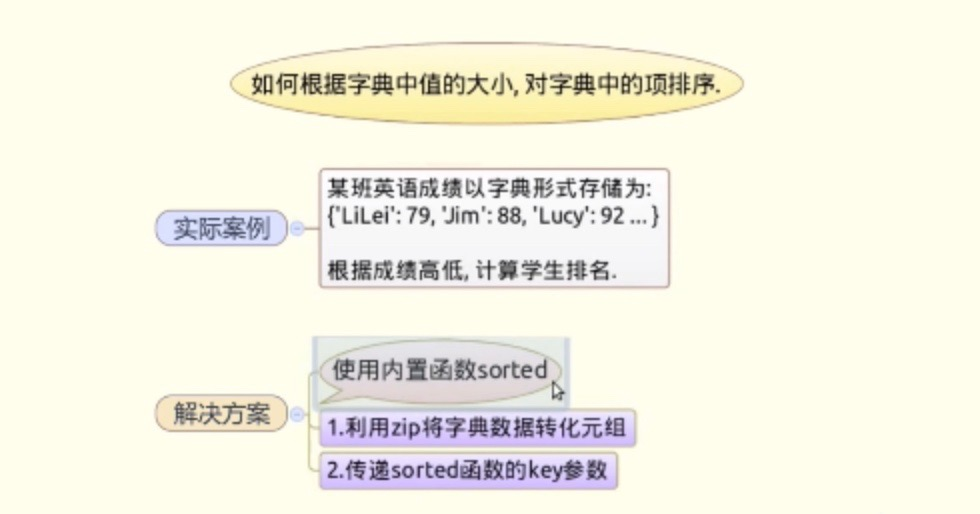
- 方法1:zip + sorted
from random import randintd = {str(k):randint(0,10) for k in range(10)}
#d.items返回值:类集合对象
print(d.items())#方法一:用zip将key与value列表组合成新的元组列表
#对元组列表执行sorted方法
result = zip(d.values(),d.keys())
#zip后里面的基本单元是tuple,这是永远不变的
#外边可以转换为list/set/tuple来包裹
new_result = sorted(result)
print(new_result)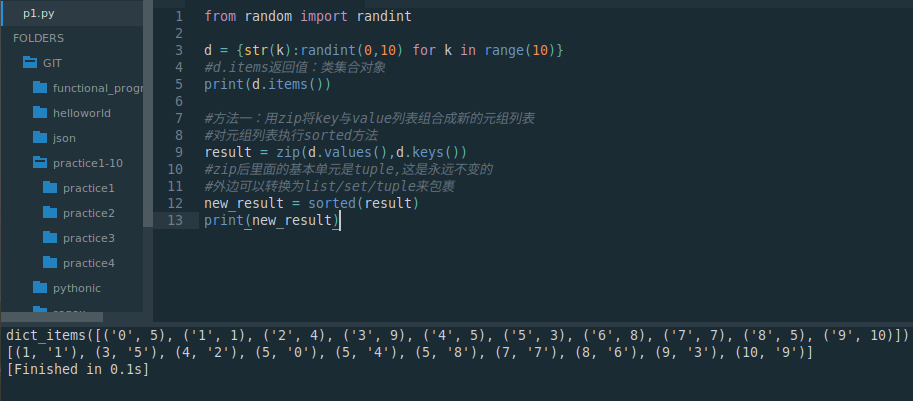
注意:以下几个函数或类的参数与返回值(学会使用help()
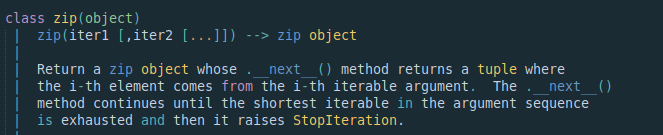
zip输入参数:iterable;返回值:zip对象(也是iterable)
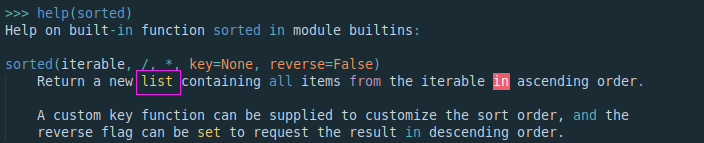
sorted函数参数:iterable;返回值:list!!!
