人工智能ai算法_AI算法比您想象的要脆弱得多
人工智能ai算法
In William Gibson’s 2010 novel Zero History, a character preparing to go in a high-stakes raid wears an oddly-patterned t-shirt that renders him invisible on the monitoring CCTVs. It’s an idea many science fiction writers have written about, and it has captivated audiences so much because it challenges the notion that AI is unbeatable and all-knowingly. With a simple trick, someone can trick the algorithm? — it is a fun idea in sci-fi, but it’s can’t happen with real machine learning algorithms. Or so we thought.
在威廉·吉布森(William Gibson)的2010年小说《 零历史》中 ,准备参加高风险突袭的角色穿着奇怪的T恤衫,使他在监视CCTV上不可见。 这是许多科幻小说家所写的想法,它吸引了很多观众,因为它挑战了AI无与伦比且无所不知的观念。 一个简单的技巧,有人可以欺骗算法吗? —在科幻小说中这是一个有趣的主意,但是在真正的机器学习算法中却不可能发生。 还是我们认为。
For good or for worse, machine learning algorithms can be tricked by slight changes to inputs, intentional or not, into its system. Recently in 2020, the cybersecurity firm McAfee showed that Mobileye — the car intelligence system used by Tesla and other auto manufacturers — could be fooled into accelerating 50 MPH over the speed limit just by plastering a strip of black tape two inches wide to a speed limit sign.
不管是好是坏,机器学习算法都可以通过对其系统中有意或无意的输入进行细微更改而被欺骗。 不久前,在2020年,网络安全公司McAfee证明,只要将一条宽2英寸的黑胶带涂在速度极限上,就可以欺骗Mobileye(特斯拉和其他汽车制造商使用的汽车智能系统)将速度提高50英里/小时。标志。
Researchers from four universities including the University of Washington and UC Berkeley discovered that road sign recognition models were completely fooled when introduced to a bit of spray paint or stickers on stop signs — all completely natural and non-malicious alterations.
来自包括华盛顿大学和加州大学伯克利分校在内的四所大学的研究人员发现,将道路标志识别模型引入停车位标志上的一些喷漆或贴纸后,会被完全愚弄,这些都是完全自然和非恶意的改动。
Researchers at MIT 3-d printed a toy turtle with a texture especially designed to make Google’s object detection system classify it as a rifle, regardless of the angle at which the turtle was viewed. One can imagine how catastrophic the result would be if these sorts of systems were utilized in public spaces to prevent shooters and a child was holding that textured toy turtle. On the other hand, think of a rifle textured not to look like one.
麻省理工学院3-d的研究人员印制了一种带有特殊纹理的玩具乌龟,该纹理专门用于使Google的物体检测系统将其分类为步枪,而不管其视角如何。 可以想象如果在公共场所使用这种系统来防止射手,而一个孩子拿着那只质感的玩具乌龟,结果将是多么灾难性的后果。 另一方面,想一想步枪的纹理看起来不一样。
As machine learning takes an ever more important role in the world, these types of so-called ‘adversarial inputs’ — designed to be malicious or not — are a serious problem in the real-world development of these algorithms. So when state-of-the-art image recognition neural networks misclassify a panda as a gibbon when a seemingly invisible adversarial filter is introduced…
随着机器学习在世界上扮演着越来越重要的角色,这些所谓的“对抗性输入”(无论是否设计为恶意的)在这些算法的实际开发中都是一个严重的问题。 因此,当采用看似不可见的对抗过滤器时,当最新的图像识别神经网络将熊猫误认为长臂猿时……
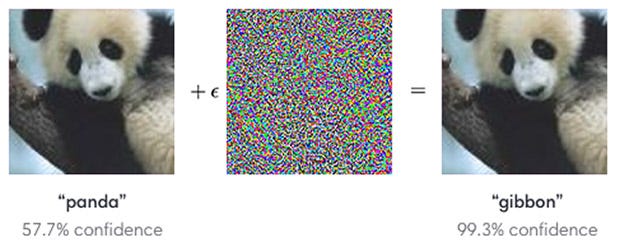
…we can’t help but wonder why neural networks have this vulnerability.
