java SSL 简单操作demo
SSL process :http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/security/jsse/JSSERefGuide.html#HowSSLWorks
1、客户端服务器谈判协商可用的加密套件:
在客户端与服务器开始的SSL session中,客户端发消息告诉服务器其自己所支持的加密套件列表:
SSLSocket.getSupportedCipherSuites() ,然后服务器选择一个较好的加密套件
2、Authenticating the Server (认证服务器)
该步骤实质为 客户端认证服务器,即客户端是否选择信任自己正在交流的服务器,其实该步骤是可选的。
服务器为了证明自己就是自己所声称的身份,服务器需要向客户端出示自己的“ public key certificate”——
公开密钥证书,如果证书有效,则客户端就可以确认服务器的身份。
服务器会与客户端交换信息使得双方同意该 secret key,例如RSA,客户端从服务器出示的 证书中获得public key,然后加密 secret key information,接着发送该加密的信息给服务器,服务器利用自己的private key 解密信息,以便认证客户端
3、Sending the Encrypted Data
Both the client and the server now have access to the same secret key. With each message, they use the cryptographic hash function, chosen in the first step of this process, and shared secret information, to compute an HMAC that they append to the message. They then use the secret key and the secret key algorithm negotiated in the first step of this process to encrypt the secure data and the HMAC. The client and server can now communicate securely using their encrypted and hashed data.
以下为ssl 消息的图:
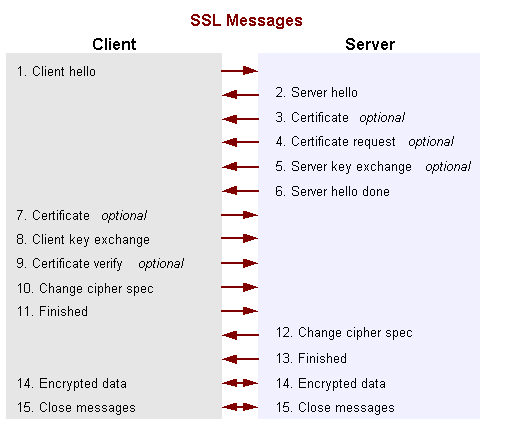
The SSL messages are sent in the following order:
Client hello - The client sends the server information including the highest version of SSL it supports and a list of the cipher suites it supports. (TLS 1.0 is indicated as SSL 3.1.) The cipher suite information includes cryptographic algorithms and key sizes.
Server hello - The server chooses the highest version of SSL and the best cipher suite that both the client and server support and sends this information to the client.
Certificate - The server sends the client a certificate or a certificate chain. A certificate chain typically begins with the server's public key certificate and ends with the certificate authority's root certificate. This message is optional, but is used whenever server authentication is required.
Certificate request - If the server needs to authenticate the client, it sends the client a certificate request. In Internet applications, this message is rarely sent.
Server key exchange - The server sends the client a server key exchange message when the public key information sent in message 3 above is not sufficient for key exchange. For example, in ciphersuites based on Diffie-Hellman, this message contains the server's DH public key.
Server hello done - The server tells the client that it is finished with its initial negotiation messages.
Certificate - If the server requests a certificate from the client in message 4, the client sends its certificate chain, just as the server did in message 3.
Note: Only a few Internet server applications ask for a certificate from the client.
Client key exchange - The client generates information used to create a key to use for symmetric encryption. For RSA, the client then encrypts this key information with the server's public key and sends it to the server. For ciphersuites based on Diffie-Hellman, this message contains the client's DH public key.
Certificate verify - This message is sent when a client presents a certificate as previously explained. Its purpose is to allow the server to complete the process of authenticating the client. When this message is used, the client sends information that it digitally signs using a cryptographic hash function. When the server decrypts this information with the client's public key, the server is able to authenticate the client.
Change cipher spec - The client sends a message telling the server to change to encrypted mode.
Finished - The client tells the server that it is ready for secure data communication to begin.
Change cipher spec - The server sends a message telling the client to change to encrypted mode.
Finished - The server tells the client that it is ready for secure data communication to begin. This is the end of the SSL handshake.