平常使用的list(a),并非是在调用函数,而是进行list内置类的实例化;输入:iterable;输出:lsit。
- 方法二:借助sorted的key参数
from random import randintd = {str(k):randint(0,10) for k in range(10)}
#dict.items()返回一个dict_items对象,是个类集合对象,而且是个iterable
for x in d.items():#从结果可知,基本元素是个元组!print(x)
#用key参数制定排序对象
result = sorted(d.items(),key=lambda x:x[1])
print(result)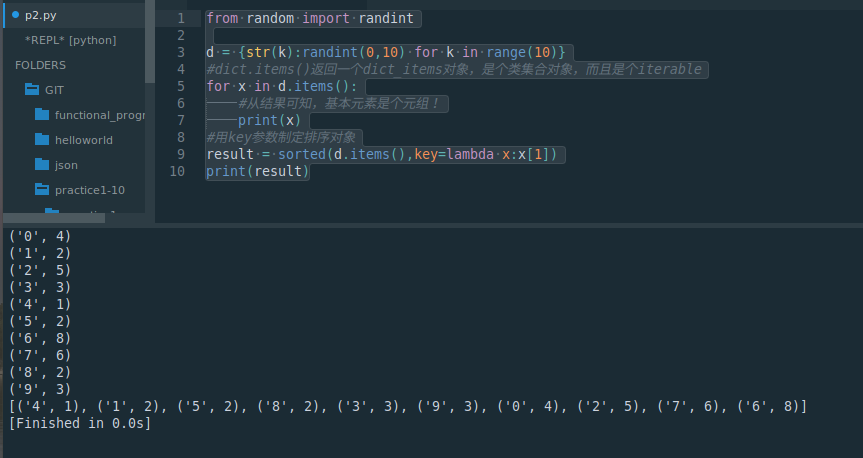
#practice5:找寻多个字典的公共key

- 方法一:循环
方法二:用dict.keys方法
- 两种实现方法
from random import randintgame1 = {x:randint(1,3) for x in "abcdef"}
print(game1)
game2 = {x:randint(1,3) for x in "abckew"}
print(game2)
game3 = {x:randint(1,3) for x in "mnef"}
print(game3)#法1:for循环
res = []
for k in game1:if k in game2 and k in game3:res.append(k)print(res)#法2:利用dict.keys方法,返回值是个类集合对象
result = game1.keys() & game2.keys() & game3.keys()
print(result)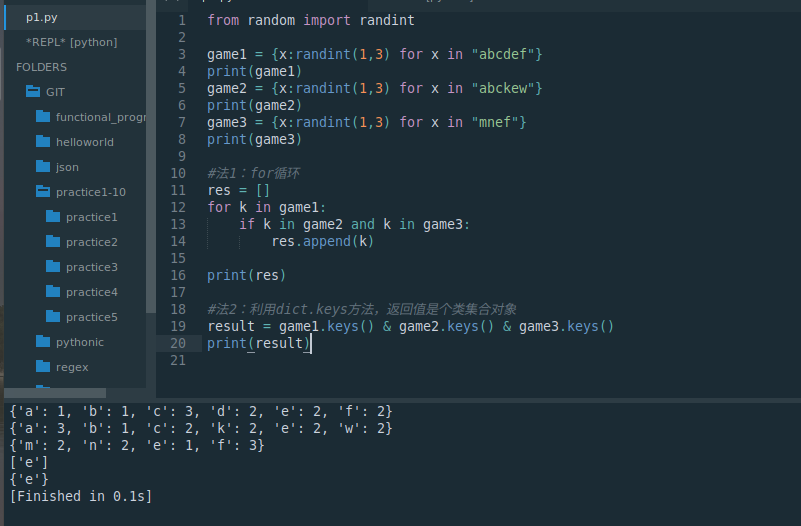
- pythonic
from random import randint
from functools import reduce
game1 = {x:randint(1,3) for x in "abcdef"}
print(game1)
game2 = {x:randint(1,3) for x in "abckew"}
print(game2)
game3 = {x:randint(1,3) for x in "mnef"}
print(game3)#注意:func不能直接为keys!!
#map函数返回值为iterator
a = map(dict.keys,[game1,game2,game3])
result = reduce(lambda x,y: x & y,a)
print(result)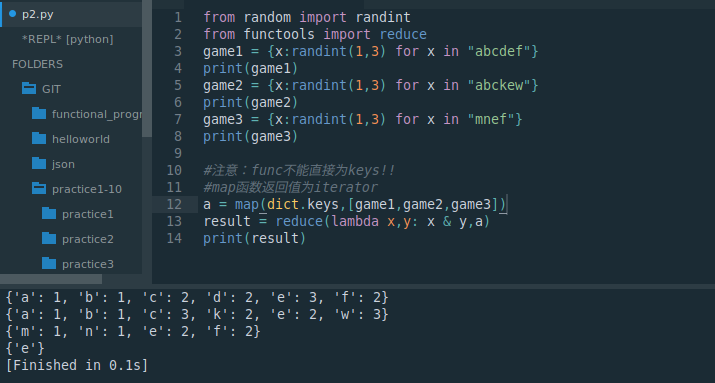
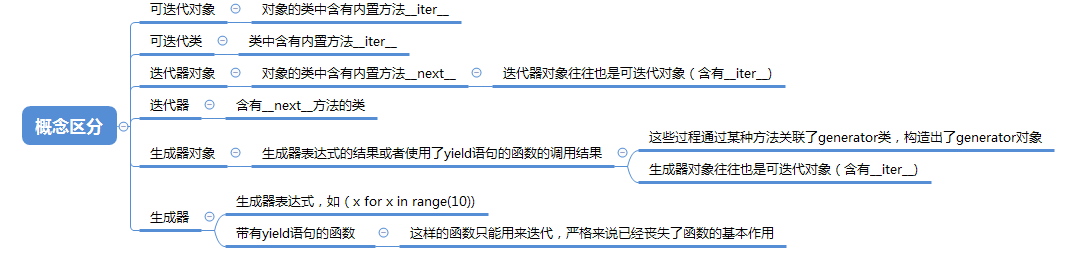
#practice6:可迭代对象与迭代器对象

- 概念区分
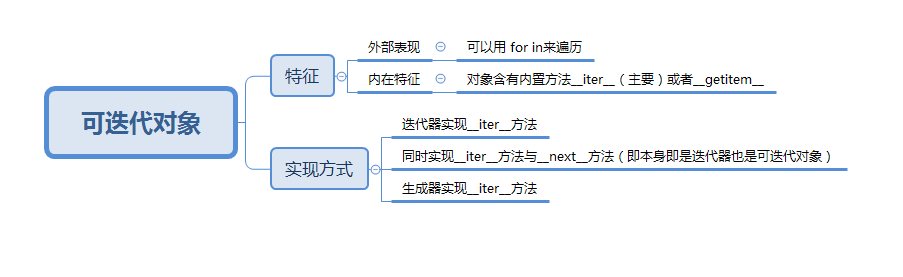
- 各种可迭代实现方案的总依循:python的迭代协议
Python 的迭代协议需要 _iter_() 方法返回一个实现了 _next_() 方法的迭代器对象。
- 可迭代对象的具体实现
3.1 方案一:迭代器方案
3.1.1 实现迭代器
import requests
import pprint
#测试代码
# r = requests.get('http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC')
# pprint.pprint(r.json())#实现一个迭代器
from collections import Iterator#构造迭代器