…我们不禁想知道为什么神经网络具有此漏洞。
Most adversarial inputs take advantage of something called a weak decision boundary. As the neural network is trained on thousands or even millions of training examples, it continually adjusts certain thresholds and rules it stores internally that dictate how it classifies the example. For example, consider a neural network trained to classify digits from 0 to 9: as it loops through countless training examples, its decision boundary becomes more and more firm in places where there is more ‘activity’. If a certain pixel has a value near 0 for half of the digits and a value near 1 for the other half, the network would store this useful information and utilize it in its predictions.
大多数对抗性输入都利用了称为弱决策边界的优势。 当神经网络在数千甚至数百万个训练示例上进行训练时,它会不断调整内部存储的某些阈值和规则,这些阈值和规则决定了如何对示例进行分类。 例如,考虑一个经过训练的将0到9的数字进行分类的神经网络:当它遍历无数训练示例时,其决策边界在“活动”更多的地方变得越来越坚定。 如果某个像素的一半数字值接近0,另一半数字值接近1,则网络将存储此有用信息并将其用于预测。
But for pixels that remain relatively constant throughout all the images, like those along the perimeter of the image, the information that specific pixel adds to the decision-making process is less clear, since almost all of them are the same value regardless of pixel value. Yet occasionally, there may be one or two images, like the 6 below, that collide with the target location. This makes that pixel extremely sensitive to any changes. The decision boundary in that dimension is then considered to be very weak.
但是对于在整个图像中保持相对恒定的像素(如沿图像周边的像素),特定像素添加到决策过程的信息不太清楚,因为几乎所有像素都是相同的值,而与像素值无关。 但有时,可能会有一两个图像(如下面的6个图像)与目标位置发生冲突。 这使得该像素对任何变化都极为敏感。 然后认为该维度上的决策边界非常弱。
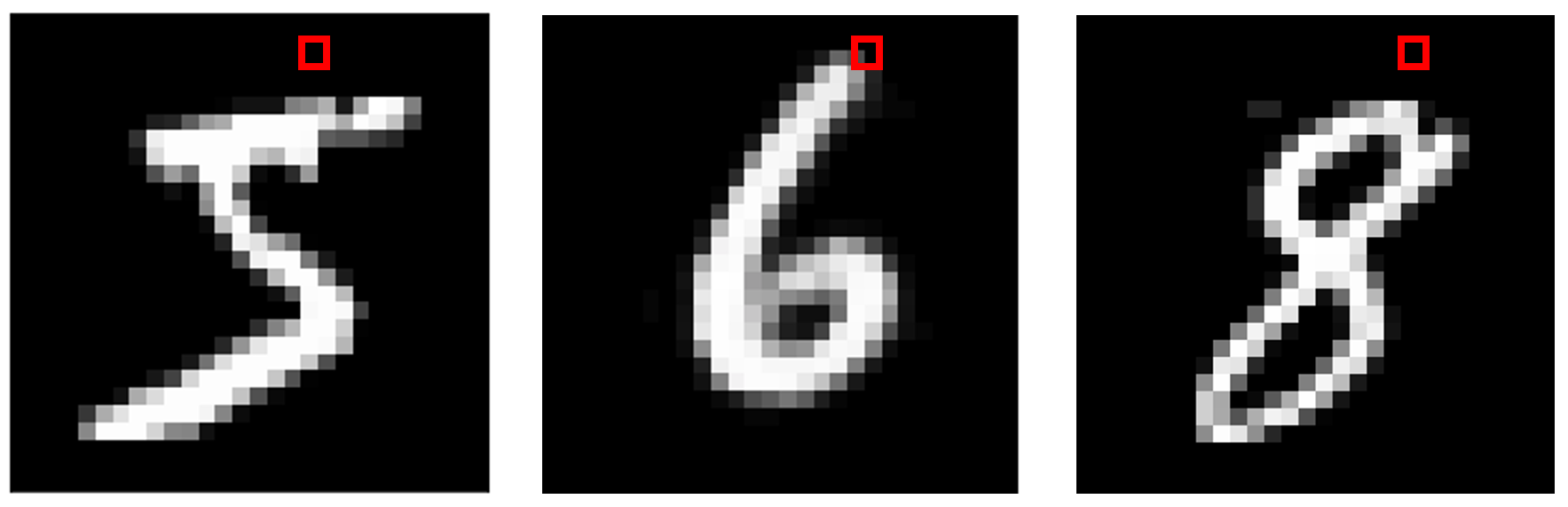
Hence, switching that pixel completely white on any image would be taking advantage of this very sensitive part of the input and would drastically increase the chance of a model marking the image as a ‘6’, since it recalls ‘6’ being the only training example that had a value other than 0 for that value. In reality, however, that pixel value has nothing to do with a 6; it might as well have been an ‘8’ or a ‘3’. By random chance, 6 happened to be the only digit that had a unique value for that pixel, but because the pixel was so sensitive, the model took away the wrong conclusion.