Encrypted data - The client and the server communicate using the symmetric encryption algorithm and the cryptographic hash function negotiated in messages 1 and 2, and using the secret key that the client sent to the server in Message 8. The handshake can be renegotiated at this time. See the next section for details.
Close Messages - At the end of the connection, each side will send a
close_notify messageto inform the peer that the connection is closed.
If the parameters generated during an SSL session are saved, these parameters can sometimes be reused for future SSL sessions. Saving SSL session parameters allows encrypted communication to begin much more quickly.
import javax.net.ssl.*;
import java.security.*;// Create/initialize the SSLContext with key materialchar[] passphrase = "passphrase".toCharArray();// First initialize the key and trust material.
KeyStore ksKeys = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
ksKeys.load(new FileInputStream("testKeys"), passphrase);
KeyStore ksTrust = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
ksTrust.load(new FileInputStream("testTrust"), passphrase);// KeyManager's decide which key material to use.
KeyManagerFactory kmf =KeyManagerFactory.getInstance("SunX509");
kmf.init(ksKeys, passphrase);// TrustManager's decide whether to allow connections.
TrustManagerFactory tmf =TrustManagerFactory.getInstance("SunX509");
tmf.init(ksTrust);sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
sslContext.init(kmf.getKeyManagers(), tmf.getTrustManagers(), null);// We're ready for the engine.
SSLEngine engine = sslContext.createSSLengine(hostname, port);// Use as client
engine.setUseClientMode(true);当下的web应用好多都转到了https,有时候需要利用java发送https请求,但是呢服务器有证书,又没有好的办法得到服务器证书,一般会自定义jsse里的信任管理器,让客户端不验证服务器的证书的有效性,此方法一般就叫绕过证书之类的,下面给一个参考demo:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URL;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;import javax.net.ssl.HostnameVerifier;
import javax.net.ssl.HttpsURLConnection;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSession;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;
import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;/** * @Title: SSLDemo1.java* @Package * @Description: TODO(用一句话描述该文件做什么)* @author huhu * @date 2016年1月21日 上午10:08:45* @version V1.0 */
public class SSLDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {trustAllHttpsCertificates();HostnameVerifier hv = new HostnameVerifier() {@Overridepublic boolean verify(String hostname, SSLSession session) {System.out.println("Warning: URL Host: " + hostname + " vs. " + session.getPeerHost()); return true; }};HttpsURLConnection.setDefaultHostnameVerifier(hv);// 在建立Https连接之前做如上处理后,后续就跟普通http处理一样URL url = new URL("https://dynamic.12306.cn/otsweb/main.jsp");HttpsURLConnection conn = (HttpsURLConnection) url.openConnection();SSLContext sc = SSLContext.getInstance("SSL");conn.connect();
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream())) ;
// String input = "" ;
//
// while((input = br.readLine()) != null){
// System.out.println(input);
// }}private static void trustAllHttpsCertificates() throws Exception{TrustManager[] tms = new TrustManager[1];TrustManager tm = new CustomTrustManager();tms[0] = tm ;SSLContext context = SSLContext.getInstance("SSL");context.init(null, tms, null);HttpsURLConnection.setDefaultSSLSocketFactory(context.getSocketFactory());}static class CustomTrustManager implements X509TrustManager{@Overridepublic void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType)throws CertificateException {}@Overridepublic void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain, String authType)throws CertificateException {}@Overridepublic X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {return null;}}
}Generating and Processing SSL/TLS data
The two main SSLEngine methods wrap() and unwrap() are responsible for generating and consuming network data respectively.
PKIX TrustManager Support
The default trust manager algorithm is "PKIX". The default can be changed by editing the ssl.TrustManagerFactory.algorithm property in the java.security file.
HostnameVerifier
public class MyHostnameVerifier implements HostnameVerifier {public boolean verify(String hostname, SSLSession session) {// pop up an interactive dialog box// or insert additional matching logicif (good_address) {return true;} else {return false;}}
}
HttpsURLConnection urlc = (HttpsURLConnection)(new URL("https://www.sun.com/")).openConnection();
urlc.setHostnameVerifier(new MyHostnameVerifier());转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/langlichong/1737072
java SSL 简单操作demo相关推荐
- github上创建java项目简单操作
github上创建java项目简单操作 参考L: github上创建java项目简单操作 - CSDN博客 http://blog.csdn.net/qq_29392425/article/detai ...