class WeatherIterator(Iterator):def __init__(self,cities):self.cities = citiesself.index = 0def getweather(self,city):r = requests.get('http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=' + city)dict_data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0]return "%s:%s,%s" % (city,dict_data['low'],dict_data['high'])def __next__(self):if self.index == len(self.cities):raise StopIterationcity = self.cities[self.index]self.index += 1return self.getweather(city)#生成迭代器对象
weatheriterator = WeatherIterator([u'北京',u'南京',u'上海'])
#迭代器对象调用next()方法
print(weatheriterator.__next__())
print(weatheriterator.__next__())
print(weatheriterator.__next__())
#没有定义__iter__方法,不是可迭代对象,所以暂时无法for in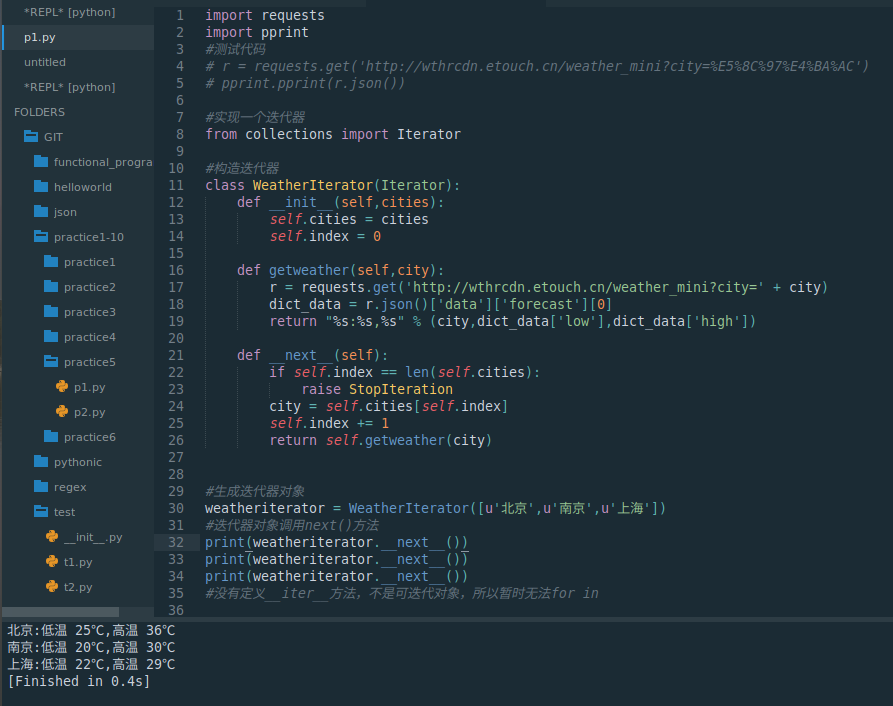
3.1.2 实现可迭代类
ather(self,city):r = requests.get('http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=' + city)dict_data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0]return "%s:%s,%s" % (city,dict_data['low'],dict_data['high'])def __next__(self):if self.index == len(self.cities):raise StopIterationcity = self.cities[self.index]self.index += 1return self.getweather(city)class WeatherIterable(Iterable):def __init__(self,cities):self.cities = citiesdef __iter__(self):#返回迭代器对象return WeatherIterator(self.cities)#生成可迭代对象
weatheriterable = WeatherIterable([u'北京',u'南京',u'上海'])#for in 遍历机制的伪过程
#第一步:weatheriterable = weatheriterable.__iter__(),weatheriterable变成了迭代器对象WeatherIterator(self.cities)
#第二步:遍历一次,就调用一次weatheritearble.next(),即WeatherIterator(self.cities).__next__(),最终返回值为天气信息字符串,赋值给x
for x in weatheriterable:print(x)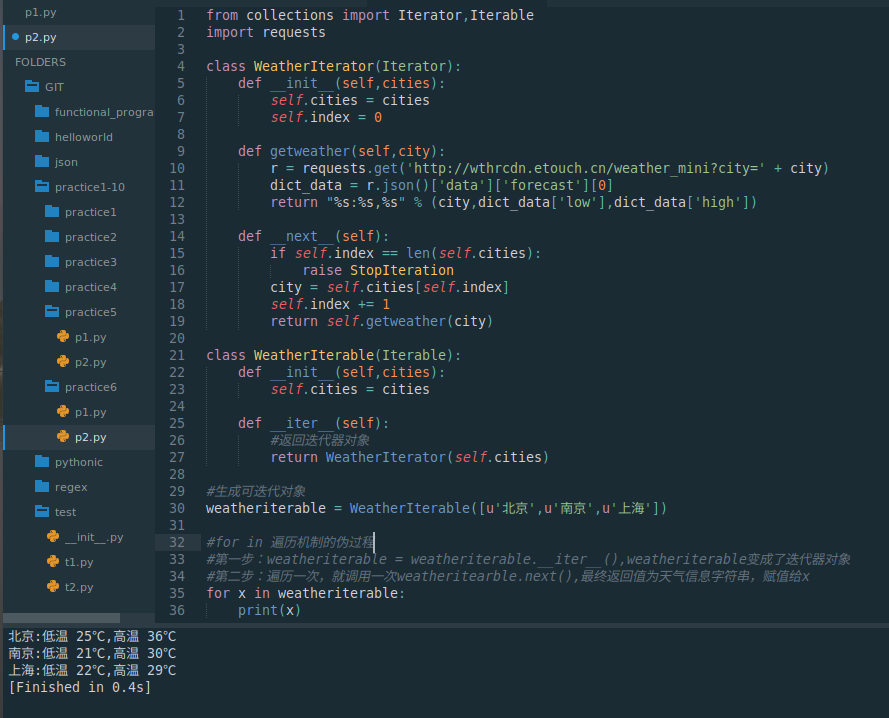
这是最标准的python迭代协议;需要建两个类,比较繁琐
3.2 方案二、合并两个类,最终使用一个类,来实现可迭代类(对方案一的简化)
from collections import Iterator,Iterable