因此,在任何图像上将该像素切换为全白将利用输入的这一非常敏感的部分,并且将大大增加模型将图像标记为“ 6”的机会,因为它回想起“ 6”是唯一的训练。例如,该值的值不是0。 然而,实际上,该像素值与6无关。 它也可能是“ 8”或“ 3”。 偶然地,6恰好是该像素唯一具有唯一值的数字,但是由于像素非常敏感,因此该模型得出了错误的结论。
Although this example utilizes the freedom to change one pixel, most modernized adversarial inputs adjust all of the pixels a little bit, which allows for more complexity and subtlety, although the reason why it works is the same as why changing one pixel in an image would work.
尽管此示例利用了更改一个像素的自由度,但是大多数现代化的对抗性输入都会稍微调整所有像素,这会带来更多的复杂性和微妙性,尽管其工作原理与更改图像中一个像素的原因相同工作。
These sorts of weak decision boundaries will inevitably exist in any neural network because of the nature of datasets, which naturally will have pixels that provide little information. However, studies in these malicious inputs show that one set of sensitive pixels in one neural network architecture do not necessarily show the same level of sensitivity in other architectures and datasets. Hence, malicious inputs are constructed based on pixel sensitivities of ‘standard’ architectures, like VGG16 or ResNet.
由于数据集的性质,这类弱决策边界将不可避免地存在于任何神经网络中,而数据集自然会具有提供很少信息的像素。 但是,对这些恶意输入的研究表明,一种神经网络体系结构中的一组敏感像素不一定在其他体系结构和数据集中显示相同水平的敏感性。 因此,恶意输入是基于“标准”架构(例如VGG16或ResNet)的像素敏感度构造的。
Certain changes, however, like the two inches of tape mentioned above, are ‘universal’ in that they attempt to target sensitive locations regardless of model structure or dataset. Adversarial filters, like the one applied to the panda image above, take advantage of several weak boundaries and sensitive combinations of inputs. These types of alterations, intentionally malicious or not, are very dangerous for applications of machine learning in places like self-driving cars.
但是,某些更改(例如上述两英寸的磁带)是“通用的”,因为它们试图以敏感位置为目标,而与模型结构或数据集无关。 对抗过滤器,就像上面的熊猫图像一样,利用了一些弱边界和输入的敏感组合 。 这些类型的更改(无论是否故意存在)对于自动驾驶汽车等场所的机器学习应用都是非常危险的。
What’s worse, physical adversarial inputs, or perbutations, aren’t actually ‘hacking’ at all. Placing stickers on stop signs, or even holding signs from different angles and perspectives, can cause sign recognition neural networks to misclassify the signs as yield and speed limit 45 signs; anyone who has been in a city has probably seen stickers on signs and other sources of natural physical perbutations at least dozens of times.
更糟糕的是,实际的对抗性输入或攻击实际上根本不是“黑客”。 在停车标志上贴上贴纸,或者甚至从不同角度和角度拿着标志,都可能导致标志识别神经网络将标志错误分类为屈服和限速45个标志; 到过城市的任何人都可能至少看过数十次自然标志物和其他自然痕迹的标贴。

These sorts of attacks don’t just happen in images, though. Simple linear NLP word-vectorized classification models (e.g. logistic regression on bag of words) that perform so well on identifying spam emails are failing more often because spammers overwhelm their email content with so-called ‘good words’ and deliberately misspell ‘bad words’ that trick the model into confidently classifying it as non-spam. Other inputs deliberately take advantage of statistical weaknesses in clustering algorithms and attempt to distort the clustering process.