- java代码简单操作Redis数据Jedis jar
java操作Redis数据API->Jedis Jedis引入 作为java码农,如何在代码中操作Redis呢? Jedis的介绍 Redis不仅可以使用命令来操作,现在基本上主流的语言都有AP ...
- 安卓访问mysql的源码_【原创源码】安卓数据库简单操作demo
[Java] 纯文本查看 复制代码public Long updateSql(String text) { ContentValues contentValues = new ContentValue ...
- java qq邮箱服务器端口_[Java教程]javamail 利用qq邮箱做邮箱服务器,简单小demo
[Java教程]javamail 利用qq邮箱做邮箱服务器,简单小demo 0 2016-07-12 10:00:10 首先maven:javax.mailmail1.4.1 用户名密码验证:1 pu ...
- java 基础api实现上传,上传文件到7牛云存储的java api一个简单的demo实现
最近在做一个项目,需要用到云存储,项目用的是七牛云.现在将项目过程中关于调用七牛云平台的java api来上传本地文件到七牛云空间的一个简单的demo展示给大家,希望对同样再用七牛云的童鞋们有所帮助. ...
- java 结构体_Java实现单链表的简单操作
文章目录 前言 一.基本实现思路 二.代码实现 1.定义结点类2.定义链表类3.测试调用4.结果 总结 前言 用Java实现单链表的简单操作,阅读本文和上一篇文章体会Java中类与C++中结构体指针的 ...
- java对mysql的简单操作的综合运用——登录+注册+修改密码
本篇博客是java对mysql的简单操作的综合运用--登录系统.java对mysql的简单操作的综合运用--注册系统.java对mysql的简单操作的综合运用--修改密码系统的整合. 因为使用的是数据 ...
- java对mysql的简单操作的综合运用——修改密码系统
本篇博客运用到: java连接mysql数据库连接 java对mysql的简单操作--修改数据 下面是修改密码系统的完整代码 import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; im ...
- java对mysql的简单操作的综合运用——登录系统
本篇博客运用到: java连接mysql数据库连接(数据搜索) 下面是登录系统的完整代码 import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.even ...
最新文章
- Fortify:五大SOA架构都有安全漏洞
- Deep Reinforcement Learning 深度增强学习资源
- debian与cenos常见命令不同处
- 软件工程实训有必要吗_软件工程实训报告的总结.docx
- 【机器学习】数据挖掘实战:金融贷款分类模型和时间序列分析
- 关于Unity中的Mesh Collider碰撞器
- linux开源文档管理系统_Linux中的系统管理员问题 免费和开源软件
- JS检测浏览器是否最大化
- v-for获取(循环次数)对象的length长度
- 重庆科技学院c语言程序设计报告,2020年重庆科技学院《911程序设计综合》硕士研究生招生复试大纲...
- 一个月薪两万的Web安全工程师要掌握哪些技能?
- WiMAX版图不止3G
- linux 镜像 多 网络,Linux内核实现多路镜像流量聚合和复制的方法
- Android使用弹出式对话框
- 通过tf的tensorboard可视化训练进度
- DB9标准的公头\母头接线定义
- Tkinter教程之Frame篇
- Kafka 安装配置及下载地址
- Cookie的SameSite属性
- 正态总体均值假设检验
热门文章
- Spring MVC上传文件后重命名读取不显示,报错已解决(The origin server did not find a current representation for the targe)
- python面向对象属性_Python面向对象属性
- docker实践第二版pdf 网盘_【漫画】什么是 docker?docker 应用场景解析
- vba判断是否为数字的方法小集
- List列表拒绝添加重复信息
- 【引用】她拒绝了他100次,但第101次他拒绝了她
- GitHub标星7700:Python从新手到大师,只要100天
- 美国62%智能音箱用户都使用了语音购物,连鹦鹉都忍不住了
- 思必驰十年创业,(现在)是一家怎样的公司?
- 白板随手一画,嗖嗖变成代码