import requestsclass WeatherIterable(Iterable):def __init__(self,cities):self.cities = citiesself.index = 0def __iter__(self):#返回迭代器对象return selfdef getweather(self,city):r = requests.get('http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=' + city)dict_data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0]return "%s:%s,%s" % (city,dict_data['low'],dict_data['high'])def __next__(self):if self.index == len(self.cities):raise StopIterationcity = self.cities[self.index]self.index += 1return self.getweather(city)weatheriterable = WeatherIterable([u'北京',u'南京',u'上海'])#伪过程
#第一步:weatheriterable = weatheriterable.__iter__(),返回weatheriterable对象本身
#对象本身就有__next__方法,是的迭代器对象;这样就满足了python迭代协议
#第二步:遍历一次,就调用一次weatheritearble.__next__(),最终返回值为天气信息字符串,赋值给x
for x in weatheriterable:print(x)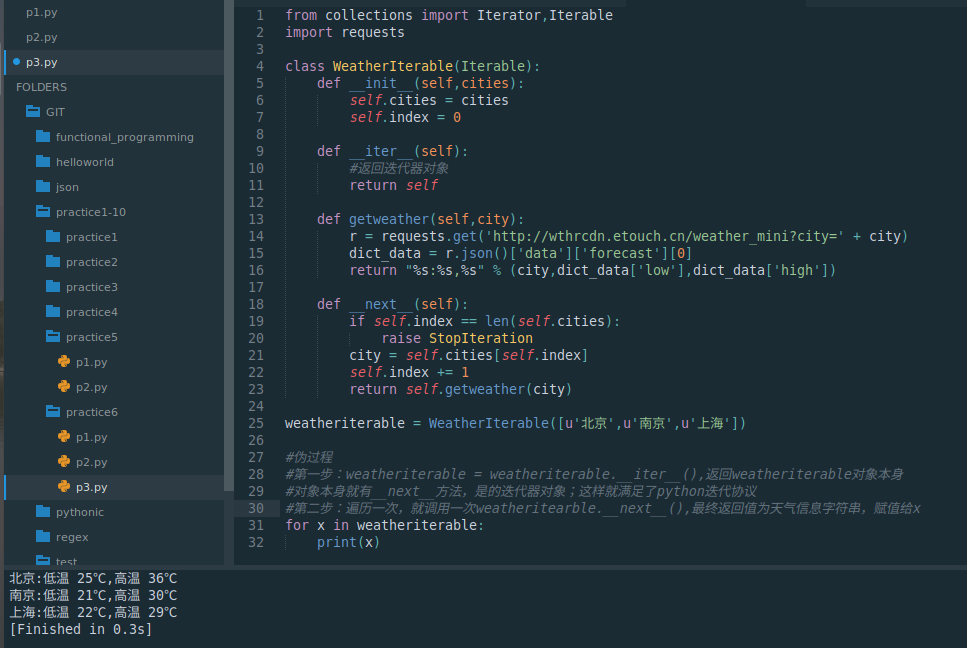
上述weatheriterable即是可迭代对象,又是迭代器对象
3.3 方案三:iter与next进一步合并,将iter方法定义为生成器(推荐)
from collections import Iterator,Iterable
import requestsclass WeatherIterable(Iterable):def __init__(self,cities):self.cities = citiesself.index = 0def __iter__(self):for x in range(len(self.cities)):city = self.cities[self.index]self.index += 1yield self.getweather(city) def getweather(self,city):r = requests.get('http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=' + city)dict_data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0]return "%s:%s,%s" % (city,dict_data['low'],dict_data['high'])weatheriterable = WeatherIterable([u'北京',u'南京',u'上海'])
#伪过程
#第一步:weatheriterable = weatheriterable.__iter__(),调用生成器,返回__iter__生成器的生成器对象
#生成器对象默认拥有__iter__与__next__方法
#所以返回生成器对象也可以视作返回迭代器对象,符合python迭代协议
#第二步:遍历一次,就调用一次【迭代器对象】.__next__(),最终返回值为天气信息字符串,赋值给x
#yield的背后可能就是调用__next__,哈哈
for x in weatheriterable:print(x)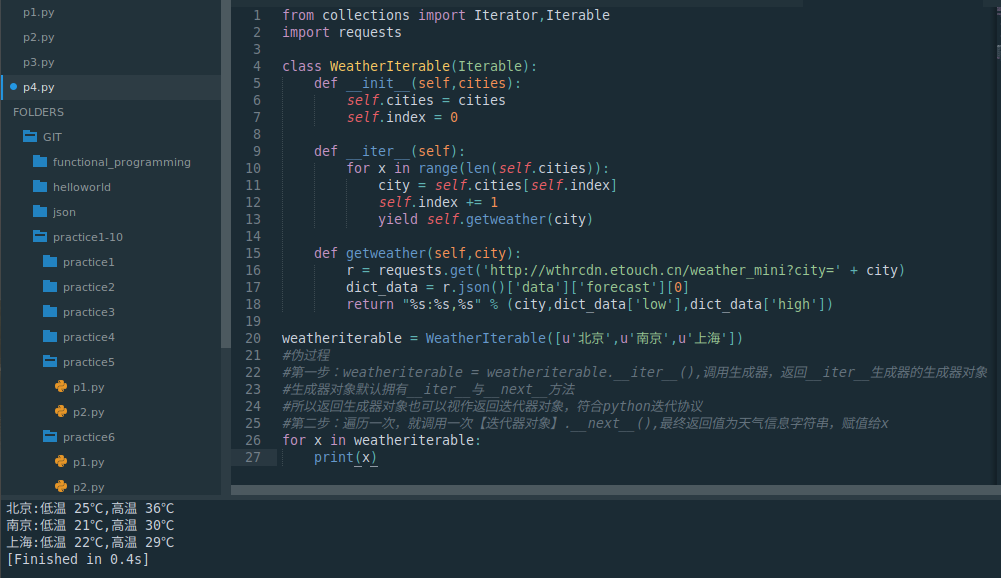
- 反向迭代
与正向迭代流程完全相同,只不过要在可迭代类中定义内置方法reversed。
from collections import Iterator,Iterable