但是,这类攻击不仅发生在图像中。 在识别垃圾邮件方面表现出色的简单线性NLP词向量化分类模型(例如,对词袋的逻辑回归)更经常失败,这是因为垃圾邮件发送者以所谓的“好词”压倒了他们的电子邮件内容,并故意拼写错误的“坏词”诱使该模型将其自信地分类为非垃圾邮件。 其他输入故意利用了聚类算法中的统计缺陷,并试图扭曲聚类过程。
So how can machine learning engineers secure their models against adversarial inputs that could lead to a disastrous outcome?
那么,机器学习工程师如何针对可能导致灾难性后果的对抗性输入来保护其模型呢?
The simplest brute-force method is adversarial training, which is when the model is trained on all sorts of possibilities of perbutations and hence becomes robust to them. One method of achieving this is with data augmentation, like the data generator found in Keras — these augmenters can flip an image, distort it around a point, turn it, change the brightness, etc. Other forms of augmentation may be to randomly scatter noise masks or to randomly apply known adversarial input filters over images. This augmentation can strengthen the decision boundaries for sensitive pixels.
最简单的暴力方法是对抗训练,这是在模型针对各种可能的抵制可能性进行训练时,对它们变得健壮。 一种实现此目的的方法是使用数据增强,例如Keras中的数据生成器-这些增强器可以翻转图像,使其围绕一个点变形,旋转,改变亮度等。其他形式的增强可能是随机分散噪声遮罩或在图像上随机应用已知的对抗输入过滤器。 这种增强可以增强敏感像素的决策边界。
Sometimes, adversarial training is enough in that it covers all the possible scenarios a machine learning model would encounter. The issue with this method, however, is that the model is explicitly told to be robust to each randomly generated potential issue, and hence have difficulty generalizing a solution to new issues, like a uniquely designed sticker.
有时,对抗训练就足够了,因为它涵盖了机器学习模型可能遇到的所有可能情况。 但是,此方法的问题在于,明确告知模型对每个随机生成的潜在问题均具有鲁棒性,因此难以概括出新问题的解决方案,例如设计独特的标签。
An alternative solution is defensive distillation, a strategy in which the model is trained based on performance predicting probabilities instead of classes. For example, if a neural network were trained to categorize cats vs dogs, the metric would not be accuracy, as in how many times the class was successfully predicted, but some function of how far off the probability was from a ground truth probability (the label). These probabilities may be supplied by human annotators or by another earlier model trained on the same task using class labels.
另一种解决方案是防御性蒸馏,该策略是根据性能预测概率而不是类别来训练模型的策略。 例如,如果训练了一个神经网络对猫与狗进行分类,则度量标准将不是准确的,因为成功预测了该类别有多少次,但是某些函数与概率相距地面真实概率(标签)。 这些概率可以由人工注释者提供,也可以由其他早期使用类标签在同一任务上训练的模型提供。
The result of defensive distillation is a model with much smoother landscapes in directions perbutations attempt to exploit (decision boundaries that are sensitive because it is narrowly torn between two classes). This makes it difficult to discover input alterations that can lead to an incorrect categorization. This method was originally created to train smaller models to imitate larger ones (model compression) for computational savings, although it has shown to work well in preventing adversarial inputs.
防御性蒸馏的结果是一个模型,该模型在尝试开发的方向上具有更加平滑的景观(决策边界之所以敏感,是因为它在两个类别之间被狭窄地撕裂了)。 这使得很难发现可能导致错误分类的输入更改。 该方法最初是为了训练较小的模型以模仿较大的模型(模型压缩)以节省计算量而创建的,尽管它在防止对抗性输入方面表现良好。
Adversarial inputs and weak decision boundaries have also been observed in the brains of animals in the study of zoology and even in human brains with visual tricks. Machine learning is already or will be in responsible of millions of lives in the form of surveillance systems, self-driving cars, automated airplanes, and missile detonation systems. We can’t let it be fooled by simple perbutations, and as AI’s presence increases, handling adversarial inputs needs to be at the forefront of every machine learning engineer’s mind.
