【翻译】Apache Hbase新特性--MOB支持(一)
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
原文链接:http://blog.cloudera.com/blog/2015/06/inside-apache-hbases-new-support-for-mobs/
HBase MOBs特性的设计背景
Apache HBase is a distributed, scalable, performant, consistent key value database that can store a variety of binary data types. It excels at storing many relatively small values (<10K), and providing low-latency reads and writes.
However, there is a growing demand for storing documents, images, and other moderate objects (MOBs) in HBase while maintaining low latency for reads and writes. One such use case is a bank that stores signed and scanned customer documents. As another example, transport agencies may want to store snapshots of traffic and moving cars. These MOBs are generally write-once.
Apache HBase是一个分布式、可扩展,高性能,一致的键值数据库,可以存储多种多样的二进制数据。存储小文件(小于10K)十分出色,读写延迟低。
随之而来,对文档、图片和其他中等大小文件的存储需求日益增长,并且要保持读写低延迟。一个典型的场景就是银行存储客户的签字或扫描的文档。另一个典型的场景,交通部门保存路况或过车快照。中等大小文件通常写入一次。
Unfortunately, performance can degrade in situations where many moderately sized values (100K to 10MB) are stored due to the ever-increasing I/O pressure created by compactions. Consider the case where 1TB of photos from traffic cameras, each 1MB in size, are stored into HBase daily. Parts of the stored files are compacted multiple times via minor compactions and eventually, data is rewritten by major compactions. Along with accumulation of these MOBs, I/O created by compactions will slow down the compactions, further block memstore flushing, and eventually block updates. A big MOB store will trigger frequent region splits, reducing the availability of the affected regions.
In order to address these drawbacks, Cloudera and Intel engineers have implemented MOB support in an HBase branch (hbase-11339: HBase MOB). This branch will be merged to the master in HBase 1.1 or 1.2, and is already present and supported in CDH 5.4.x, as well.
不幸的是,存储文件大小在100k到10M之间时,由于压缩导致的持续增长的读写压力,会导致性能下降。想象一下这样的场景,交通摄像头每天产生1TB的照片存到Hbase里,每个文件1MB。一部分文件被多次压缩以达到最小化。数据因为压缩被重复写入。随着中等大小文件数量的积累,压缩产生的读写会使压缩变慢,进一步阻塞memstore刷新,最终阻止更新。大量的MOB存储会触发频繁的region分割,相应region的可用性下降。
为了解决这个问题,Cloudera和Intel的工程师在Hbase的分支实现了对MOB的支持。 (hbase-11339: HBase MOB)。(译者注:这个特性并没有出现在1.1和1.2版本,而是被合入的2.0.0版本)。你可以在CDH 5.4.x中获取。
Operations on MOBs are usually write-intensive, with rare updates or deletes and relatively infrequent reads. MOBs are usually stored together with their metadata. Metadata relating to MOBs may include, for instance, car number, speed, and color. Metadata are very small relative to the MOBs. Metadata are usually accessed for analysis, while MOBs are usually randomly accessed only when they are explicitly requested with row keys.
Users want to read and write the MOBs in HBase with low latency in the same APIs, and want strong consistency, security, snapshot and HBase replication between clusters, and so on. To meet these goals, MOBs were moved out of the main I/O path of HBase and into a new I/O path.
In this post, you will learn about this design approach, and why it was selected.
对MOB的操作通常集中在写入,很少更新或删除,读取不频繁。MOB通常跟元数据一起被存储。元数据相对MOB很小,通常用来统计分析,而MOB一般通过明确的row key来获取。
用户希望在Hbase中用相同的API来读写MOB文件,并且集群之间保持低延迟,强一致、安全、快照和Hbase副本等特性。要达到这一目标,必须将MOB从 HBase主要的读写目录移到新的读写目录。
可行方案分析
There were a few possible approaches to this problem. The first approach we considered was to store MOBs in HBase with a tuned split and compaction policies—a bigger desired MaxFileSize decreases the frequency of region split, and fewer or no compactions can avoid the write amplification penalty. That approach would improve write latency and throughput considerably. However, along with the increasing number of stored files, there would be too many opened readers in a single store, even more than what is allowed by the OS. As a result, a lot of memory would be consumed and read performance would degrade.