import requestsclass WeatherIterable(Iterable):def __init__(self,cities):self.cities = citiesself.index = 0def __iter__(self):for x in range(len(self.cities)):city = self.cities[self.index]self.index += 1yield self.getweather(city) def __reversed__(self):#在这个函数内设计代码,实现反向逻辑即可for x in range(len(self.cities)):self.index -= 1city = self.cities[self.index]yield self.getweather(city) def getweather(self,city):r = requests.get('http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=' + city)dict_data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0]return "%s:%s,%s" % (city,dict_data['low'],dict_data['high'])weatheriterable = WeatherIterable([u'北京',u'南京',u'上海'])for x in weatheriterable:print(x)
print("*"*20)
for x in reversed(weatheriterable):print(x)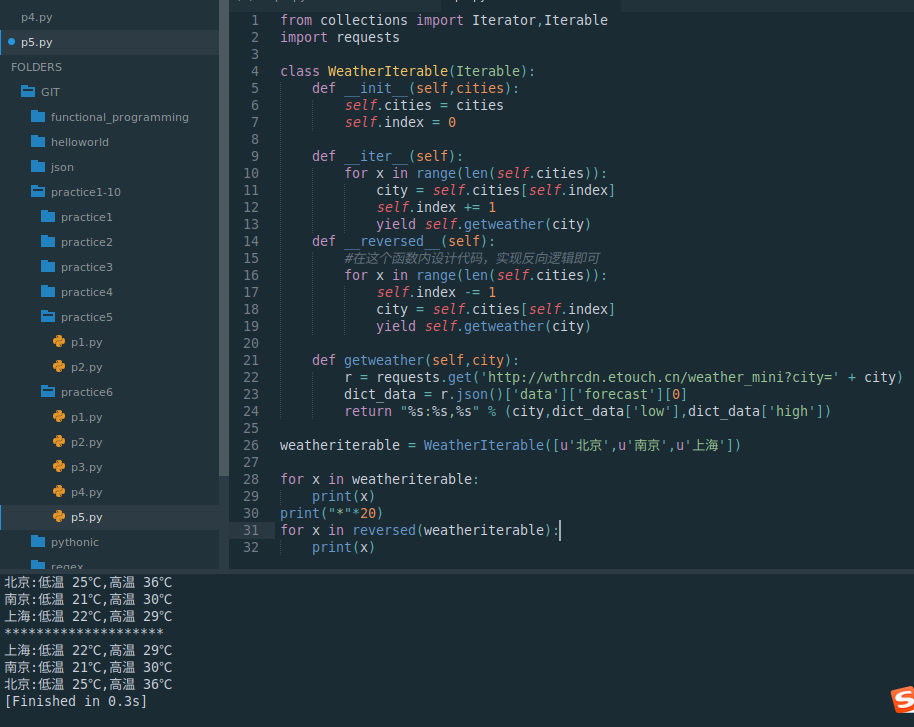
- 可迭代对象切片
from collections import Iterator,Iterable
import requests
from itertools import isliceclass WeatherIterable(Iterable):def __init__(self,cities):self.cities = citiesself.index = 0def __iter__(self):for x in range(len(self.cities)):city = self.cities[self.index]self.index += 1yield self.getweather(city) def __reversed__(self):#在这个函数内设计代码,实现反向逻辑即可for x in range(len(self.cities)):self.index -= 1city = self.cities[self.index]yield self.getweather(city) def getweather(self,city):r = requests.get('http://wthrcdn.etouch.cn/weather_mini?city=' + city)dict_data = r.json()['data']['forecast'][0]return "%s:%s,%s" % (city,dict_data['low'],dict_data['high'])weatheriterable = WeatherIterable([u'北京',u'南京',u'上海',u'广州'])
#weatheriteterable是可迭代对象,但不是迭代器对象
#网上有的将islice操作称为迭代器切片;但个人认为可迭代对象切片更准确
print(dir(weatheriterable))
for x in islice(weatheriterable,0,2):print(x)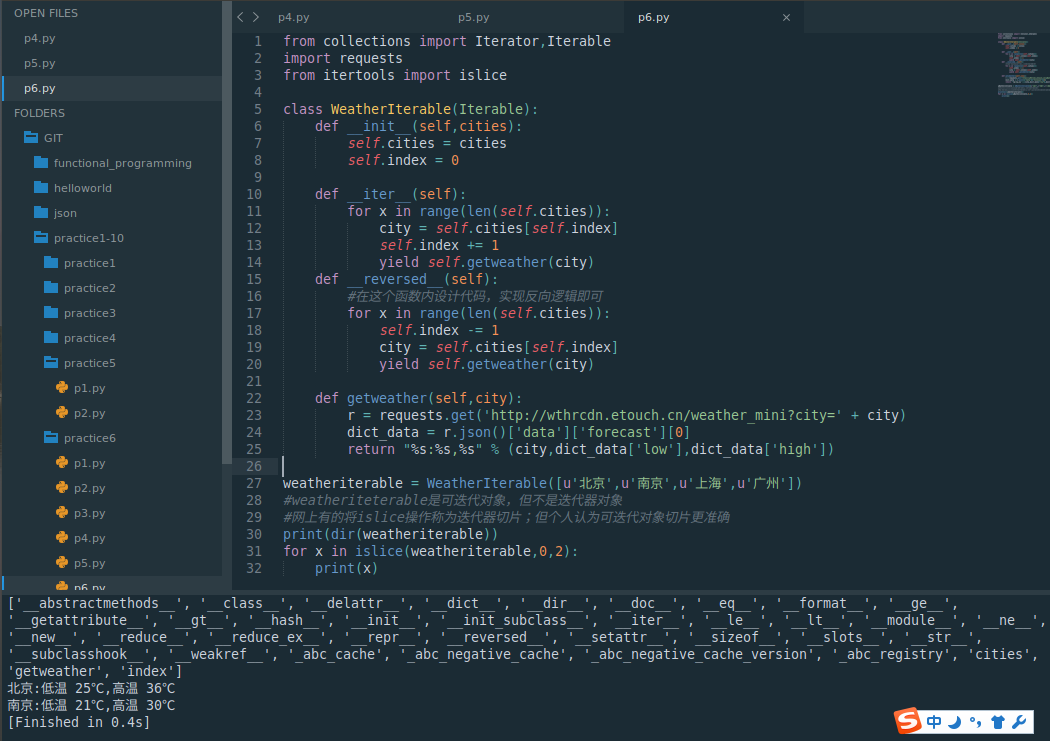
islice(a,3)表示0:3;islice(a,3,None)表示3:结束;不可以用负数index进行切片!