在动物学的动物学研究中,甚至在具有视觉技巧的人脑中,也观察到了对抗性输入和较弱的决策界限。 机器学习已经或将以监视系统,自动驾驶汽车,自动飞机和导弹爆炸系统的形式对数百万条生命负责。 我们不能让它被简单的支持所迷惑,并且随着AI的出现率的增加,处理对抗性输入必须摆在每位机器学习工程师的脑海中。
更多阅读 (More Reading)
One Pixel Attack for Fooling Deep Neural Networks
愚弄深度神经网络的一种像素攻击
Robust Physical-World Attacks on Deep Learning Visual Classification
深度学习视觉分类的强大物理世界攻击
Distillation as a Defense to Adversarial Perturbations against Deep Neural Networks
蒸馏作为对抗深度神经网络的对抗性扰动的防御
翻译自: https://medium.com/swlh/machine-learning-algorithms-are-much-more-fragile-than-you-think-25fdb3939fee
人工智能ai算法
http://www.taodudu.cc/news/show-1874153.html
相关文章:
- 自然语言理解gpt_GPT-3:自然语言处理的创造潜力
- ai中如何建立阴影_在投资管理中采用AI:公司如何成功建立
- ibm watson_IBM Watson Assistant与Web聊天的集成
- ai替代数据可视化_在药物发现中可视化AI初创公司
- 软件测试前景会被ai取代吗_软件测试人员可能很快会被AI程序取代
- ansys电力变压器模型_最佳变压器模型的超参数优化
- 一年成为ai算法工程师_我作为一名数据科学研究员所学到的东西在一年内成为了AI领导者...
- openai-gpt_为什么GPT-3感觉像是编程
- 医疗中的ai_医疗保健中自主AI的障碍
- uber大数据_Uber创建了深度神经网络以为其他深度神经网络生成训练数据
- http 响应消息解码_响应生成所需的解码策略
- 永久删除谷歌浏览器缩略图_“暮光之城”如何永久破坏了Google图片搜索
- 从头实现linux操作系统_从头开始实现您的第一个人工神经元
- 语音通话视频通话前端_无需互联网即可进行数十亿视频通话
- 优先体验重播matlab_如何为深度Q网络实施优先体验重播
- 人工智能ai以算法为基础_为公司采用人工智能做准备
- ieee浮点数与常规浮点数_浮点数如何工作
- 模型压缩_模型压缩:
- pytorch ocr_使用PyTorch解决CAPTCHA(不使用OCR)
- pd4ml_您应该在本周(7月4日)阅读有趣的AI / ML文章
- aws搭建深度学习gpu_选择合适的GPU进行AWS深度学习
- 证明神经网络的通用逼近定理_在您理解通用逼近定理之前,您不会理解神经网络。...
- ai智能时代教育内容的改变_人工智能正在改变我们的评论方式
- 通用大数据架构-_通用做法-第4部分
- 香草 jboss 工具_使用Tensorflow创建香草神经网络
- 机器学习 深度学习 ai_人工智能,机器学习和深度学习。 真正的区别是什么?...
- 锁 公平 非公平_推荐引擎也需要公平!
- 创建dqn的深度神经网络_深度Q网络(DQN)-II
- kafka topic:1_Topic️主题建模:超越令牌输出
- dask 于数据分析_利用Dask ML框架进行欺诈检测-端到端数据分析
人工智能ai算法_AI算法比您想象的要脆弱得多相关推荐
- 人工智能ai算法_AI算法和联邦贸易委员会
人工智能ai算法 On the business blog of the Federal Trade Commission there is a piece written the 8th of Ap ...
- 人工智能AI课 推荐算法详解和实现
Model-Based 协同过滤算法 随着机器学习技术的逐渐发展与完善,推荐系统也逐渐运用机器学习的思想来进行推荐.将机器学习应用到推荐系统中的方案真是不胜枚举.以下对Model-Based CF算法 ...
- c++svd算法_AI算法工程师面试6
60道AI算法高频面试题 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/1GavvCY7wUetMvC61gxkLgmp.weixin.qq.com 机器学习(15题) 参考: 为什么LR模 ...