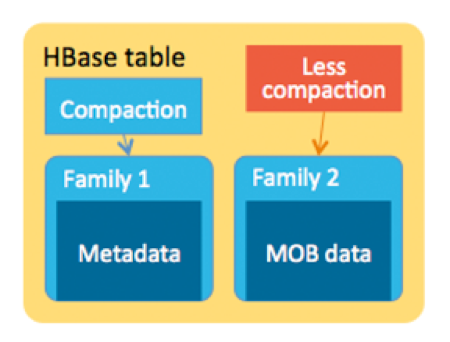
解决这个问题有潜在的方法。第一种,优化分割(split)和压缩策略——一个更大的MaxFileSize来降低region分割频率,减少或者不压缩来避免写入恶化。这样会改善写入延迟,吞吐量好得多。但是,随着文件数量的增长,一次存储会打开非常多的reader,甚至超过操作系统的限制。结果就是内存被耗光,性能下降。
Another approach was to use an HBase + HDFS model to store the metadata and MOBs separately. In this model, a single file is linked by an entry in HBase. This is a client solution, and the transaction is controlled by the client—no HBase-side memories are consumed by MOBs. This approach would work for objects larger than 50MB, but for MOBs, many small files lead to inefficient HDFS usage since the default block size in HDFS is 128MB.
For example, let’s say a NameNode has 48GB of memory and each file is 100KB with three replicas. Each file takes more than 300 bytes in memory, so a NameNode with 48GB memory can hold about 160 million files, which would limit us to only storing 16TB MOB files in total.
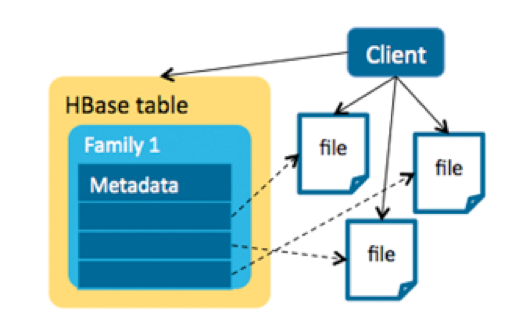
另外一种方式可以采用HBase+HDFS的方式来分开存储元数据和MOB文件。一个文件对应一个Hbase入口。这是客户端的解决方案,事务在客户端控制。MOB不会消耗Hbase的内存。存储的对象可以超过50MB。但是,大量的小文件使HDFS利用率不高,因为默认的块大小是128M。
举个例子,NameNode有48G内存,每个文件100KB,3个副本。每个文件在内存中占用300字节,48G内存可以存大约1.6亿文件,限制了存储的总文件大小仅仅16T。
As an improvement, we could have assembled the small MOB files into bigger ones—that is, a file could have multiple MOB entries–and store the offset and length in the HBase table for fast reading. However, maintaining data consistency and managing deleted MOBs and small MOB files in compactions are difficult. Furthermore, if we were to use this approach, we’d have to consider new security policies, lose atomicity properties of writes, and potentially lose the backup and disaster recovery provided by replication and snapshots.
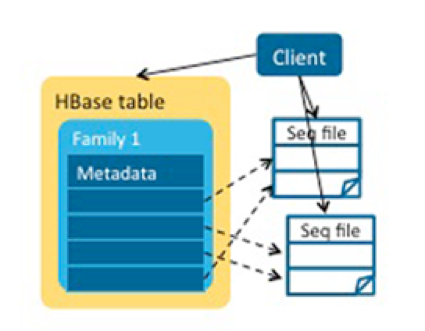
我们可以许多小的MOB合成一个大文件,一个文件有多个MOB入口,通过存储偏移量(offset)和长度来加快读取。不过维护数据一致性,管理删除的文件和压缩后的小文件十分困难。而且,我们还需要考虑安全策略,失去写数据的原子性,可能会丢失由复制和快照提供的备份和灾难恢复。
HBase MOB 架构设计
In the end, because most of the concerns around storing MOBs in HBase involve the I/O created by compactions, the key was to move MOBs out of management by normal regions to avoid region splits and compactions there.