#practice7:字符串拆分

- 方法一:自己设计函数(使用字符串处理函数split)
def mysplit(s,split_keys):#a为初始列表,字符串转列表的方法如下a = [s]for split_key in split_keys:#t为分割后的暂时列表t = []#list操作是必须的,否则t.extend无法生效#Python中即使某个操作有返回值,也可以不赋值list(map(lambda x: t.extend(x.split(split_key)),a))##将分割后的列表赋值给初始列表,进入下一轮循环a = treturn as = 'ab;cd|efg|hi,jkl|mn\topq;rst,uvw\txyz'
result = mysplit(s,';,|\t')
print(result)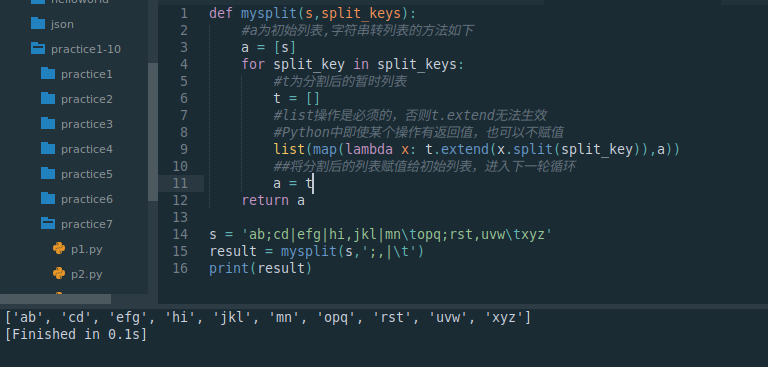
- 方法二:re.split函数
import res = 'ab;cd|efg|hi,jkl|mn\topq;rst,uvw\txyz'
result = re.split(r'[;|,\t]+',s)
print(result)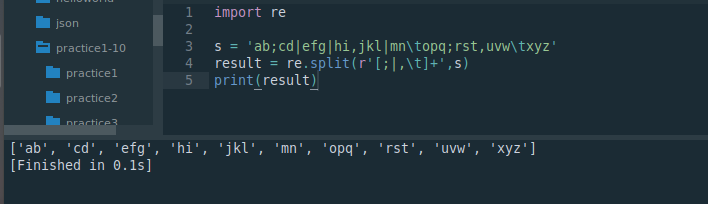
#practice8:判断字符串开头/结尾是某个字符串

- 简单示例,使用字符串方法startwith与endwith
import osfiles = os.listdir('/home/openlab')
print(files)
for x in files:if x.endswith('.py'):print('*'*20 + x)#注意:不是elseif#startswith与endswith使用多个参数时,只能用元组将参数括起来,参数间关系为或!elif x.startswith(('.s','.x')):print('#'*20 + x)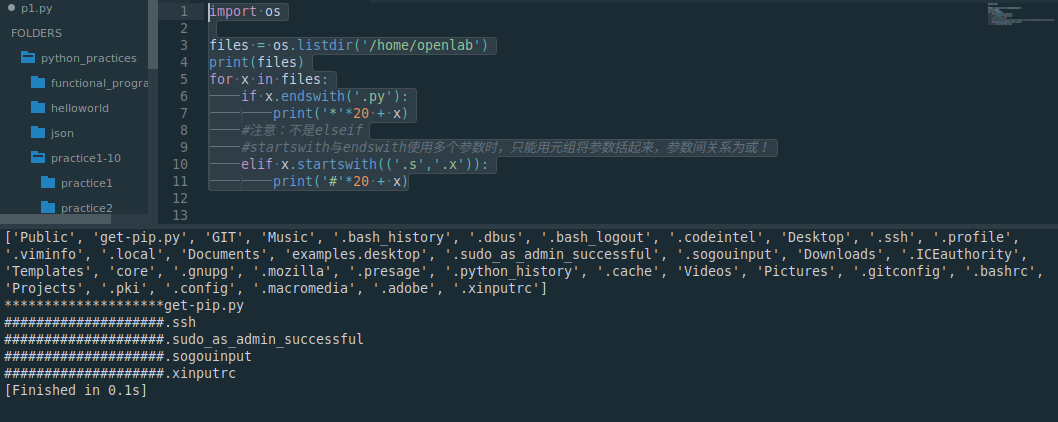
- 文件、命令相关操作补充
import subprocess,os#调用check_output,执行命令并返回结果
out_bytes = subprocess.check_output(['ls','-l'])
out_text = out_bytes.decode('utf-8')
print(out_text)
#调用system函数,执行命令并将状态码返回
return_code = os.system('touch 1.txt')
print(return_code)import stat
#返回stat对象
result = os.stat('p2.py')
#返回十进制的文件mode(包括权限等一系列信息)
print(result.st_mode)
#转换为八进制便于观察
print(oct(result.st_mode))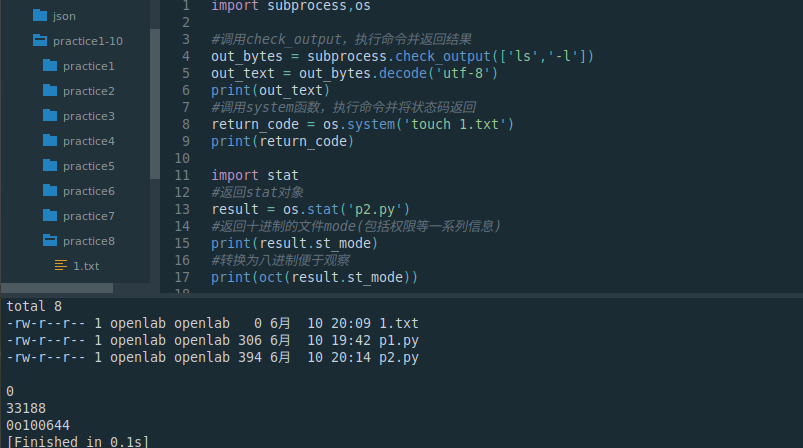
- 实际实例
import os,stat
import subprocessdef show_status(path='.'):output_bytes = subprocess.check_output(['ls','-l',path])output_text = output_bytes.decode('utf-8')print(output_text)show_status()
#找当前文件夹下的Python文件,并为文件的拥有者以及相同用户组的成员添加可执行权限
files = os.listdir('.')