- 人工智能ai以算法为基础_智能扬声器和AI将为您的医师带来超强能力
人工智能ai以算法为基础 by Kevin Seals 通过凯文海豹 智能扬声器和AI将为您的医师带来超强能力 (Smart speakers and A.I. will give your phys ...
- 谷歌:新人工智能(AI)算法预测人类死亡时间,意念可指挥机器人
谷歌AI新算法 日前,谷歌新出炉的一项研究报告称,该公司已开发出一种新人工智能(AI)算法,可预测人的死亡时间,且准确率高达95%.据报道,这项AI技术对医院患者面临的一系列临床问题进行了测试.在研究 ...
- 2020全国人工智能大赛AI+无线通信 复赛算法分享
2020全国人工智能大赛 AI+无线通信 复赛算法分享(第八名 无名王者队) 赛题说明 赛题背景 赛题任务 数据简介 数据说明 数据下载 评测标准 赛题分析 赛题难点 传统算法的思路 复赛算法分享 预 ...
- 从人工智能 (AI)发展应用看算法测试的测试策略
https://www.toutiao.com/a6708688571563246087/ 随着人工智能的发展与应用,AI测试逐渐进入到我们的视野,传统的功能测试策略对于算法测试而言,心有余而力不足, ...
- AI人工智能发展的经典算法
AI人工智能发展的经典算法 文章目录 AI人工智能发展的经典算法 前言 一.智力挑战 二.计算方面的挑战 三.人工神经网络 四.因果推理 五.迁移学习 六.元学习 七.自主学习 小结 前言 近年来,计 ...
- 非计算机专业如何转行AI,找到算法offer?
作者 | Nick-Atom 责编 | 琥珀 [AI科技大本营导读]目前,各行业都在尝试着用机器学习/深度学习来解决自身行业的需求.在这个过程中,最为稀缺的也是高质量人工智能人才. 这一年我们见证了不 ...
- 防止被算力“锁死”,人工智能进化急需革命性算法
来源:搜狐,以上文章观点仅代表文章作者,仅供参考,以抛砖引玉! "深度学习所需的大规模样本数据对于算力产生巨大需求,但近日美国麻省理工学院等研究机构的报告显示,深度学习正在逼近算力极限,而提 ...
最新文章
- java怎么表示log2_Java程序员修炼之道 之 Logging(2/3) - 怎么写Log
- GBDT指标重要性计算
- 跪求AI编程语言--纯中文代码
- LCD1602液晶显示模块的单片机驱动深入详解之硬件篇
- C++中const用法总结(转)
- ACM学习历程—Hihocoder 1290 Demo Day(动态规划)
- 使用 JavaScriptService 在.NET Core 里实现DES加密算法
- 冒泡排序 和 归并排序
- Hibernate上路_16-继承关系映射
- python爬取js动态网页_Python 爬取网页中JavaScript动态添加的内容(一)
- Android生命周期工具类,Android倒计时工具类
- 云视通手机下载的文件存储位置_小白版丨IPFS网络怎么存储、下载文件?怎么托管网站?...
- win7 下安装python用的dlib库
- StringUtils简单判断字符串是否为null或者空字符串
- Ubuntu 周立功CAN分析仪 USBCAN-II 驱动
- 油气田开发之油气水井维护性修井作业
- 根据消费定额生成菜单的算法(原创)
- 【无标题】全国矢量地图下载
- 机器学习:PCA(使用梯度上升法求解数据主成分 Ⅰ )
- 深度学习概念挖掘——GPU
热门文章
- 添加到当前最上层view
- 学习笔记_Java_day12_Cookie
- pku1274 The Perfect Stall
- HDU10月月赛总结
- 【点滴】向Sql Express数据库文件中注册Asp.NET 2.0用户管理模块
- 七月算法机器学习5 回归分析与工程应用
- 传智播客 Web静态服务器-6-epoll
- A New Romance Is Likely to End up like Your Previous Relationship 为什么每次恋爱总会走向相似的结局?
- Python学习笔记 之 函数进阶
- Atitit webdav的使用与配置总结attilax总结 目录 1. 支持的协议 2 1.1. http File unc 2 2. 应用场景 2 2.1. 远程文件管理实现功能 文件建立