The HBase MOB design is similar to the HBase + HDFS approach because we store the metadata and MOBs separately. However, the difference lies in a server-side design: memstore caches the MOBs before they are flushed to disk, the MOBs are written into a HFile called “MOB file” in each flush, and each MOB file has multiple entries instead of single file in HDFS for each MOB. This MOB file is stored in a special region. All the read and write can be used by the current HBase APIs.
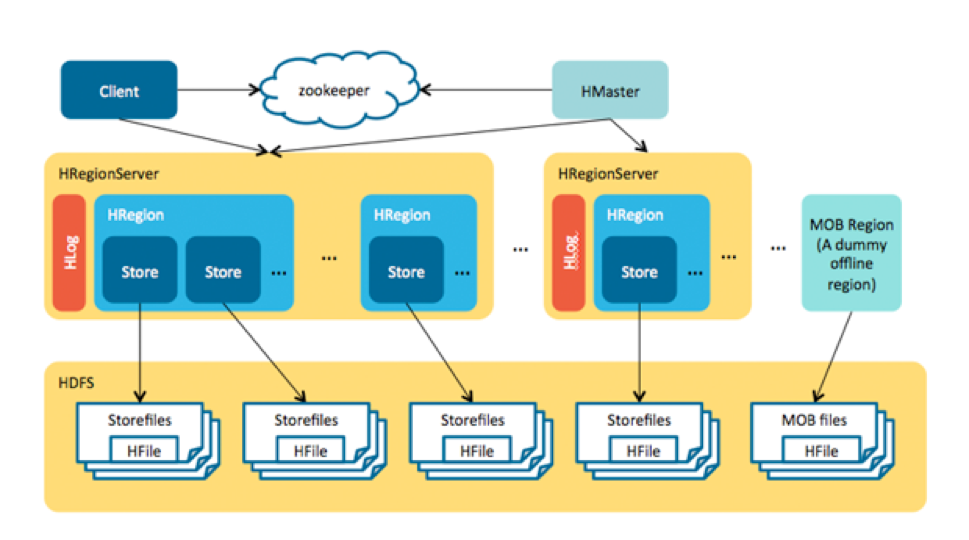
最后,由于大部分担心来自于压缩带来的IO,最关键的是将MOB移出正常region的管理来避免region分割和压缩。
HBase MOB设计类似于Hbase+HDFS的方式,将元数据和MOB分开存。不同的是服务端的设计。中等大小文件在被刷到磁盘前缓存在memstore里,每次刷新,中等大小文件被写入特殊的HFile文件—“MOB File”。每个中等文件有多个MOB入口,而不像HDFS只有一个入口。MOB file被放在特殊的region。读写都通过现有的Hbase API。
未完,见下一篇:https://my.oschina.net/u/234661/blog/1553060
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/u/234661/blog/1553005
【翻译】Apache Hbase新特性--MOB支持(一)相关推荐
- Docker 1.5新特性:支持IPV6、只读容器、容器运行监控,还有彩蛋
本文讲的是Docker 1.5新特性:支持IPV6.只读容器.容器运行监控,还有彩蛋,[编者的话]Docker 1.5是今年Docker第一个发布版本,在这个版本中Docker加入很多期望已久的新功能 ...
- switch 字符串 java_JDK7新特性switch支持字符串
在JDK7中,switch语句的判断条件增加了对字符串类型的支持.由于字符串的操作在编程中使用频繁,这个新特性的出现为Java编程带来了便利.接下来通过一个案例演示一下在switch语句中使用字符串进 ...