for file in files:if file.endswith('py'):#采用或的方式添加权限os.chmod(file,os.stat(file).st_mode | stat.S_IXGRP | stat.S_IXUSR)show_status()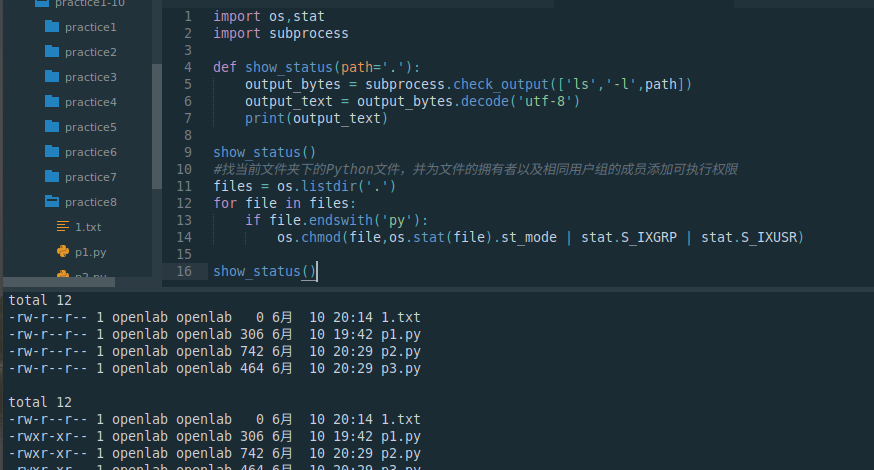
关于stat模块:
https://www.cnblogs.com/maseng/p/3386140.html
#practice9:文本字符串替换(正则表达式分组的使用)
import rewith open('/var/log/dpkg.log') as f:text = f.read()
#注意:re.sub并不会对text做出改变,而是返回新的字符串!
new_text = re.sub(r'(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})',r'(\1)(\2)(\3)',text)
'''
也可以换一种写法(使用分组名称):
new_text = re.sub(r'(?P<year>\d{4})-(?P<month>\d{2})-(?P<day>\d{2})',r'(\g<year>)(\g<month>)(\g<day>)',text)
'''
print(text)
print(new_text)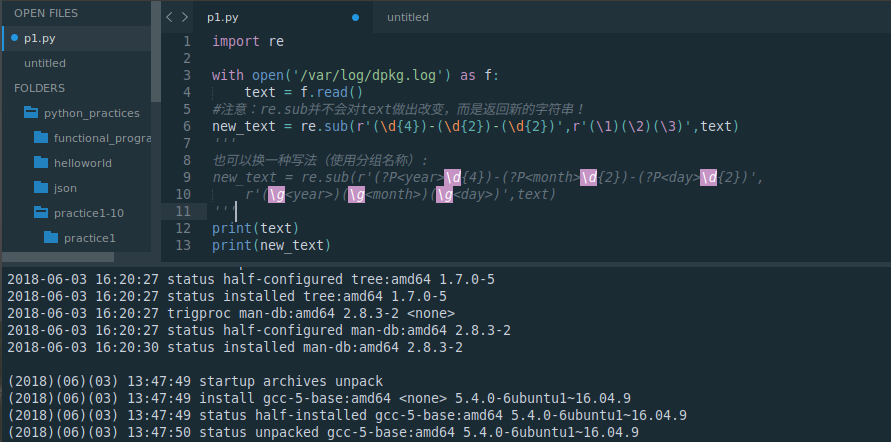
#practice10:字符串拼接(join方法)与字符串对齐
- 字符串拼接
l = ['1','2','ss','q']
#相比于加号拼接,下列方法不仅简洁,而且占用内存小!