- OpenSSL 1.1.1 新特性: 全面支持国密SM2/SM3/SM4加密算法
OpenSSL项目最近6个月添加了许多新特性, 包括对中国SM2/SM3/SM4算法的支持: SM2椭圆曲线: https://github.com/openssl/openssl/pull/4793 ...
- kubernetes1.4新特性:支持两种新的卷插件
背景介绍 在Kubernetes中卷的作用在于提供给POD持久化存储,这些持久化存储可以挂载到POD中的容器上,进而给容器提供持久化存储. 从图中可以看到结构体PodSpec有个属性是Volumes, ...
- Kubernetes1.7新特性:支持绕过docker,直接通过containerd管理容器
背景情况 从Docker1.11版本开始,Docker依赖于containerd和runC来管理容器,containerd是控制runC的后台程序,runC是Docker公司按照OCI标准规范编写的一 ...
- Mozilla新特性只支持https网站
Mozilla的官方博客2015.4.30正式宣布了淘汰HTTP的方案. 其中包括:设定一个日期,所有的新特性将只提供给HTTPS网站:HTTP网站将逐步被禁止访问浏览器功能,尤其是那些与用户安全和隐 ...
- asp.net core 6 新特性,支持HTTP/3 端点发布
???? 序言 Http3 协议构建在UDP的基础上,是的,就这么神奇,以前被誉为不稳定大神的UDP,现在承担起可靠通讯协议的底层协议.为了消除UDP的不确定性,在UDP协议之上,新增了QUIC协议. ...
- C# 4.0 新特性之支持 Contra-variance (转)
我们已经知道数组的 Variance.接口和委托的 Covariance 的概念和基本用法.本文介绍在 Variance 上的另外一种情况,即 Contra-variance. Contra-vari ...
- Android4.0新特性 中文翻译
转自http://www.eoeandroid.com/thread-103300-1-1.html android4.0 SDK发布有一段时间了,在eoe上找到了翻译过的新特性说明,特转载 Andr ...
最新文章
- 实战:RocketMQ削峰,这一篇就够了
- 雷林鹏分享:jQuery EasyUI 数据网格 - 创建页脚摘要
- AngularJs学习笔记--unit-testing
- 11.分页(10-10-12)
- 单点登录Redis存储Session及SessionId问题说明与集群实战-1
- roku能不能安装软件_如何阻止假期更改Roku主题
- Java方法中的参数太多,第1部分:自定义类型
- 在oracle中处理日期大全
- WCF分布式开发步步为赢系列
- 网页浏览器 市面上存在的网页浏览器
- mysql stop salve_MySQL主从切换
- asp.net gridview 模板列 弹出窗口编辑_如何使用极速PDF编辑器的注释工具?
- BigDecimal使用不当,老板的损失照样从你工资里扣
- linux和Windows之间共享文件
- 小程序之botton默认带边框的问题
- [转载] 晓说——第17期:揭秘战争秘闻 朝鲜战争62年祭(下)
- 面向对象概念及对象、抽象、类的解释
- linux服务器视频转换,linux下视频格式转换工具
- youku吉他弹唱视频
- CycleGAN中欺骗相反域的鉴别器是什么意思
热门文章
- 使用uni-app开发微信小程序之登录模块
- 剑指Offer Ⅱ 001. 整数除法(力扣剑指Offer专项突击版——整数_1)
- 游戏计算机性能要求,游戏主机只能玩游戏?只要性能够强悍,什么需求都能满足!...
- python知识:numpy的维度之变
- html 地址坐标图标,浏览器地址栏中显示自定义小图标
- python语言基础与应用 mooc答案_Python语言基础与应用_中国大学mooc慕课_期末考试选修课答案...
- android can为啥能发收不到数据_拼多多登录时手机收不到短信验证码怎么办
- (POST请求中的三种数据请求格式.application/x-www-form-urlencoded和multipart/form-data和application/json)
- 2021-04-24 人工智能必读书单 Python
- webpack4.x热更新,自动刷新