result = ''.join(l)
print(result)
result = 'AA'.join(l)
print(result)
#join参数是iterable即可,所以用生成器表达式生产一个generator对象(是iterable)也合理
result = ''.join((str(x) for x in range(10)))
print(result)
字符串对齐
方法一: 调用字符串方法
方法二: format函数
a = 'wakaka'
a1 = a.ljust(20)
a2 = a.rjust(20)
a3 = a.center(20)
print(a1)
print(len(a1))
print(a2)
print(a3)a1 = format(a,'<20')
a2 = format(a,'>20')
a3 = format(a,'^20')
print(a1)
print(len(a1))
print(a2)
print(a3)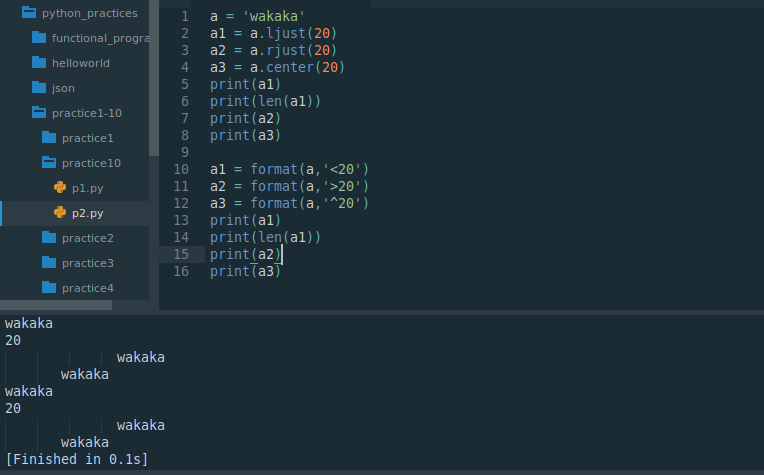
- 实际应用
from random import randint
dict1 = {str(x):randint(10,20) for x in ['wakaka','dd','ffs']}
#取最长值的方法
test = map(len,dict1.keys())
#map对象可以直接max!
max_len = max(test)
for k in dict1:print(k.ljust(max_len) + ":" + str(dict1[k]))
python3练习题:1-10相关推荐
- python编程一球从100米_【Python3练习题 015】 一球从100米高度自由落下,每次落地后反跳回原高度的一半,再落下。求它在第10次落地时,共经过多少米?第10次反弹多高?...
问题:一球从某高度自由落下,每次落地后反跳回原高度的一半:再落下,求它在第n次落地时,共经过多少米?第n次反弹多高? import java.util.Scanner; //题目:一球从100米高度自 ...
- P1469 找筷子(python3实现)-- 10分
"""P1469 找筷子(python3实现)-- 10分 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1469""" ...
- python3练习题:并发编程(21-25)
关于python3中的并发编程,经过这些天的学习,归纳如下: #practice21:多线程 线程的定义 方法一:直接Thread()构造 方法二:构造Thread的子类 #多线程的使用 from u ...
- python3练习题:11-20
practice11: excel读写(xlsx文件) 1. excel读 excel内容 import xlrd#不可以使用-来代替/home/openlab book = xlrd.open_wo ...
- python3学习笔记10(迭代器和生成器)
参考http://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-iterator-generator.html 迭代器 迭代器对象从集合的第一个元素开始访问,直到所有的元素被访问完结束 ...
- Python3.5 Django1.10 Scrapy1.2 Ubuntu16.04 HTML5
1.Python3.5 1. 虚拟环境 venv python3.4 创建虚拟环境(py3.4自带venv,不需要安装) Ubuntu 16.4 python3.5升级python3.6 sudo a ...
- 个人计算机中央处理器一般称为,计算机考试题库:计算机基础练习题(10)
[导读] 2016年中公事业单位考试网为各位考生提供事业单位计算机专业知识学习,包括事业单位考试计算机常识.计算机基础知识试题及答案,为大家带来的是<计算机基础练习题(10)>,希望可以帮 ...
- python3 练习题 day01
#练习题:'''1.简述变量命名规范'''#变量名由数字.字母.下划线组成#变量名可以字母和下划线开头,不能以数字开头,并且不能全为数字#变量名不能太长,且要有意义#最好使用驼峰或下划线格式命令#变量 ...
- Python3快速入门—10.知识扩展
10.Python3扩展 10.1异常 10.1.1常见异常 程序在运行时产生的错误称为异常. 在官网https://docs.python.org/3/library/exceptions.html ...
- 【Python3练习题 002】企业发放的奖金根据利润提成
# [Python练习题 002]企业发放的奖金根据利润提成.# 利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%:利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成,高于10万元的部分, ...
最新文章
- 连续霸榜 Github!又有一个 Linux 神器出现了
- weblogic升级之ddconverter
- v3是c语言吗 yolo_YOLOv3
- mybatis实现一对多关系《DeptEmp》
- Dubbo面试题锦集
- synchronized关键字理解
- null对象访问static属性或方法
- Maven入门学习,安装及创建项目
- python语音库_Python中的Python文本到语音
- C++ char 类型:字符型和最小的整型
- MySQL · 性能优化 · SQL错误用法详解
- Flink 中的应用部署:当前状态与新应用模式
- Android页面传值b,android数据传递(一)之activityA传递到activityB
- Java线程池ThreadPoolExecutor使用与解析
- matlab——knnsearch用法介绍
- 杀毒软件 McAfee 创始人狱中身亡,75 年传奇人生画下句号
- matlab 四维等值面图,一个4列数组怎样画出三维等值面图
- 红手指云手机屏蔽方案
- 悟空遥控器 android 5.1,悟空遥控器服务端
- 2019,关于我的故事
热门文章
- 几乎死循环的存储过程
- Intellij Idea生成serialVersionUID的方法
- 设A和B是两个按元素值递增有序的单链表,写一算法将A和B归并为按按元素值递减有序的单链表C,试分析算法的时间复杂度。(利用上篇带有头结点的线性链表操作)...
- SQL注入—我是如何一步步攻破一家互联网公司的
- block 实现原理详解(一)
- 利用OpenCV的VideoWriter类实现视频的写操作
- c++中类的构造函数的初始化成员列表详解
- 计算机应用基础851,清华大学851西方经济学考研参考书目及考研真题
- SSL WS-Security--Web Service安全保障
- threejs加载obj模型_Vulkan编程指南(章节31-载入模型)
